«Классы и номенклатура неорганических соединений»
... compounds C. the nature of compounds D. temperature of the system E. the presence of catalyst 11. How affects solubility of gases in a liquid if the temperature tend to increase? A. *decrease B. increase C. does not change D. to become unlimited E. increase and after does not change 12. The compound ...
... compounds C. the nature of compounds D. temperature of the system E. the presence of catalyst 11. How affects solubility of gases in a liquid if the temperature tend to increase? A. *decrease B. increase C. does not change D. to become unlimited E. increase and after does not change 12. The compound ...
Electronic excitation gives informative fragmentation of polypeptide
... being again the most abundant. The absence of low-mass y ions in the MSAD spectrum could be due to the massdiscrimination effect of the gated trapping, but it could also be an inherent feature of MSAD. For other molecules, the tendency of MSAD to promote formation of ions with high m/z was also noti ...
... being again the most abundant. The absence of low-mass y ions in the MSAD spectrum could be due to the massdiscrimination effect of the gated trapping, but it could also be an inherent feature of MSAD. For other molecules, the tendency of MSAD to promote formation of ions with high m/z was also noti ...
Addition of ketene to ethylene oxide
... This Thesis - Open Access is brought to you for free and open access by Scholars' Mine. It has been accepted for inclusion in Masters Theses by an authorized administrator of Scholars' Mine. This work is protected by U. S. Copyright Law. Unauthorized use including reproduction for redistribution req ...
... This Thesis - Open Access is brought to you for free and open access by Scholars' Mine. It has been accepted for inclusion in Masters Theses by an authorized administrator of Scholars' Mine. This work is protected by U. S. Copyright Law. Unauthorized use including reproduction for redistribution req ...
Exam Review_Key_All Topics.082
... 1. What is the purpose of a fractionating column and how does it work? A Fractionating column is used to separate a mixture into its component parts by differences in boiling points. The fractionating column is filled with beads that allow for condensation. The bottom of the flask is heated and the ...
... 1. What is the purpose of a fractionating column and how does it work? A Fractionating column is used to separate a mixture into its component parts by differences in boiling points. The fractionating column is filled with beads that allow for condensation. The bottom of the flask is heated and the ...
Lab 1
... of heat and electricity, ductile (can be drawn into a wire), and malleable (can be molded into a shape). Some metals such as sodium or calcium may have a white coating of oxide formed by reacting with oxygen in the air. If these are cut, you can see the fresh shiny metal underneath. In contrast, non ...
... of heat and electricity, ductile (can be drawn into a wire), and malleable (can be molded into a shape). Some metals such as sodium or calcium may have a white coating of oxide formed by reacting with oxygen in the air. If these are cut, you can see the fresh shiny metal underneath. In contrast, non ...
Chemistry I
... Cl + e → Cl Negative ions = anions. anions. Cations derived from metal name (sodium (cat)ion (cat)ion,, silver (cat)ion (cat)ion)) or have the suffix –ium (NH4+ = ammonium ion) Anions from nonnon-metal atoms have the suffix –ide (chloride) in compounds with oxygen –ate (SO42-=sulfate) or –ite (SO32- ...
... Cl + e → Cl Negative ions = anions. anions. Cations derived from metal name (sodium (cat)ion (cat)ion,, silver (cat)ion (cat)ion)) or have the suffix –ium (NH4+ = ammonium ion) Anions from nonnon-metal atoms have the suffix –ide (chloride) in compounds with oxygen –ate (SO42-=sulfate) or –ite (SO32- ...
Theoretical problems (official version)
... (Agas are molecules A in the gaseous state, Aads are the same molecules on the surface) with the equilibrium constant K: nAads (mol/m 2 ) К pAgas (bar) (such assumption holds if a small number of molecules is adsorbed on the surface) Adsorption properties of graphene can be estimated from the data ...
... (Agas are molecules A in the gaseous state, Aads are the same molecules on the surface) with the equilibrium constant K: nAads (mol/m 2 ) К pAgas (bar) (such assumption holds if a small number of molecules is adsorbed on the surface) Adsorption properties of graphene can be estimated from the data ...
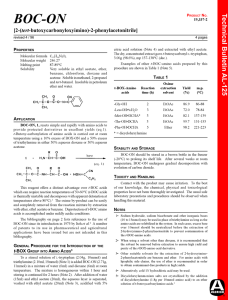
BOC-ON - Sigma
... Active Analog of the C-Terminal Heptapeptide with ,-Hydroxynorleucine Sulfate Replacing Tyrosine Sulfate. J. Med. Chem. 1978, 21, 1030. 13 Cachia, P.J.; Sykes, B.D.; Hodges, R.S. Calcium-dependant Inhibitory Region of Troponin: A protein Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Interaction between T ...
... Active Analog of the C-Terminal Heptapeptide with ,-Hydroxynorleucine Sulfate Replacing Tyrosine Sulfate. J. Med. Chem. 1978, 21, 1030. 13 Cachia, P.J.; Sykes, B.D.; Hodges, R.S. Calcium-dependant Inhibitory Region of Troponin: A protein Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Interaction between T ...
Part One Time: 50 minutes Value: 50 % Instructions : Shade in the
... If 67 mL of skidoo oil was completely dissolved in 879 mL of gasoline, which statement below would accurately describe the resulting solution? A. 67 mL of solute and 879 mL of solvent B. 67 mL of solvent and 879 mL of solute C. 67 mL of solvent and 946 mL of solute D. 879 mL of solute and 946 mL of ...
... If 67 mL of skidoo oil was completely dissolved in 879 mL of gasoline, which statement below would accurately describe the resulting solution? A. 67 mL of solute and 879 mL of solvent B. 67 mL of solvent and 879 mL of solute C. 67 mL of solvent and 946 mL of solute D. 879 mL of solute and 946 mL of ...
2 Chemical equilibrium occurs when a reaction and its reverse
... The ratio of [NO2]2 to [N2O4] remains constant (within error) at this temperature no matter what the initial concentrations of NO2 and N2O4 are. ...
... The ratio of [NO2]2 to [N2O4] remains constant (within error) at this temperature no matter what the initial concentrations of NO2 and N2O4 are. ...
Unit D: Quantitative Relationships in Chemical Change
... CuSO4(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s) ...
... CuSO4(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + Cu(OH)2(s) ...
5. Formulae, equations and amounts of substance
... conical flask during a titration to wash the sides of the flask so that all the acid on the side is washed into the reaction mixture to react with the alkali. It does not affect the titration reading as water does not react with the reagents or change the number of moles of acid added. Only distille ...
... conical flask during a titration to wash the sides of the flask so that all the acid on the side is washed into the reaction mixture to react with the alkali. It does not affect the titration reading as water does not react with the reagents or change the number of moles of acid added. Only distille ...
AP Chemistry: Chapter 13 Gaseous Equilibrium Section 1: Multiple
... A rigid container holds a mixture of graphite pellets (C(s)), H2O(g), CO(g), and H2(g) at equilibrium. State whether the number of moles of CO(g) in the container will increase, decrease, or remain the same after each of the following disturbances is applied to the original mixture. For each case, a ...
... A rigid container holds a mixture of graphite pellets (C(s)), H2O(g), CO(g), and H2(g) at equilibrium. State whether the number of moles of CO(g) in the container will increase, decrease, or remain the same after each of the following disturbances is applied to the original mixture. For each case, a ...
Lab 1
... Calculate the standard deviation for the following set of coins, and express to the appropriate number of significant figures: ...
... Calculate the standard deviation for the following set of coins, and express to the appropriate number of significant figures: ...
unit 7 h chem notes - chemical equations
... 1. Hydrogen gas reacts with chlorine gas to yield Hydrogen chloride. 2. Carbon reacts with oxygen gas to form Carbon dioxide. 3. Lithium reacts with chlorine gas to form Lithium Chloride. 4. Calcium reacts with Bromine to yield Calcium Bromide. 5. Hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas to yield water. ...
... 1. Hydrogen gas reacts with chlorine gas to yield Hydrogen chloride. 2. Carbon reacts with oxygen gas to form Carbon dioxide. 3. Lithium reacts with chlorine gas to form Lithium Chloride. 4. Calcium reacts with Bromine to yield Calcium Bromide. 5. Hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas to yield water. ...