nervous tissue organization neurons neuroglia action potentials
... synaptic plasticity = the ability of a synapse to change synaptic potentiation = ability to make transmission easier immediate = able to hold for a few seconds short term = remember for a few sec to hours, then forgotten working = stored in brain & can be recalled by new input, facilitated synapses ...
... synaptic plasticity = the ability of a synapse to change synaptic potentiation = ability to make transmission easier immediate = able to hold for a few seconds short term = remember for a few sec to hours, then forgotten working = stored in brain & can be recalled by new input, facilitated synapses ...
OLED_Optogenetics_abstract_v3_wo_links
... contact with the OLED, while the OLED was driven in steady state (voltage pulse length > 1s). A maximum brightness of 0.85 mW/mm2 was reached at 14 V, which is sufficient to trigger action potentials in neurons that are transfected with relatively light-sensitive ion channels (e.g. ChR2 C128S [7], C ...
... contact with the OLED, while the OLED was driven in steady state (voltage pulse length > 1s). A maximum brightness of 0.85 mW/mm2 was reached at 14 V, which is sufficient to trigger action potentials in neurons that are transfected with relatively light-sensitive ion channels (e.g. ChR2 C128S [7], C ...
Slide ()
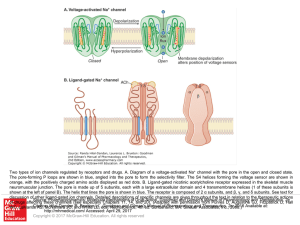
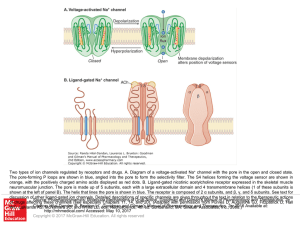
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Brain and Consciousness - Oakton Community College
... 2. Soma processes the message and generates an electric charge ...
... 2. Soma processes the message and generates an electric charge ...
Essentials of Anatony and Physiology, 5e (Martini
... Tetrodotoxin prevents sodium channels from opening. What effect would this have on the function of neurons? The all-or-none principle states that… How do depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization affect membrane potential? What is the refractory period? What does the sodium-potassium pum ...
... Tetrodotoxin prevents sodium channels from opening. What effect would this have on the function of neurons? The all-or-none principle states that… How do depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization affect membrane potential? What is the refractory period? What does the sodium-potassium pum ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... A subcortical structure that regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst and sexual behavior Pituitary Gland The “master gland”. Secretes stimulating hormones to all but two of the endocrine glands. Without stimulating hormones the rest of the endocrine system could not function. Limbic System A grou ...
... A subcortical structure that regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst and sexual behavior Pituitary Gland The “master gland”. Secretes stimulating hormones to all but two of the endocrine glands. Without stimulating hormones the rest of the endocrine system could not function. Limbic System A grou ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... How neurons communicate • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... How neurons communicate • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
Endocrine system: anatomy, Histology and Embryology
... into the blood that targets distant tissues to produce specific response. ...
... into the blood that targets distant tissues to produce specific response. ...
Notes Intro to Nervous System and Neurons
... 6 Types of Support Cells 1. Astrocytes (CNS) – star-shaped cells – Most abundant of the glial cells Mainly function between neurons and capillaries • Bridging the two • Communication between the two • Barrier between the two – Control the chemical environment of the brain (taking in extra K+ or neu ...
... 6 Types of Support Cells 1. Astrocytes (CNS) – star-shaped cells – Most abundant of the glial cells Mainly function between neurons and capillaries • Bridging the two • Communication between the two • Barrier between the two – Control the chemical environment of the brain (taking in extra K+ or neu ...
Synthetic neurons
... environment and sends it to brain • Takes commands from the brain to moves muscles ...
... environment and sends it to brain • Takes commands from the brain to moves muscles ...
Bradley`s.
... neuron becomes positively charged making it depolarized. Once negative ions rush back in the neuron will return to a negative charge. Then the same process occurs as the next group of channels flips open briefly ...
... neuron becomes positively charged making it depolarized. Once negative ions rush back in the neuron will return to a negative charge. Then the same process occurs as the next group of channels flips open briefly ...
Brightness and Lightness - UMD Space Physics Group
... • Lateral inhibition: – Increased illumination of one region of the retina diminishes the signal to the brain from its neighboring region. – When the overall light-intensity increases, lateral inhibition increases, and the increase is largely ignored by brain. (the result is Weber’s law, the overall ...
... • Lateral inhibition: – Increased illumination of one region of the retina diminishes the signal to the brain from its neighboring region. – When the overall light-intensity increases, lateral inhibition increases, and the increase is largely ignored by brain. (the result is Weber’s law, the overall ...
Spinal nerves
... frequently cited cytoarchitectural organization of the human cortex. Many of the areas Brodmann defined based solely on their neuronal organization have since been correlated closely to diverse cortical functions. For example, Brodmann areas 1, 2 and 3 are the primary somatosensory cortex; area 4 is ...
... frequently cited cytoarchitectural organization of the human cortex. Many of the areas Brodmann defined based solely on their neuronal organization have since been correlated closely to diverse cortical functions. For example, Brodmann areas 1, 2 and 3 are the primary somatosensory cortex; area 4 is ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... Einstein's brain weighed only 1,230 grams, which is less than the average adult male brain (about 1,400 grams). One of the differences that were found between Einstein’s brain compared to others was increased number of glial cells. It is known from animal studies that as we go from invertebrates to ...
... Einstein's brain weighed only 1,230 grams, which is less than the average adult male brain (about 1,400 grams). One of the differences that were found between Einstein’s brain compared to others was increased number of glial cells. It is known from animal studies that as we go from invertebrates to ...
Nerves Powerpoint
... • All neurons release a neurotransmitter at the end of the axon! – Acetylcholine is most common and usually stimulating – Dopamine and serotonin are commonly used in the brain and may be stimulating or inhibiting – There are many others! ...
... • All neurons release a neurotransmitter at the end of the axon! – Acetylcholine is most common and usually stimulating – Dopamine and serotonin are commonly used in the brain and may be stimulating or inhibiting – There are many others! ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.