Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... 2. Motor (efferent) neurons Carry impulses from CNS 3. Interneurons (association neurons) Found in neural pathways in CNS Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... 2. Motor (efferent) neurons Carry impulses from CNS 3. Interneurons (association neurons) Found in neural pathways in CNS Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
Chapter 33
... basilar membrane to vibrate up and down causing its hair cells to bend. The bending of the hair cells depolarizes their membranes sending action potentials that travel via the auditory nerve to the brain. ...
... basilar membrane to vibrate up and down causing its hair cells to bend. The bending of the hair cells depolarizes their membranes sending action potentials that travel via the auditory nerve to the brain. ...
Single Unit Recording
... electrode introduced into the brain of a living animal will detect electrical activity that is generated by the neurons adjacent to the electrode tip. If the electrode is a microelectrode, with a tip size of 3 to 10 micrometers, the electrode will often isolate the activity of a single neuron. The a ...
... electrode introduced into the brain of a living animal will detect electrical activity that is generated by the neurons adjacent to the electrode tip. If the electrode is a microelectrode, with a tip size of 3 to 10 micrometers, the electrode will often isolate the activity of a single neuron. The a ...
Slide ()
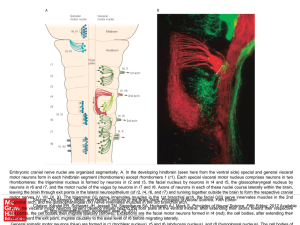
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Synapses and neuronal signalling
... • Active maintenance of the resting membrane potential • Depolarising and hyperpolarising currents • Input resistance of neurons determines the magnitude of passive changes in membrane potential • Membrane capacitance prolongs the timecourse of signals • Membrane and cytoplasmic resistance affect th ...
... • Active maintenance of the resting membrane potential • Depolarising and hyperpolarising currents • Input resistance of neurons determines the magnitude of passive changes in membrane potential • Membrane capacitance prolongs the timecourse of signals • Membrane and cytoplasmic resistance affect th ...
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY Zsolt Liposits and Imre Kalló 2016
... symbioses. The second lecture demonstrates the unique morphology and the excitability of neurons and some basic networks established by them. The third lecture explains how information is conveyed via nerve fibers between distant locations in the human body. One has gained sufficient knowledge, if u ...
... symbioses. The second lecture demonstrates the unique morphology and the excitability of neurons and some basic networks established by them. The third lecture explains how information is conveyed via nerve fibers between distant locations in the human body. One has gained sufficient knowledge, if u ...
The Biology of Mind take
... Neurobiologists and other investigators understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
... Neurobiologists and other investigators understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
The Nervous System
... • As the action potential passes, gates in the potassium channels open, allowing potassium (K+) ions to flow OUT of the cell • This restores the negative potential in the axon. ...
... • As the action potential passes, gates in the potassium channels open, allowing potassium (K+) ions to flow OUT of the cell • This restores the negative potential in the axon. ...
The Biology of Mind take 2
... Neurobiologists and other investigators understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
... Neurobiologists and other investigators understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
Ch03b
... sense organs to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons carry information from the CNS to muscles ...
... sense organs to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons carry information from the CNS to muscles ...
Lecture 9
... Computational neuroscience studies the nervous system from the point of view of its functionality and relies both on experimental data and on theoretical models of individual neurons and networks • Single neuron descriptions/models • Signal processing through synapses • Small circuits • Large neura ...
... Computational neuroscience studies the nervous system from the point of view of its functionality and relies both on experimental data and on theoretical models of individual neurons and networks • Single neuron descriptions/models • Signal processing through synapses • Small circuits • Large neura ...
General Psychology Chapter 2 - Sarah Rach
... • Inhibitory: like pushing its break • Threshold: the minimum intensity of a neuron • If the excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals exceeds the threshold – the signals combined trigger an action potential ...
... • Inhibitory: like pushing its break • Threshold: the minimum intensity of a neuron • If the excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals exceeds the threshold – the signals combined trigger an action potential ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... ____ 14. Direct stimulation of the motor cortex would be most likely to result in a. movement of the mouth and lips. b. feelings of anger. c. acceleration of heartbeat. d. intense pain. e. a sensation of being touched on the arm. ____ 15. Our lips are more sensitive than our knees to sensations of t ...
... ____ 14. Direct stimulation of the motor cortex would be most likely to result in a. movement of the mouth and lips. b. feelings of anger. c. acceleration of heartbeat. d. intense pain. e. a sensation of being touched on the arm. ____ 15. Our lips are more sensitive than our knees to sensations of t ...
Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the
... identify when exactly and in which type of neurons Runx1t1is expressed in the developing dorsal root ganglion. My results show that the expression of Runx1t1 is very strong during embryonic development, at a time when different types of neurons are being specified. In the future, we are planning to ...
... identify when exactly and in which type of neurons Runx1t1is expressed in the developing dorsal root ganglion. My results show that the expression of Runx1t1 is very strong during embryonic development, at a time when different types of neurons are being specified. In the future, we are planning to ...
Chapter 3
... • Inside the neuron has a negative ionic charge • (negative inside/positive outside) = resting potential • Neurons are selectively permeable (usually blocking POSITIVELY charged sodium ions until given the signal to fire • Depolarization occurs when neurons allow sodium ions inside causing neurologi ...
... • Inside the neuron has a negative ionic charge • (negative inside/positive outside) = resting potential • Neurons are selectively permeable (usually blocking POSITIVELY charged sodium ions until given the signal to fire • Depolarization occurs when neurons allow sodium ions inside causing neurologi ...
1. Receptor cells
... The Biological Foundations of Behavior • The nervous system: the most complicated system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting ...
... The Biological Foundations of Behavior • The nervous system: the most complicated system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting ...
... The process of cooling chicken carcasses by immersing them in mixture of cold water and ice (chillers) is complex. It is very difficult to represent it by a transport phenomenon model. In this work, artificial neural networks were used with an intermediary layer in the description and modeling of th ...
Chapter 5: The First Two Years
... other neurons via their axons – Synapse—The intersection between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of other neurons • Synapses are critical in communication links in the brain ...
... other neurons via their axons – Synapse—The intersection between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of other neurons • Synapses are critical in communication links in the brain ...
Biology 12 Name: Nervous System Practice Exam Types of Neurons
... c) The length of the recovery phase would be reduced. d) The frequency of action potentials would be increased. 20. Why can an impulse traveling along an axon not reverse its direction? a) The myelin sheath will only permit one-way travel of an impulse. b) Sodium gates remain closed until the impuls ...
... c) The length of the recovery phase would be reduced. d) The frequency of action potentials would be increased. 20. Why can an impulse traveling along an axon not reverse its direction? a) The myelin sheath will only permit one-way travel of an impulse. b) Sodium gates remain closed until the impuls ...