The Nervous System
... • This situation is known as the relative refractory period. Imagine, if you will, a toilet. When you pull the handle, water floods the bowl. This event takes a couple of seconds and you cannot stop it in the middle. Once the bowl empties, the flush is complete. Now the upper tank is empty. If you t ...
... • This situation is known as the relative refractory period. Imagine, if you will, a toilet. When you pull the handle, water floods the bowl. This event takes a couple of seconds and you cannot stop it in the middle. Once the bowl empties, the flush is complete. Now the upper tank is empty. If you t ...
Nervous System
... 2. Cerebellum: Controls your balance (keeps you upright). 3. Medulla: Controls involuntary movement: breathing, ...
... 2. Cerebellum: Controls your balance (keeps you upright). 3. Medulla: Controls involuntary movement: breathing, ...
The Nervous System
... portion of the brain; controlling the senses, movement of muscles, thinking, and speech. CEREBELLUM – Section near the brain stem that controls balance, posture, and coordination. BRAIN STEM – Controls some important automatic body functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure and digestion ...
... portion of the brain; controlling the senses, movement of muscles, thinking, and speech. CEREBELLUM – Section near the brain stem that controls balance, posture, and coordination. BRAIN STEM – Controls some important automatic body functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure and digestion ...
Part 1 (nerve impulses, ppt file)
... and does in the heart. You can detect the changes in potential caused by this depolarization wave by using conductors placed on the body. This is called an electrocardiogram ...
... and does in the heart. You can detect the changes in potential caused by this depolarization wave by using conductors placed on the body. This is called an electrocardiogram ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... Gross anatomy of the Brain Cerebral Cortex and Localization Hemispheric Function ...
... Gross anatomy of the Brain Cerebral Cortex and Localization Hemispheric Function ...
The Human Nervous System
... The Neuron ~functional unit of the nervous system! All neurons have 3 main parts: 1. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. 2. The cell body contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts m ...
... The Neuron ~functional unit of the nervous system! All neurons have 3 main parts: 1. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. 2. The cell body contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts m ...
Postdoctoral Researcher /Research Associate Bio
... and Reconfigurable Computing Research Group, NUI Galway, one of four collaborating European institutions working on the project “Emulating the C. elegans nervous system: A blueprint for brain-inspired computational architectures”. The C. elegans project is funded by the European Commission Seventh F ...
... and Reconfigurable Computing Research Group, NUI Galway, one of four collaborating European institutions working on the project “Emulating the C. elegans nervous system: A blueprint for brain-inspired computational architectures”. The C. elegans project is funded by the European Commission Seventh F ...
COURSE: 7065
... Brain and cognitive development of the infant Parts of the brain and their functions Brain stem---controls involuntary activities such as breathing Cerebrum---directs motor activities Cerebellum---controls muscular coordination, balance, and posture Pituitary gland---releases hormones that c ...
... Brain and cognitive development of the infant Parts of the brain and their functions Brain stem---controls involuntary activities such as breathing Cerebrum---directs motor activities Cerebellum---controls muscular coordination, balance, and posture Pituitary gland---releases hormones that c ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... Located outside of the skull and spine Serves to bring sensory information into the CNS and carry motor signals out of the CNS ...
... Located outside of the skull and spine Serves to bring sensory information into the CNS and carry motor signals out of the CNS ...
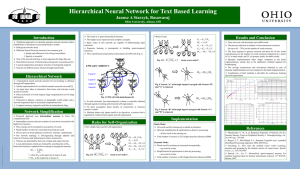
Hierarchical Neural Network for Text Based Learning
... Traditional approach is to describe semantic network structure and/or probabilities of transition in associated Markov models Biological networks learn Different Neural Network structures, but common goal Simple and efficient to solve the given problem Sparsity is essential Size of the n ...
... Traditional approach is to describe semantic network structure and/or probabilities of transition in associated Markov models Biological networks learn Different Neural Network structures, but common goal Simple and efficient to solve the given problem Sparsity is essential Size of the n ...
Fast neural network simulations with population density methods Duane Q. Nykamp Daniel Tranchina
... distribution in v: fV (v, t) = ρ(v, g, s, t)dg ds. Thus, we can reduce the dimension back to one by computing just fV (v, t). The evolution equation for fV , obtained by integrating (3) with respect to ~x = (g, s), depends on the unknown quantity µG|V (v, t), which is the expected value of Gi given ...
... distribution in v: fV (v, t) = ρ(v, g, s, t)dg ds. Thus, we can reduce the dimension back to one by computing just fV (v, t). The evolution equation for fV , obtained by integrating (3) with respect to ~x = (g, s), depends on the unknown quantity µG|V (v, t), which is the expected value of Gi given ...
Chapter 03 - Jen Wright
... 14. Please explain the difference between the ontogeny and phylogeny of the brain. 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, an ...
... 14. Please explain the difference between the ontogeny and phylogeny of the brain. 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, an ...
Unit: Regulation Notes
... • A reflex starts with the 1) receptor (recognizes the stimulus), goes to the 2) sensory neuron (sends signal to brain), to the 3) interneuron (routes the impulse to the correct part of the brain), to the 4) motor neuron (alerts the muscle), and then to the 5) effector (the muscle or gland) Ex. Touc ...
... • A reflex starts with the 1) receptor (recognizes the stimulus), goes to the 2) sensory neuron (sends signal to brain), to the 3) interneuron (routes the impulse to the correct part of the brain), to the 4) motor neuron (alerts the muscle), and then to the 5) effector (the muscle or gland) Ex. Touc ...
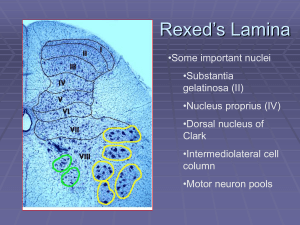
Rexed`s Lamina
... Fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus carry signals from arm and leg Decussation of 2nd order neuron in medulla 3rd order neuron in thalamus carries signal to cerebral cortex ...
... Fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus carry signals from arm and leg Decussation of 2nd order neuron in medulla 3rd order neuron in thalamus carries signal to cerebral cortex ...
neurotransmitters.
... Chapter 2-Neuroscience-explains how our biology underlies our mental & behavior processes. Biological Psychologists study the links between biological activity and psychological events. ...
... Chapter 2-Neuroscience-explains how our biology underlies our mental & behavior processes. Biological Psychologists study the links between biological activity and psychological events. ...
divergent plate boundary
... • Neural networks are configured for a specific application, such as pattern recognition or data classification, through a learning process • In a biological system, learning involves adjustments to the synaptic connections between neurons same for artificial neural networks (ANNs) ...
... • Neural networks are configured for a specific application, such as pattern recognition or data classification, through a learning process • In a biological system, learning involves adjustments to the synaptic connections between neurons same for artificial neural networks (ANNs) ...
here - WPI
... all primarily dependent upon contrasts in light intensity rather than color. The brain is able to group parts of an image together, as well as separating images from each other or from their backgrounds. This means that perception requires various elements to be organized so that related ones are gr ...
... all primarily dependent upon contrasts in light intensity rather than color. The brain is able to group parts of an image together, as well as separating images from each other or from their backgrounds. This means that perception requires various elements to be organized so that related ones are gr ...
ANATOMICAL TERMS
... This can be treated before birth by inserting a shunt which drains the fluid from the ventricles into a vein in the neck ...
... This can be treated before birth by inserting a shunt which drains the fluid from the ventricles into a vein in the neck ...
Neural Tissue - Decker
... Telodendria end at synaptic terminals (synaptic bulbs) * Synaptic terminals are a part of a synapse ...
... Telodendria end at synaptic terminals (synaptic bulbs) * Synaptic terminals are a part of a synapse ...
Nervous System powerpoint new
... – On top of protection, the myelin sheath allows for faster conduction of impulses and greater power of regeneration – The myelin sheath is NOT continuous but rather forms intermitted gaps called the Nodes of Ranvier. Impulses will now ‘jump’ from Node to Node rather then slowly moving through the e ...
... – On top of protection, the myelin sheath allows for faster conduction of impulses and greater power of regeneration – The myelin sheath is NOT continuous but rather forms intermitted gaps called the Nodes of Ranvier. Impulses will now ‘jump’ from Node to Node rather then slowly moving through the e ...
BIOPSYCHOLOGY notes
... neurotransmitters move from axon terminal to dendrites Tiny, near spherical packets within Stores the NT until the action the axon terminal that contain high potential triggers its release concentrations of neurotransmitters into the synapse ...
... neurotransmitters move from axon terminal to dendrites Tiny, near spherical packets within Stores the NT until the action the axon terminal that contain high potential triggers its release concentrations of neurotransmitters into the synapse ...
Nociceptive system
... level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
Nerve tissue for stu..
... 2. PNS (peripheral nervous system) – peripheral nerves and ganglia B) Functionally nervous system is divided into the: 1. Somatic nervous system (sensory and motor innervation) 2. Autonomic nervous system (involuntary innervation of smooth muscles, glands) C) Microscopic structure of the nerve tissu ...
... 2. PNS (peripheral nervous system) – peripheral nerves and ganglia B) Functionally nervous system is divided into the: 1. Somatic nervous system (sensory and motor innervation) 2. Autonomic nervous system (involuntary innervation of smooth muscles, glands) C) Microscopic structure of the nerve tissu ...