chapter the nervous system and the effects of drugs
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... responses to changes. 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolar ...
... responses to changes. 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolar ...
IV. PSYCHOBIOLOGY
... carries messages between them. – If severed, demonstrates how both sides work together. ...
... carries messages between them. – If severed, demonstrates how both sides work together. ...
Types of neurons
... Dendrites Information collectors Receive inputs from neighboring neurons Inputs may number in thousands If receives enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
... Dendrites Information collectors Receive inputs from neighboring neurons Inputs may number in thousands If receives enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
brainy tests - WordPress.com
... There are no neurons that lack a soma, but there are neurons that lack dendrites, and others that lack an axon. ...
... There are no neurons that lack a soma, but there are neurons that lack dendrites, and others that lack an axon. ...
17-01-05 1 Golgi - stained neurons Neuronal function
... main metabolic centre of neuron main (but not only) site of protein synthesis lots of mitochondria lots of endoplasmic reticulum size in vertebrates: small: 8 µm e.g. granule cells in cerebellum large: 50 µm layer V motor cortical neurons largest: 200 µm Mauthner cell in fish brainstem size in inver ...
... main metabolic centre of neuron main (but not only) site of protein synthesis lots of mitochondria lots of endoplasmic reticulum size in vertebrates: small: 8 µm e.g. granule cells in cerebellum large: 50 µm layer V motor cortical neurons largest: 200 µm Mauthner cell in fish brainstem size in inver ...
File
... sensitivity to excitatory and inhibitory signals by Diverging neural pathways influence several neurons ...
... sensitivity to excitatory and inhibitory signals by Diverging neural pathways influence several neurons ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... cross the small space between two neurons called the synapse. Then the neurotransmitters attach to receptor sites (on the dendrites) of the surrounding neurons. These are the chemicals in the brain that doctors often refer to people with mental illnesses as ...
... cross the small space between two neurons called the synapse. Then the neurotransmitters attach to receptor sites (on the dendrites) of the surrounding neurons. These are the chemicals in the brain that doctors often refer to people with mental illnesses as ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... http://diwww.epfl.ch/~gerstner/SPNM/SPNM.html for excellent additional material (some reproduced here). • Just a piece of passive dendrite can yield complicated differential equations which have been extensively studied by electronicians in the context of the study of coaxial cables (TV antenna cabl ...
... http://diwww.epfl.ch/~gerstner/SPNM/SPNM.html for excellent additional material (some reproduced here). • Just a piece of passive dendrite can yield complicated differential equations which have been extensively studied by electronicians in the context of the study of coaxial cables (TV antenna cabl ...
Introduction to neural computation
... • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is made of general purpose stuff that has the ability to turn into special purpose hardware in response to experience. – This gives rapid parallel computation plus flexibility – Conventional comp ...
... • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is made of general purpose stuff that has the ability to turn into special purpose hardware in response to experience. – This gives rapid parallel computation plus flexibility – Conventional comp ...
file - Athens Academy
... In addition to helping us maintain our sanity, having an imbalance in this neurotransmitter plays a role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease. ...
... In addition to helping us maintain our sanity, having an imbalance in this neurotransmitter plays a role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease. ...
Cell Structure: From an Information Processing View
... Efferent or motor neuron: conduct impulses from the central nervous system to the effector organs (such as muscles and glands) are called motor (or efferent) neurons ...
... Efferent or motor neuron: conduct impulses from the central nervous system to the effector organs (such as muscles and glands) are called motor (or efferent) neurons ...
Brain-Computer Interface
... differences in the voltage between neurons. The signal is then amplified, and filtered by a computer program. ...
... differences in the voltage between neurons. The signal is then amplified, and filtered by a computer program. ...
Slide ()
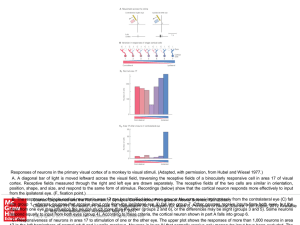
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
Synapses
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... Ex. The rods and cones of the eye; pressure receptors in the skin. Sensory neurons transmit information from the eyes and other sensors that detect stimuli to the brain or spinal cord for processing. Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons or make local connections in the brain and spin ...
... Ex. The rods and cones of the eye; pressure receptors in the skin. Sensory neurons transmit information from the eyes and other sensors that detect stimuli to the brain or spinal cord for processing. Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons or make local connections in the brain and spin ...
Brain models: the next generation
... produce neural responses that are statistically independent. Similarly, Olshausen shows that if neural responses to natural movies are forced to be sparse and independent, the receptive fields that result resemble those found physiologically in V1. These two lines of research provide paradigmatic ex ...
... produce neural responses that are statistically independent. Similarly, Olshausen shows that if neural responses to natural movies are forced to be sparse and independent, the receptive fields that result resemble those found physiologically in V1. These two lines of research provide paradigmatic ex ...
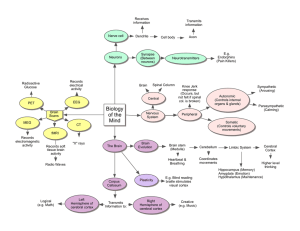
The Biology of Mind
... Neurons do NOT touch each other- the space in between is call the synapse. ...
... Neurons do NOT touch each other- the space in between is call the synapse. ...
The Brain and Nervous System - Mr. Conzen
... How do we function? People are made up of billions of cells - in Psychology we focus on the nervous system. Nervous system sends messages throughout the body that encompass thought, perception, emotion, etc. ...
... How do we function? People are made up of billions of cells - in Psychology we focus on the nervous system. Nervous system sends messages throughout the body that encompass thought, perception, emotion, etc. ...
Neurons, Neurons, Neurons!
... throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs i ...
... throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs i ...
9-Lecture1(updated)
... A broad class of models that mimic functioning inside the human brain There are various classes of NN models. They are different from each other depending on Problem types Structure of the model Model building algorithm ...
... A broad class of models that mimic functioning inside the human brain There are various classes of NN models. They are different from each other depending on Problem types Structure of the model Model building algorithm ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse) or over a long distance (from the secretory organ, through the blood, to its site of action). ...
... its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse) or over a long distance (from the secretory organ, through the blood, to its site of action). ...
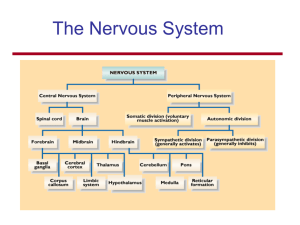
The Nervous System
... The Neuron: A Powerful Computer • Neural impulses: The brain in action – Ions – Action potential – All-or-none law – Myelin ...
... The Neuron: A Powerful Computer • Neural impulses: The brain in action – Ions – Action potential – All-or-none law – Myelin ...