Test Question 1 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive
... AW: Signal strength represents H+ concentration. Signal frequency is determined by the specific local magnetic field strength. With frequency encoding or phase encoding the spatial origin of the signal can be determined in a 2-dimensional plane It is also possible to measure increased local neural a ...
... AW: Signal strength represents H+ concentration. Signal frequency is determined by the specific local magnetic field strength. With frequency encoding or phase encoding the spatial origin of the signal can be determined in a 2-dimensional plane It is also possible to measure increased local neural a ...
Nervous tissues
... sheath of dense connective tissue, the epineurium surrounds the nerve. This sheath penetrates the nerve to form the perineurium which surrounds bundles of nerve fibres. blood vessels of various sizes can be seen in the epineurium. The endoneurium, which consists of a thin layer of loose connective t ...
... sheath of dense connective tissue, the epineurium surrounds the nerve. This sheath penetrates the nerve to form the perineurium which surrounds bundles of nerve fibres. blood vessels of various sizes can be seen in the epineurium. The endoneurium, which consists of a thin layer of loose connective t ...
excitatory neurotransmitter
... Glutamate is a neurotransmitter in the CNS. It is involved in a range of activities in the brain including: learning, memory, perception, thinking and movement. When glutamate is released into the synapse it is absorbed by NMDA receptor sites on the post-synaptic dendrites. Glutamate is excitatory, ...
... Glutamate is a neurotransmitter in the CNS. It is involved in a range of activities in the brain including: learning, memory, perception, thinking and movement. When glutamate is released into the synapse it is absorbed by NMDA receptor sites on the post-synaptic dendrites. Glutamate is excitatory, ...
nitz - UCSD Cognitive Science
... – different neurons map different positions (all directions are represented) – rotation of the environment boundaries = rotation of the place fields ...
... – different neurons map different positions (all directions are represented) – rotation of the environment boundaries = rotation of the place fields ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
The Nervous System The master and
... The Nervous System The master _________________ and _________________ system of the body Method of communication? _________________ impulses The Three Overlapping Functions It uses millions of sensory receptors to _________________ _________________ called _________________ inside and outside the bo ...
... The Nervous System The master _________________ and _________________ system of the body Method of communication? _________________ impulses The Three Overlapping Functions It uses millions of sensory receptors to _________________ _________________ called _________________ inside and outside the bo ...
neurons
... 1 Synaptic terminals: Bring signals from other neurons. 2 Dendrites: Receive signals from other neurons. ...
... 1 Synaptic terminals: Bring signals from other neurons. 2 Dendrites: Receive signals from other neurons. ...
AP Biology - Pleasantville High School
... The correct order of a reflex arc is: sensory receptor --> sensory neuron-->Spinal cord (CNS) --> motor neuron --> effector (muscle or gland) 5. The Nerve Impulse A. Passage of a nerve impulse within a Neuron i. Resting potential - polarized membrane -higher concentration of potassium ions (K+) ins ...
... The correct order of a reflex arc is: sensory receptor --> sensory neuron-->Spinal cord (CNS) --> motor neuron --> effector (muscle or gland) 5. The Nerve Impulse A. Passage of a nerve impulse within a Neuron i. Resting potential - polarized membrane -higher concentration of potassium ions (K+) ins ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential. ...
... excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential. ...
Nerves Powerpoint
... • Neurons have three general structures: – Soma (cell body) – Axon (signal transmission) – Dendrite (signal reception) ...
... • Neurons have three general structures: – Soma (cell body) – Axon (signal transmission) – Dendrite (signal reception) ...
Chapters 1,2,3 - UCSD Cognitive Science
... from gap to gap, which is much faster than having the electrical signal travel down the entire length of the axon. This type of electrical conduction is called “______ ". Once the electrical signal reaches the ______ ______, it causes the release of __________ into the synapse, which is the connecti ...
... from gap to gap, which is much faster than having the electrical signal travel down the entire length of the axon. This type of electrical conduction is called “______ ". Once the electrical signal reaches the ______ ______, it causes the release of __________ into the synapse, which is the connecti ...
Neuron Teacher Key 5-17-16
... 2. What are two characteristics that distinguish nerve cells from other cells? Nerve cells are unique in that they transmit signals and utilize chemical communication. _______________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the difference between a nerve cell and a nerve? ...
... 2. What are two characteristics that distinguish nerve cells from other cells? Nerve cells are unique in that they transmit signals and utilize chemical communication. _______________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the difference between a nerve cell and a nerve? ...
Nervous Systems
... basilar membrane to vibrate up and down causing its hair cells to bend. The bending of the hair cells depolarizes their membranes sending action potentials that travel via the auditory nerve to the brain. ...
... basilar membrane to vibrate up and down causing its hair cells to bend. The bending of the hair cells depolarizes their membranes sending action potentials that travel via the auditory nerve to the brain. ...
Supplementary Figure Legends - Word file
... Supplementary Figure 1: Example responses to pure tones and harmonic complex tones from a pitchselective neuron (a, d) (Unit M36n-514) and a non-pitch-selective neuron (b, e) (Unit M2p-140). a. Pure tone frequency response from a pitch-selective neuron. b. Pure tone frequency response from a non-pit ...
... Supplementary Figure 1: Example responses to pure tones and harmonic complex tones from a pitchselective neuron (a, d) (Unit M36n-514) and a non-pitch-selective neuron (b, e) (Unit M2p-140). a. Pure tone frequency response from a pitch-selective neuron. b. Pure tone frequency response from a non-pit ...
GABA A Receptor
... Ions channels are not suitable for causing prolonged postsynaptic neuronal changes (such as those needed for memory and other prolonged changes) because they close within millisecond Activation of second messenger systems in the postsynaptic neuronal cell itself achieves long term effects The most c ...
... Ions channels are not suitable for causing prolonged postsynaptic neuronal changes (such as those needed for memory and other prolonged changes) because they close within millisecond Activation of second messenger systems in the postsynaptic neuronal cell itself achieves long term effects The most c ...
nervous system
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes (axons/dendrite ...
... of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specialized, slender processes (axons/dendrite ...
1-The cell body
... 2- Various glial cells (Gr. glia, glue), which have short processes, support and protect neurons, and participate in many neural activities, neural nutrition, and defense of cells in the CNS. 1-NEURONS The functional unit in both the CNS and PNS is the neuron or nerve cell. Some neuronal components ...
... 2- Various glial cells (Gr. glia, glue), which have short processes, support and protect neurons, and participate in many neural activities, neural nutrition, and defense of cells in the CNS. 1-NEURONS The functional unit in both the CNS and PNS is the neuron or nerve cell. Some neuronal components ...
Abstract n Bio - Prof Arto Nurmikko
... electrical microcircuits in the brain has been a central research topic of modern neuroscience for at least a century. More recently, engineers, physicists, and mathematicians have been bringing their tools of trade to both experimental and theoretical research in brain science. Pursu ...
... electrical microcircuits in the brain has been a central research topic of modern neuroscience for at least a century. More recently, engineers, physicists, and mathematicians have been bringing their tools of trade to both experimental and theoretical research in brain science. Pursu ...
Ch. 3 S. 1
... neuron to the dendrites of other neurons. In order for a message to be sent from one neuron to another neuron, it must cross the synapse. The synapse is a junction between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. Messages travel in only one direction. Thus, messages are ...
... neuron to the dendrites of other neurons. In order for a message to be sent from one neuron to another neuron, it must cross the synapse. The synapse is a junction between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. Messages travel in only one direction. Thus, messages are ...
Supporting Information S1.
... MEA recording system with an inter-node spacing of 200 m. Consequently, here we show that neurites can extend significantly from the soma over multiple nodes, up to 800 m (4 nodes). (Right) The same culture was counterstained with an antibody against βTubIII to show the whole network development. ...
... MEA recording system with an inter-node spacing of 200 m. Consequently, here we show that neurites can extend significantly from the soma over multiple nodes, up to 800 m (4 nodes). (Right) The same culture was counterstained with an antibody against βTubIII to show the whole network development. ...
power point for chap 11
... Axons of the CNS • myelinated and unmyelinated fibers present • Myelin sheaths formed by oligodendrocytes • Nodes of Ranvier widely spaced ...
... Axons of the CNS • myelinated and unmyelinated fibers present • Myelin sheaths formed by oligodendrocytes • Nodes of Ranvier widely spaced ...
Name: Block: Date
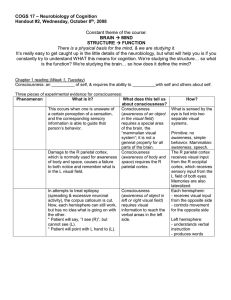
... ancient part of brain important in emotions, memory, learning record of brains electrical activity thin, gray, outer covering of cerebrum, most complex part of brain, consciousness resides here ...
... ancient part of brain important in emotions, memory, learning record of brains electrical activity thin, gray, outer covering of cerebrum, most complex part of brain, consciousness resides here ...