OCR Gateway Science
... (d) At what time does reaction D finish? (e) What volume of gas is produced after 10 seconds in reaction D? (f) Suggest the maximum volume of gas produced by using 0.01 g of magnesium. (g) How does the volume of hydrogen given off depend on the mass of magnesium used? ...
... (d) At what time does reaction D finish? (e) What volume of gas is produced after 10 seconds in reaction D? (f) Suggest the maximum volume of gas produced by using 0.01 g of magnesium. (g) How does the volume of hydrogen given off depend on the mass of magnesium used? ...
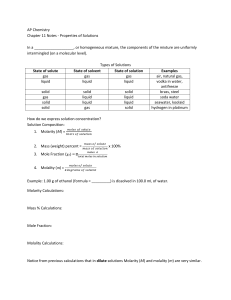
Types of Aqueous Reactions
... Are these products solids, liquids, gases, or aqueous? Depends! They are ionic, so they could be solids. But, they could also be aqueous. How? If they are water soluble solids then they are aqueous! (The reactants are in water already) Does it make a difference? ...
... Are these products solids, liquids, gases, or aqueous? Depends! They are ionic, so they could be solids. But, they could also be aqueous. How? If they are water soluble solids then they are aqueous! (The reactants are in water already) Does it make a difference? ...
AP Chemistry - West Bloomfield School District
... Write the name of the metal (it is always written first.) as it appears on the periodic table. Check on the periodic table to see if the METAL has a variable-charge. If it has more than one charge, you must use ROMAN numerals. (I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X) Memorize these now if you d ...
... Write the name of the metal (it is always written first.) as it appears on the periodic table. Check on the periodic table to see if the METAL has a variable-charge. If it has more than one charge, you must use ROMAN numerals. (I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X) Memorize these now if you d ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 11 Notes - Properties of Solutions In a , or
... Sample Exercise 11.8 on page 528: Calculate the Molar mass by Boiling Point Elevation: A solution was prepared by dissolving 18.00 g glucose in 150.0 g water. The resulting solution was found to have a boiling point of 100.34 ºC. Calculate the molar mass of glucose. Glucose is a molecular solid that ...
... Sample Exercise 11.8 on page 528: Calculate the Molar mass by Boiling Point Elevation: A solution was prepared by dissolving 18.00 g glucose in 150.0 g water. The resulting solution was found to have a boiling point of 100.34 ºC. Calculate the molar mass of glucose. Glucose is a molecular solid that ...
AH 2015 incl MG
... made up to the mark with deionised water. 25·0 cm3 samples of this solution were titrated with 0·050 mol l−1 sulphuric acid. ...
... made up to the mark with deionised water. 25·0 cm3 samples of this solution were titrated with 0·050 mol l−1 sulphuric acid. ...
NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL CHEMISTRY EXAMINATION (1995
... From these data, she can conclude that a) both Ba(IO 3 ) 2 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. b) both PbCrO4 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. c) Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , and PbCrO4 are insoluble in water. d) all of Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Mg(ClO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , PbCrO4 , and CaCrO 4 are in ...
... From these data, she can conclude that a) both Ba(IO 3 ) 2 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. b) both PbCrO4 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. c) Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , and PbCrO4 are insoluble in water. d) all of Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Mg(ClO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , PbCrO4 , and CaCrO 4 are in ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context
... 57) Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize? A) ionic bonds B) both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds C) polar covalent bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) both polar covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds 58) Temperature usually increases when water condenses. Which behavior of water is most directl ...
... 57) Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize? A) ionic bonds B) both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds C) polar covalent bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) both polar covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds 58) Temperature usually increases when water condenses. Which behavior of water is most directl ...
File
... a student wishes to use the Nernst equation to find the equilibrium constant. What number should the student use for “n” in the Nernst equation? ________16. Which of the following solutions would form a buffer when added to 50.0 mL of 2.00 molar NH3? I. 25.0 mL of 2.00 molar NH4Cl II. 25.0 mL of 2.0 ...
... a student wishes to use the Nernst equation to find the equilibrium constant. What number should the student use for “n” in the Nernst equation? ________16. Which of the following solutions would form a buffer when added to 50.0 mL of 2.00 molar NH3? I. 25.0 mL of 2.00 molar NH4Cl II. 25.0 mL of 2.0 ...
2014_S4_CHM_NORMAL (ALL)
... Directions : Each question below (Question Nos. 45 to 50) consists of two separate statements. Decide whether each of the two statements is true or false; if both are true, then decide whether or not the second statement is a correct explanation of the first statement. Then select one option from A ...
... Directions : Each question below (Question Nos. 45 to 50) consists of two separate statements. Decide whether each of the two statements is true or false; if both are true, then decide whether or not the second statement is a correct explanation of the first statement. Then select one option from A ...
Properties of Systems in Equilibrium - Le
... where Qsp is called the solubility product reaction quotient. Note that, upon mixing two solutions, one containing A+ and the other containing B-, if Qsp < Ksp the system is not at equilibrium, but since no solid AxBy is present the reaction cannot shift to the right and therefore no reaction will b ...
... where Qsp is called the solubility product reaction quotient. Note that, upon mixing two solutions, one containing A+ and the other containing B-, if Qsp < Ksp the system is not at equilibrium, but since no solid AxBy is present the reaction cannot shift to the right and therefore no reaction will b ...
SAMPLE EXERCISE 4.5 Comparing Acid Strengths
... Analyze: Our task is to write a net ionic equation for a precipitation reaction, given the names of the reactants present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular ...
... Analyze: Our task is to write a net ionic equation for a precipitation reaction, given the names of the reactants present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular ...
C:\D\Books\Cambridge University Press\CUP Problems\Problems.wpd
... 95. Chemical oxygen demand was determined by weighing an appropriate amount of the aqueous sample followed by refluxing with sulfuric acid containing potassium dichromate (and silver sulfate as catalyst). The surplus of dichromate was determined by iodometry (or alternatively, titration with iron(II ...
... 95. Chemical oxygen demand was determined by weighing an appropriate amount of the aqueous sample followed by refluxing with sulfuric acid containing potassium dichromate (and silver sulfate as catalyst). The surplus of dichromate was determined by iodometry (or alternatively, titration with iron(II ...
(General Equilibrium) Part 1
... reactants but the concentrations are _______ necessarily at equilibrium. 2. Predict direction of reaction by comparing the value of Qc to Kc. a. Qc < Kc; _________________ products reaction goes from __________________ b. Qc > Kc; _________________ products reaction goes from ___________________ c ...
... reactants but the concentrations are _______ necessarily at equilibrium. 2. Predict direction of reaction by comparing the value of Qc to Kc. a. Qc < Kc; _________________ products reaction goes from __________________ b. Qc > Kc; _________________ products reaction goes from ___________________ c ...
Presentation by class of 2013
... FILL IN THE GAP! Water is being produced ………………. as ............, compared to Iodide. ...
... FILL IN THE GAP! Water is being produced ………………. as ............, compared to Iodide. ...
File
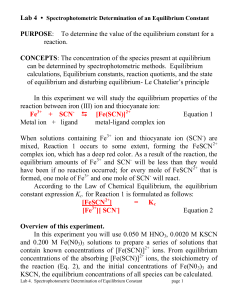
... 4. Write the Mass-action expression of the Law of Chemical Equilibrium for the following reversible reactions. a) C3H7OH(l) + CH3COOH(l) CH3COOC3H7(l) + H2O(l) b) 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) c) NH4Cl (s) NH3 (g) + HCl(g) 5. At 25 °C, Kc =0.0146 for the following reaction: PCl5 PCl3 + Cl2 If, a ...
... 4. Write the Mass-action expression of the Law of Chemical Equilibrium for the following reversible reactions. a) C3H7OH(l) + CH3COOH(l) CH3COOC3H7(l) + H2O(l) b) 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) c) NH4Cl (s) NH3 (g) + HCl(g) 5. At 25 °C, Kc =0.0146 for the following reaction: PCl5 PCl3 + Cl2 If, a ...
PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a
... base. (This is just like a Bronsted-Lowry base that accepts a proton by forming a covalent bond with the H+. The H+ (proton) does not have any electrons but will form covalent bonds with another that has alone pair of electrons. The Fe3+ ion accepts the lone pair of electrons acting as a Lewis acid. ...
... base. (This is just like a Bronsted-Lowry base that accepts a proton by forming a covalent bond with the H+. The H+ (proton) does not have any electrons but will form covalent bonds with another that has alone pair of electrons. The Fe3+ ion accepts the lone pair of electrons acting as a Lewis acid. ...
Topic 1: Quantitative Chemistry
... 8.2 Properties of acids and bases 8.2.1 Outline the characteristic properties of acids and bases in aqueous solution. 8.3 Strong and weak acids and bases 8.3.1 Distinguish between strong and weak acids and bases in terms of the extent of dissociation, reaction with water and electrical conductivity. ...
... 8.2 Properties of acids and bases 8.2.1 Outline the characteristic properties of acids and bases in aqueous solution. 8.3 Strong and weak acids and bases 8.3.1 Distinguish between strong and weak acids and bases in terms of the extent of dissociation, reaction with water and electrical conductivity. ...
Physical Chemistry Laboratory
... K Fm The van’t Hoff i factor is a measure of the deviations of behavior of an electrolyte solution from an ideal solution of a non-electrolyte. It was observed that van’t Hoff i values increased with decreasing concentration of the salt (increasing dilution), and appeared to approach integral values ...
... K Fm The van’t Hoff i factor is a measure of the deviations of behavior of an electrolyte solution from an ideal solution of a non-electrolyte. It was observed that van’t Hoff i values increased with decreasing concentration of the salt (increasing dilution), and appeared to approach integral values ...