Head: Special Senses
... Retina is outgrowth of brain Neurons have specialized receptors at end with “photo pigment” proteins (rhodopsins) – Rod cells function in dim light, not color-tuned – Cone cells have three types: blue, red, green – In color blindness, gene for one type of rhodopsin is deficient, usually red or green ...
... Retina is outgrowth of brain Neurons have specialized receptors at end with “photo pigment” proteins (rhodopsins) – Rod cells function in dim light, not color-tuned – Cone cells have three types: blue, red, green – In color blindness, gene for one type of rhodopsin is deficient, usually red or green ...
Slide 1
... Diverse molecular families control the growth and guidance of developing axons. A. A large family of classical cadherins promote cell and axonal adhesion, primarily through homophilic interactions between cadherin molecules on adjacent neurons. Adhesive interactions are mediated through interactions ...
... Diverse molecular families control the growth and guidance of developing axons. A. A large family of classical cadherins promote cell and axonal adhesion, primarily through homophilic interactions between cadherin molecules on adjacent neurons. Adhesive interactions are mediated through interactions ...
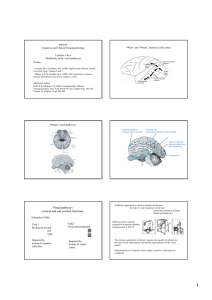
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... Specialised cells and brain areas for recognition of specific category of objects (as reviewed in Lectures 1&2) e.g. face cells in the ventral stream ...
... Specialised cells and brain areas for recognition of specific category of objects (as reviewed in Lectures 1&2) e.g. face cells in the ventral stream ...
Neural Modeling and Computational Neuroscience
... Mathematical models of neural microcircuits are suitable to implement the liquid Microcircuits are characterized by large diversity of mechanisms involved in temporal spike generation Liquid: a layer of interconnected neurons ...
... Mathematical models of neural microcircuits are suitable to implement the liquid Microcircuits are characterized by large diversity of mechanisms involved in temporal spike generation Liquid: a layer of interconnected neurons ...
Trauma and Brain Neurobiology
... The more the neural system is activated, the more the system will change in response to activation. This change is in response to “patterned, repetitive behavior.” (Perry, 2006) ...
... The more the neural system is activated, the more the system will change in response to activation. This change is in response to “patterned, repetitive behavior.” (Perry, 2006) ...
Control and Coordination -Organ systems
... A neurotransmitter chemical released from one nerve cell attaches to receptor sites on another nerve cell. When enough receptor sites have been filled by the neurotransmitter chemicals, an impulse is initiated in the nerve cell receiving the neurotransmitters. Psychoactive drugs interfere with eithe ...
... A neurotransmitter chemical released from one nerve cell attaches to receptor sites on another nerve cell. When enough receptor sites have been filled by the neurotransmitter chemicals, an impulse is initiated in the nerve cell receiving the neurotransmitters. Psychoactive drugs interfere with eithe ...
pdf - Llano Lab
... Bordi and LeDoux, 1994; Linke, 1999). The MGBm also displays significant heterogeneity with respect to the intrinsic properties such that some neurons do not display bursting and there are subpopulations of neurons in the MGBm with large, reticular, non-bushy morphology (Winer and Morest, 1983; Smith ...
... Bordi and LeDoux, 1994; Linke, 1999). The MGBm also displays significant heterogeneity with respect to the intrinsic properties such that some neurons do not display bursting and there are subpopulations of neurons in the MGBm with large, reticular, non-bushy morphology (Winer and Morest, 1983; Smith ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... cells. Growth, survival and differentiation of neurons: Neural precursor cells. Cell proliferation. Neuron induction. Cell migration. Neuronal death during development. Electrical properties of neurons: Capacitance, transference of charge and Ohm’s Law Passive properties of the plasmic membrane. Mem ...
... cells. Growth, survival and differentiation of neurons: Neural precursor cells. Cell proliferation. Neuron induction. Cell migration. Neuronal death during development. Electrical properties of neurons: Capacitance, transference of charge and Ohm’s Law Passive properties of the plasmic membrane. Mem ...
unit 5: the nervous and endocrine systems
... - The axon: a long fibre with small branches at the end - The myelin pod. Neurons can’t divide like other cells. When neurons die they are not replaced by other neurons. Neurons aren’t joined together one by one, between one neuron and the next there is a space. ...
... - The axon: a long fibre with small branches at the end - The myelin pod. Neurons can’t divide like other cells. When neurons die they are not replaced by other neurons. Neurons aren’t joined together one by one, between one neuron and the next there is a space. ...
Slide 1
... 2. Temporal Summation – Stimulating a dendrite at a high frequency 3. Combined – stimulating multiple dendrites at a high frequency Graded Potentials are summed together at the Axon Hillock “Trigger Zone” • If summation of graded potentials reaches threshold stimulus (-55mV), an action potential is ...
... 2. Temporal Summation – Stimulating a dendrite at a high frequency 3. Combined – stimulating multiple dendrites at a high frequency Graded Potentials are summed together at the Axon Hillock “Trigger Zone” • If summation of graded potentials reaches threshold stimulus (-55mV), an action potential is ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Cells are densely packed and intertwined Two main cell types: 1. Neurons Excitable – transmit electrical signals 2. Glial cells – support cells Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
... Cells are densely packed and intertwined Two main cell types: 1. Neurons Excitable – transmit electrical signals 2. Glial cells – support cells Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
11th International Conference Advances in Pneumology Cologne
... the decrease of cough number (control:16, DLH1:6, DLH2:1) and neuronal activity of lumbar nerve neuronal population during cough (and also during quiet breathing). In spite of shortening of cough phrenic activity (compared to quiet breathing) which was not observed in experiment on animals, our simu ...
... the decrease of cough number (control:16, DLH1:6, DLH2:1) and neuronal activity of lumbar nerve neuronal population during cough (and also during quiet breathing). In spite of shortening of cough phrenic activity (compared to quiet breathing) which was not observed in experiment on animals, our simu ...
The promise of stem cells in the therapy of
... The stem cells hold potentials to develop cell replacement therapies for various neurodegerative disease, including AD. The subtype-specific neurons from stem cells might be the most ideal donor cells to replace the same type of neurons lost through disease. The embryo stem cell (ESC)-derived dopami ...
... The stem cells hold potentials to develop cell replacement therapies for various neurodegerative disease, including AD. The subtype-specific neurons from stem cells might be the most ideal donor cells to replace the same type of neurons lost through disease. The embryo stem cell (ESC)-derived dopami ...
ecture 23- special senses
... project beyond the epithelial surface and provide the base for up to 20 cilia. Cilia They contain receptors called odorant-binding proteins that match specific odorant particles. They can only be stimulated by water-soluble and lipid-soluble particles that can diffuse through the overlaying mucus. D ...
... project beyond the epithelial surface and provide the base for up to 20 cilia. Cilia They contain receptors called odorant-binding proteins that match specific odorant particles. They can only be stimulated by water-soluble and lipid-soluble particles that can diffuse through the overlaying mucus. D ...
The Nervous System
... • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – All nerve tissue (neurons) outside the brain and spinal cord. They include: • 12 Cranial (head) nerves that enervate the head/senses • 31 pairs of spinal nerves that enervate the arms, trunk, and ...
... • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – All nerve tissue (neurons) outside the brain and spinal cord. They include: • 12 Cranial (head) nerves that enervate the head/senses • 31 pairs of spinal nerves that enervate the arms, trunk, and ...
PARKINSON DISEASE
... Newer dopamine agonists include : lisuride , pergolide , ropinirol , Cabergoline and pramipexole have longer time of action than L- dopa . They are given 1-2 daily with less tendency to cause dyskinesia and on-off phenomena. Their main SEs are confusion ,occasionally delusion and sleep disturbances ...
... Newer dopamine agonists include : lisuride , pergolide , ropinirol , Cabergoline and pramipexole have longer time of action than L- dopa . They are given 1-2 daily with less tendency to cause dyskinesia and on-off phenomena. Their main SEs are confusion ,occasionally delusion and sleep disturbances ...
Neurodegenerative Diseases
... Newer dopamine agonists include : lisuride , pergolide , ropinirol , Cabergoline and pramipexole have longer time of action than L- dopa . They are given 1-2 daily with less tendency to cause dyskinesia and on-off phenomena. Their main SEs are confusion ,occasionally delusion and sleep disturbances ...
... Newer dopamine agonists include : lisuride , pergolide , ropinirol , Cabergoline and pramipexole have longer time of action than L- dopa . They are given 1-2 daily with less tendency to cause dyskinesia and on-off phenomena. Their main SEs are confusion ,occasionally delusion and sleep disturbances ...
Resting Potential
... • Microglia can destroy cells that are old &/or damaged • A – healthy neuron • B – neuron being destroyed & DNA breaking apart • C – microglia removing debris ...
... • Microglia can destroy cells that are old &/or damaged • A – healthy neuron • B – neuron being destroyed & DNA breaking apart • C – microglia removing debris ...
chronic morphine exposure affects visual response latency of the
... found that LGN neurons in morphine-treated cats exhibited significantly longer response latency than those in saline-treated cats. This suggests that visual information transfer is delayed in LGN cells by morphine administration. Chronic morphine exposure induces adaptation of the neural system to o ...
... found that LGN neurons in morphine-treated cats exhibited significantly longer response latency than those in saline-treated cats. This suggests that visual information transfer is delayed in LGN cells by morphine administration. Chronic morphine exposure induces adaptation of the neural system to o ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • The clock’s rhythm usually does not exactly match environmental events. • Experiments in which humans have been deprived of external cues have shown that biological clock has a period of about 25 hours. ...
... • The clock’s rhythm usually does not exactly match environmental events. • Experiments in which humans have been deprived of external cues have shown that biological clock has a period of about 25 hours. ...
Poster No: 1064 - Orthopaedic Research Society
... root was exposed to compression at 7.5 gram force (gf) clipping power. In the present study, the strength of the spring clips used for nerve root compression was determined with an Instron-type tensile tester.2 After awakening from the anesthetic, the animals were maintained for 1 week, or 3 weeks a ...
... root was exposed to compression at 7.5 gram force (gf) clipping power. In the present study, the strength of the spring clips used for nerve root compression was determined with an Instron-type tensile tester.2 After awakening from the anesthetic, the animals were maintained for 1 week, or 3 weeks a ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.