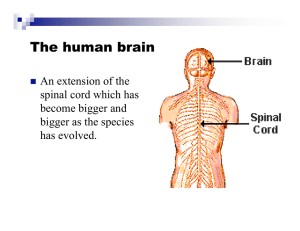
collinsnervoussystem (1)
... Neural Bases of Psychology: Neural Communication • Within a neuron, communication occurs through an action potential (neural impulse that carries information along the axon of a neuron). ...
... Neural Bases of Psychology: Neural Communication • Within a neuron, communication occurs through an action potential (neural impulse that carries information along the axon of a neuron). ...
PPT and questions for class today.
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Cell Body or Soma The control center of the neuron. Function: Directs impulses from the dendrites to the axon. Nucleus Control center of the Soma. Function: Tells the soma what to do. Axon Pathway for the nerve impulse (electrical message) from the soma to the opposite end of the neuron. My ...
... Cell Body or Soma The control center of the neuron. Function: Directs impulses from the dendrites to the axon. Nucleus Control center of the Soma. Function: Tells the soma what to do. Axon Pathway for the nerve impulse (electrical message) from the soma to the opposite end of the neuron. My ...
Powerpoint
... – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) ...
... – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission
... that carries signals between neurons as well as other cells in the body. These chemicals are released from the end of one neuron and cross the synapse to receptor sites in the next neuron. ...
... that carries signals between neurons as well as other cells in the body. These chemicals are released from the end of one neuron and cross the synapse to receptor sites in the next neuron. ...
Neurons_and_Neurotranmission
... that carries signals between neurons as well as other cells in the body. These chemicals are released from the end of one neuron and cross the synapse to receptor sites in the next neuron. ...
... that carries signals between neurons as well as other cells in the body. These chemicals are released from the end of one neuron and cross the synapse to receptor sites in the next neuron. ...
Ch. 2 Practice
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
neurophilosophical foundations 2 levels of organization cell theory
... • Why did they look at the same thing but see something different? • For Golgi, what mattered was communication through nerves--for which purposes a continuous network was needed • For Cajal, neurons were basic units that functioned independently and out of which a system could be built • Charles Sc ...
... • Why did they look at the same thing but see something different? • For Golgi, what mattered was communication through nerves--for which purposes a continuous network was needed • For Cajal, neurons were basic units that functioned independently and out of which a system could be built • Charles Sc ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... 3.The Nervous System 4.The Brain 5.Measuring Techniques 6.The Endocrine System ...
... 3.The Nervous System 4.The Brain 5.Measuring Techniques 6.The Endocrine System ...
Chapter 2 quiz level - easy topic: neurons
... 3) Specialized cells in the brain which send and receive information are called: A) gonads. B) ganglia C) limbic cells. ...
... 3) Specialized cells in the brain which send and receive information are called: A) gonads. B) ganglia C) limbic cells. ...
Concepts of Neurobiology
... Consists of right and left hemisphere connected by a large group of nerves called the corpus callosum. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes: Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Temporal lobes Occipital lobes B. Diencephalon The diencephalon connects the cerebrum with the lower brain str ...
... Consists of right and left hemisphere connected by a large group of nerves called the corpus callosum. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes: Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Temporal lobes Occipital lobes B. Diencephalon The diencephalon connects the cerebrum with the lower brain str ...
Module Two
... was the center of all thoughts and emotions. But we now know that the brain and the rest of the nervous system are the power behind our psychological life and much of our physical being. ...
... was the center of all thoughts and emotions. But we now know that the brain and the rest of the nervous system are the power behind our psychological life and much of our physical being. ...
Ch 49 Pract Test Nervous System
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
Your Nervous System
... impulse along length of axon All or None Principle – must reach a threshold level or the impulse dies Covered by a white covering called a myelin sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after d ...
... impulse along length of axon All or None Principle – must reach a threshold level or the impulse dies Covered by a white covering called a myelin sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after d ...
UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... as character traits c. Correctly focused attention on the fact that various parts of the brain have different functions C. Biological psychology ...
... as character traits c. Correctly focused attention on the fact that various parts of the brain have different functions C. Biological psychology ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
The skin performs all of the following except
... the neuron and other organelles Axon – caries the nerve impulse from cell body to other neurons and muscles ...
... the neuron and other organelles Axon – caries the nerve impulse from cell body to other neurons and muscles ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function – responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. M ...
... sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function – responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. M ...
Cognitive Psychology
... neurons behave. Use these models to try and better understand cognitive processing in the brain. ...
... neurons behave. Use these models to try and better understand cognitive processing in the brain. ...
Types of neurons
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...