Biological_Bases
... a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon Electrical message firing generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane This process is due to stimulation from either heat, chemicals, pressure or light ...
... a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon Electrical message firing generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane This process is due to stimulation from either heat, chemicals, pressure or light ...
Connections of the Hypothalamus
... Model of the basic plan of the hypothalamus. It is convenient to start with the activation of a particular node (black) in the behavior control column. Note two classes of output. One consists of ‘descending’ projections to brainstem, and in some cases spinal, regions associated with the somatic and ...
... Model of the basic plan of the hypothalamus. It is convenient to start with the activation of a particular node (black) in the behavior control column. Note two classes of output. One consists of ‘descending’ projections to brainstem, and in some cases spinal, regions associated with the somatic and ...
The Visual System: The Nature of Light
... • Light-sensitive surface with cells that convert light energy to nerve impulses • At the back of the eyeball • Made up of three layers of cells – Receptor cells (Rods & Cones) – Bipolar cells – Ganglion cells ...
... • Light-sensitive surface with cells that convert light energy to nerve impulses • At the back of the eyeball • Made up of three layers of cells – Receptor cells (Rods & Cones) – Bipolar cells – Ganglion cells ...
Mechanisms of development: cell movement
... Again, see http://golgi.ana.ed.ac.uk/coursenotes/ for slides and movies ...
... Again, see http://golgi.ana.ed.ac.uk/coursenotes/ for slides and movies ...
The basics of brain communication
... • The Brain Stem Houses the Basic Programs of Survival • The Cerebellum is Essential for Movement • Subcortical Structures Control Emotions and Appetitive Behaviors • The Cerebral Cortex Underlies Complex Mental Activity • Splitting the Brain Splits the Mind • What to Believe? Using Psychological Re ...
... • The Brain Stem Houses the Basic Programs of Survival • The Cerebellum is Essential for Movement • Subcortical Structures Control Emotions and Appetitive Behaviors • The Cerebral Cortex Underlies Complex Mental Activity • Splitting the Brain Splits the Mind • What to Believe? Using Psychological Re ...
Cellular Components of Nervous Tissue
... Whereas dendrites and the cell body can be characterized as domains of the neuron that receive afferents, the axon, at the other pole of the neuron, is responsible for transmitting neural information. This information may be primary, in the case of a sensory receptor, or processed information that h ...
... Whereas dendrites and the cell body can be characterized as domains of the neuron that receive afferents, the axon, at the other pole of the neuron, is responsible for transmitting neural information. This information may be primary, in the case of a sensory receptor, or processed information that h ...
From: Shadmehr R., Wise S.P. “The computational neurobiology of
... of the actin sites that can bind the myosin heads – Therefore the myosin attaches to the acting and the head rotates ...
... of the actin sites that can bind the myosin heads – Therefore the myosin attaches to the acting and the head rotates ...
Plant Response to Internal and External Signals
... • Red light triggers the conversion of Pr to Pfr • Far-red light triggers the conversion of Pfr to Pr • The conversion of Pr to Pfr is faster than the reverse process • Sunlight, containing both red and far-red light, increases the ratio of Pfr to Pr and triggers ...
... • Red light triggers the conversion of Pr to Pfr • Far-red light triggers the conversion of Pfr to Pr • The conversion of Pr to Pfr is faster than the reverse process • Sunlight, containing both red and far-red light, increases the ratio of Pfr to Pr and triggers ...
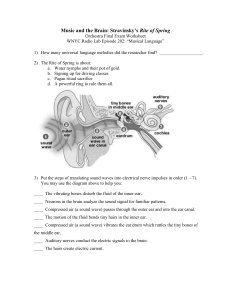
Music and the Brain: Stravinsky`s Rite of Spring
... b. irregular, jagged nerve impulse patterns c. loud impulse patterns d. euphoria 6) When auditory neurons struggle to make sense of a sound they release: a. the dogs b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. ...
... b. irregular, jagged nerve impulse patterns c. loud impulse patterns d. euphoria 6) When auditory neurons struggle to make sense of a sound they release: a. the dogs b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. ...
Document
... Nucleus raphe magnus neurons release serotonin at their nerve endings. Neurons with cell bodies located within the spinal cord that are stimulated by input from nucleus raphe magnus neurons release -endorphin at their nerve endings. d. All of the above are true. 10. Massaging the skin or applicatio ...
... Nucleus raphe magnus neurons release serotonin at their nerve endings. Neurons with cell bodies located within the spinal cord that are stimulated by input from nucleus raphe magnus neurons release -endorphin at their nerve endings. d. All of the above are true. 10. Massaging the skin or applicatio ...
View CV as a PDF - Cedars
... This is to study stem cells isolated from umbilical tissue have advantages including non ethical issue, less immune-related problem, differentiating into several cell types. The main purpose of this project is to examine whether umbilical derived stem cells can preserve vision after subretinal injec ...
... This is to study stem cells isolated from umbilical tissue have advantages including non ethical issue, less immune-related problem, differentiating into several cell types. The main purpose of this project is to examine whether umbilical derived stem cells can preserve vision after subretinal injec ...
Auditory (Cochlear) System
... (receptor) potential in the hair cells and transmitter to be released onto the peripheral terminals of cochlear nerve fibers (cell bodies in the spiral ganglion). Summation of synaptic potentials generates an action potential in ...
... (receptor) potential in the hair cells and transmitter to be released onto the peripheral terminals of cochlear nerve fibers (cell bodies in the spiral ganglion). Summation of synaptic potentials generates an action potential in ...
Hearing Part 2
... Frequency Tuning in Hair Cells • Hair cells have oscillating waves of depolarizations that are unique to each hair cell • If the frequency of sound wave matches the innate oscilliation of membrane depolarization, then the response amplitude is large • A high frequency tuned hair cell has strong dep ...
... Frequency Tuning in Hair Cells • Hair cells have oscillating waves of depolarizations that are unique to each hair cell • If the frequency of sound wave matches the innate oscilliation of membrane depolarization, then the response amplitude is large • A high frequency tuned hair cell has strong dep ...
Dynamics of Spontaneous Activity in Neocortical Slices
... neocortical brain slices can sustain spontaneous activity. In the past, slices have been used to study the responses of neurons to electrical or pharmacological stimulations. At the same time, EPSPs and IPSPs are routinely recorded intracellularly from neurons in slices even under conditions in whic ...
... neocortical brain slices can sustain spontaneous activity. In the past, slices have been used to study the responses of neurons to electrical or pharmacological stimulations. At the same time, EPSPs and IPSPs are routinely recorded intracellularly from neurons in slices even under conditions in whic ...
afaf-el-ansary-king-saud-university-saudi
... neural membranes is important for resting membrane and this usually maintained by ATP-dependent ion pumps, such as a Na+/K+ pump. ATP depletion induces impairment in the repolarization of neural membranes after a depolarizing stimulus. Defective repolarization can relieve a voltage dependent Mg+ b ...
... neural membranes is important for resting membrane and this usually maintained by ATP-dependent ion pumps, such as a Na+/K+ pump. ATP depletion induces impairment in the repolarization of neural membranes after a depolarizing stimulus. Defective repolarization can relieve a voltage dependent Mg+ b ...
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
... - record, using loose patch, from a bunch of cells in culture - add blockers - record again - found quantitative support for the balanced regime. J. Neurophys., 83:808-827, 828-835, 2000 ...
... - record, using loose patch, from a bunch of cells in culture - add blockers - record again - found quantitative support for the balanced regime. J. Neurophys., 83:808-827, 828-835, 2000 ...
UNIT 4 – HOMEOSTASIS 8.1 – Human Body Systems and H
... - Once an action potential reaches the area of the terminal button, it initiates the following sequence of events. 1) Calcium ions (Ca2+) diffuse into the terminal buttons. 2) The calcium influx causes vesicles containing neurotransmitters to fuse with the presynaptic membrane. 3) Neurotransmitter i ...
... - Once an action potential reaches the area of the terminal button, it initiates the following sequence of events. 1) Calcium ions (Ca2+) diffuse into the terminal buttons. 2) The calcium influx causes vesicles containing neurotransmitters to fuse with the presynaptic membrane. 3) Neurotransmitter i ...
Neural Networks (NN)
... the neuron acts just like the biological neuron described earlier (subtracting the threshold from the weighted sum and comparing with zero is equivalent to comparing the weighted sum to the threshold). Actually, the step function is rarely used in artificial neural networks, as will be discussed. No ...
... the neuron acts just like the biological neuron described earlier (subtracting the threshold from the weighted sum and comparing with zero is equivalent to comparing the weighted sum to the threshold). Actually, the step function is rarely used in artificial neural networks, as will be discussed. No ...
Nervous System
... Sympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its energy. ...
... Sympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its energy. ...
current status of stem cell treatments for cerebral palsy
... cells (BM-MSCs) can migrate to the brain and improve function following injury. These cells can produce neurons in a dish, but are unable to create mature, functional neurons in live animals. Instead, their benefit comes from providing nutritional and structural support to the region of injury. Neur ...
... cells (BM-MSCs) can migrate to the brain and improve function following injury. These cells can produce neurons in a dish, but are unable to create mature, functional neurons in live animals. Instead, their benefit comes from providing nutritional and structural support to the region of injury. Neur ...
Science - edl.io
... messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord inside your backbone. Motor nerves carry messages back from the brain to all the muscles and glands in your body. So how do they pass along messages? Through the marvels of chemistry and a kind of electricity! Neurons a ...
... messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord inside your backbone. Motor nerves carry messages back from the brain to all the muscles and glands in your body. So how do they pass along messages? Through the marvels of chemistry and a kind of electricity! Neurons a ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.