Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex
... whole central nervous systems of pwPMS we investigate whether a tract specific pattern of neurodegeneration contributes to the loss of motor function in pwPMS. Here, we present preliminary data on stereological estimates of neuronal cell loss in limb specific areas of the MS primary motor cortex (PM ...
... whole central nervous systems of pwPMS we investigate whether a tract specific pattern of neurodegeneration contributes to the loss of motor function in pwPMS. Here, we present preliminary data on stereological estimates of neuronal cell loss in limb specific areas of the MS primary motor cortex (PM ...
The Visual System
... Receive direct input from the LGN. Respond to points or bars of light in a particular orientation and location. ...
... Receive direct input from the LGN. Respond to points or bars of light in a particular orientation and location. ...
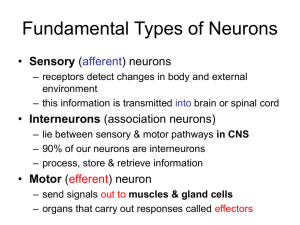
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... • Neuronal communication is based on mechanisms for producing electrical potentials & currents – electrical potential - difference in concentration of charged particles between different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to another within the cell • Li ...
... • Neuronal communication is based on mechanisms for producing electrical potentials & currents – electrical potential - difference in concentration of charged particles between different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to another within the cell • Li ...
Ch 4 V Cortexb - Texas A&M University
... – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
... – Simple cortical cell – Complex cortical cell – End-stopped cortical cell ch 4 ...
Slide ()
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available dorsal medulla are part of the nucleus of the solitary tract. The A1 and C1 groups in the ventral medulla are located near the nucleus ambiguus. Both at: http: ...
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available dorsal medulla are part of the nucleus of the solitary tract. The A1 and C1 groups in the ventral medulla are located near the nucleus ambiguus. Both at: http: ...
nitz - UCSD Cognitive Science
... given that different hippocampal neurons bear different place fields, the firing rates of those neurons at any given time can be used to predict the animal’s position in the environment for a set of neurons, the firing rates across the full set describe the ‘pattern’ of activity across the full popu ...
... given that different hippocampal neurons bear different place fields, the firing rates of those neurons at any given time can be used to predict the animal’s position in the environment for a set of neurons, the firing rates across the full set describe the ‘pattern’ of activity across the full popu ...
P-retinal ganglion cells
... For a cell that has separated and elongated on and off regions (simple RF), you need the following effective stimulus: It must excite the specific segment of the retina innervated by receptors in the excitatory zone (specific position on the retina and also a specific (excitatory) position in the RF ...
... For a cell that has separated and elongated on and off regions (simple RF), you need the following effective stimulus: It must excite the specific segment of the retina innervated by receptors in the excitatory zone (specific position on the retina and also a specific (excitatory) position in the RF ...
Document
... For a cell that has separated and elongated on and off regions (simple RF), you need the following effective stimulus: It must excite the specific segment of the retina innervated by receptors in the excitatory zone (specific position on the retina and also a specific (excitatory) position in the RF ...
... For a cell that has separated and elongated on and off regions (simple RF), you need the following effective stimulus: It must excite the specific segment of the retina innervated by receptors in the excitatory zone (specific position on the retina and also a specific (excitatory) position in the RF ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... 2. Conductivity – able to carry an impulse down its length B. The Electrochemical gradient & the Resting Potential 1. The energy for an impulse is supplied by the neuron. 2. Neurons create a chemical imbalance between the inside and the outside of the cell membrane (Potential difference). 3. This ch ...
... 2. Conductivity – able to carry an impulse down its length B. The Electrochemical gradient & the Resting Potential 1. The energy for an impulse is supplied by the neuron. 2. Neurons create a chemical imbalance between the inside and the outside of the cell membrane (Potential difference). 3. This ch ...
Count the black dots
... Fast transitions controlled by POAH Consistent with Szymusiak et al 1998 ...
... Fast transitions controlled by POAH Consistent with Szymusiak et al 1998 ...
glossary - HBO.com
... impairment of memory and other cognitive abilities. Amyloid precursor protein (APP)—the larger protein from which beta-amyloid is formed. ApoE gene—a gene that codes for a protein that carries cholesterol to and within cells; different forms of the ApoE gene are associated with differing risks for l ...
... impairment of memory and other cognitive abilities. Amyloid precursor protein (APP)—the larger protein from which beta-amyloid is formed. ApoE gene—a gene that codes for a protein that carries cholesterol to and within cells; different forms of the ApoE gene are associated with differing risks for l ...
THE VISUAL SYSTEM
... • Optic chiasm: pt at which the optic nerves from the inside half of each eye cross over and then project to the opposite half of the brain • Optic fibers then diverge along 2 paths • Main path projects into thalamus; retinal axons synapse in the ...
... • Optic chiasm: pt at which the optic nerves from the inside half of each eye cross over and then project to the opposite half of the brain • Optic fibers then diverge along 2 paths • Main path projects into thalamus; retinal axons synapse in the ...
Brainfunction - Oakton Community College
... Brains exposed to enriched and challenging environments become smarter due to the growth of new extensive neural networks. Neuroplasticity or the ability to establish new neural networks occurs throughout life but does require more time and effort during adulthood. ...
... Brains exposed to enriched and challenging environments become smarter due to the growth of new extensive neural networks. Neuroplasticity or the ability to establish new neural networks occurs throughout life but does require more time and effort during adulthood. ...
Language within our grasp:
... • Mirror neurons were discovered in single-cell recording in area F5: ventral [= lower] premotor cortex • They discharge during active movements of the hand and/or mouth • They are sensitive to different purposes – Some discharge during grasping; some during (specific kinds of) holding; some during ...
... • Mirror neurons were discovered in single-cell recording in area F5: ventral [= lower] premotor cortex • They discharge during active movements of the hand and/or mouth • They are sensitive to different purposes – Some discharge during grasping; some during (specific kinds of) holding; some during ...
Characteristic for receptor cells
... cells that respond to amino acids, to humans, most amino acids taste bitter, alanine and serine sweet, a few such as salts of glutamic acid have unique taste, umami, neither sour, salty, sweet, or bitter ...
... cells that respond to amino acids, to humans, most amino acids taste bitter, alanine and serine sweet, a few such as salts of glutamic acid have unique taste, umami, neither sour, salty, sweet, or bitter ...
Neuron (Nerve Cell)
... Medical Procedures & the Brain • How do we know about the brain, its regions, parts & functions? • How have we been able to diagnose problems within the nervous system? • Where & how did the first medical procedures investigating the nervous system occur? ...
... Medical Procedures & the Brain • How do we know about the brain, its regions, parts & functions? • How have we been able to diagnose problems within the nervous system? • Where & how did the first medical procedures investigating the nervous system occur? ...
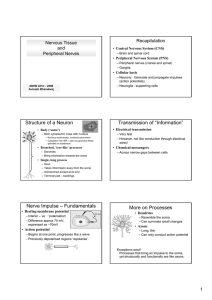
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... Takes information away from the soma Unbranched except at its end Terminal part – swellings ...
... Takes information away from the soma Unbranched except at its end Terminal part – swellings ...
presentation
... Two astrocytic microdomains connected to two networks are able to interact with each other. The network connected to M1 spikes at a higher frequency and is able to trigger SICs (Slow Inward Currents) in b ...
... Two astrocytic microdomains connected to two networks are able to interact with each other. The network connected to M1 spikes at a higher frequency and is able to trigger SICs (Slow Inward Currents) in b ...
Anatomy and Physiology of the Retina
... angles, we can measure what is called the Stiles-Crawford effect, published in 1933. The Stiles-Crawford effect refers to the fact that that cones are more sensitive (by a factor of 10) to light which enters the eye from the center of the pupil (axial light) than we are to light entering from the ma ...
... angles, we can measure what is called the Stiles-Crawford effect, published in 1933. The Stiles-Crawford effect refers to the fact that that cones are more sensitive (by a factor of 10) to light which enters the eye from the center of the pupil (axial light) than we are to light entering from the ma ...
I. The Nervous System
... 3. AXON- carries impulses away from the cell body. a. Schwann cells- accessory cells that make myelin sheath b. myelin sheath- lipids that cover part of some axons, conducts signal faster c. nodes of Ranvier- breaks in myelin sheath, leave cell exposed to access ions needed for impulse ...
... 3. AXON- carries impulses away from the cell body. a. Schwann cells- accessory cells that make myelin sheath b. myelin sheath- lipids that cover part of some axons, conducts signal faster c. nodes of Ranvier- breaks in myelin sheath, leave cell exposed to access ions needed for impulse ...
Chapter Outlines - Cengage Learning
... understanding and producing language, is caused by damage to Broca’s area or Wernicke’s area. Many areas of the brain are related to language; several are associated with specific semantic abilities. The Divided Brain in a Unified Self 1. Split-Brain Studies. Split-brain (severed corpus callosum) da ...
... understanding and producing language, is caused by damage to Broca’s area or Wernicke’s area. Many areas of the brain are related to language; several are associated with specific semantic abilities. The Divided Brain in a Unified Self 1. Split-Brain Studies. Split-brain (severed corpus callosum) da ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.