Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: The Organic
... sample with a “pulse” of radio waves of all frequencies and detecting which frequencies are given off as the sample relaxed to its original spin state distribution. Once it has relaxed, another pulse can be applied. In the same time as it would take to acquire data for one spectrum using a CW-NMR, d ...
... sample with a “pulse” of radio waves of all frequencies and detecting which frequencies are given off as the sample relaxed to its original spin state distribution. Once it has relaxed, another pulse can be applied. In the same time as it would take to acquire data for one spectrum using a CW-NMR, d ...
Amines - WordPress.com
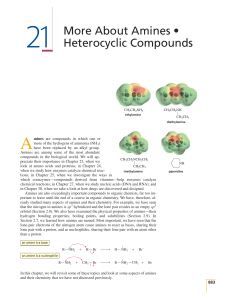
... simplest aromatic amine. Its simple derivatives are named using the prefixes o-, m-, p-, or numbers to locate substituents. Several derivatives of aniline have common names that are still widely used. Among those are toluidine for a methyl-substituted aniline and anisidine for a methoxysubstituted a ...
... simplest aromatic amine. Its simple derivatives are named using the prefixes o-, m-, p-, or numbers to locate substituents. Several derivatives of aniline have common names that are still widely used. Among those are toluidine for a methyl-substituted aniline and anisidine for a methoxysubstituted a ...
슬라이드 1
... The addition of halides to transition-metal species with low oxidation states is a common reaction in transition-metal chemistry and is called oxidative addition. The formal oxidation state of copper after addition is 3+. This step is followed by combination of two of the alkyl groups from c ...
... The addition of halides to transition-metal species with low oxidation states is a common reaction in transition-metal chemistry and is called oxidative addition. The formal oxidation state of copper after addition is 3+. This step is followed by combination of two of the alkyl groups from c ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - Aldehydes and Ketones C=O C C C
... occurs with both aldehydes and ketones involves addition to the polar C=O double bond (oxygen has a greater electronegativity) attacked by nucleophiles at the positive carbon centre alkenes are non-polar and are attacked by electrophiles ...
... occurs with both aldehydes and ketones involves addition to the polar C=O double bond (oxygen has a greater electronegativity) attacked by nucleophiles at the positive carbon centre alkenes are non-polar and are attacked by electrophiles ...
Chemical Bonding II
... In ethylene, H2C=CH2, the sp2 orbitals are used to make one of the bonds between the carbon atoms and the bonds between carbon and hydrogen. These bonds have electron density along the internuclear (bond) axis. This type of bond is called a σ (sigma) bond. ...
... In ethylene, H2C=CH2, the sp2 orbitals are used to make one of the bonds between the carbon atoms and the bonds between carbon and hydrogen. These bonds have electron density along the internuclear (bond) axis. This type of bond is called a σ (sigma) bond. ...
Reprinted from The Journal of Physical Chemistry, lgg5, 99
... liquid crystalsdescribedabove,5'hsulfur atoms in the long chain molecule dihexadecyl disulfide have been reported to have enhanced conductivity compared to the alkyl chains when imaged on graphite." In the expenmentsdescribedhere, we have investigated the effect of diff-erentfunctional groups (at th ...
... liquid crystalsdescribedabove,5'hsulfur atoms in the long chain molecule dihexadecyl disulfide have been reported to have enhanced conductivity compared to the alkyl chains when imaged on graphite." In the expenmentsdescribedhere, we have investigated the effect of diff-erentfunctional groups (at th ...
2s - Chemistry
... orbitals • when the combining atomic orbitals are identical and equal energy, the weight of each atomic orbital in the molecular orbital are equal • when the combining atomic orbitals are different kinds and energies, the atomic orbital closest in energy to the molecular orbital contributes more to ...
... orbitals • when the combining atomic orbitals are identical and equal energy, the weight of each atomic orbital in the molecular orbital are equal • when the combining atomic orbitals are different kinds and energies, the atomic orbital closest in energy to the molecular orbital contributes more to ...
NCERT/CBSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 12 textbook
... C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N and NH3 In gas phase there is no hydrogen bonding , therefore stabalisation due to hydrogen bonding is not there. Therfore the only effect to determine the strength is the inductive effect.The +I effect increases with increase in the alkyl group.Therefore the basic stren ...
... C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N and NH3 In gas phase there is no hydrogen bonding , therefore stabalisation due to hydrogen bonding is not there. Therfore the only effect to determine the strength is the inductive effect.The +I effect increases with increase in the alkyl group.Therefore the basic stren ...
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH)
... product. Thus, the alkene, which usually has a lower boiling point than the starting alcohol, can be removed by distillation as it is formed, thus driving the equilibrium to the right to favor production of more product. ...
... product. Thus, the alkene, which usually has a lower boiling point than the starting alcohol, can be removed by distillation as it is formed, thus driving the equilibrium to the right to favor production of more product. ...
Document
... • Cr6+ oxidations are characterized by a color change, as the red-orange Cr6+ reagent is reduced to green Cr3+. • Some devices used to measure blood alcohol content make use of this color change—Oxidation of CH3CH2OH, the 1° alcohol in alcoholic beverages, with orange K2Cr2O7 forms CH3COOH and green ...
... • Cr6+ oxidations are characterized by a color change, as the red-orange Cr6+ reagent is reduced to green Cr3+. • Some devices used to measure blood alcohol content make use of this color change—Oxidation of CH3CH2OH, the 1° alcohol in alcoholic beverages, with orange K2Cr2O7 forms CH3COOH and green ...
Benzyne Mechanism
... Benzylic halides are 100 times more reactive than primary halides via SN2. Transition state is stabilized by ring. ...
... Benzylic halides are 100 times more reactive than primary halides via SN2. Transition state is stabilized by ring. ...
Preview Sample 2
... 7. Isotopes are different forms of the same element that A. differ in their number of neutrons. B. differ in their number of protons. C. are all produced artificially. D. cannot form covalent bonds. E. cannot form ions. ...
... 7. Isotopes are different forms of the same element that A. differ in their number of neutrons. B. differ in their number of protons. C. are all produced artificially. D. cannot form covalent bonds. E. cannot form ions. ...
Powerpoint - U of L Class Index
... For more complex splitting patterns (i.e. where more than one coupling constant is involved), we often use tree diagrams: ...
... For more complex splitting patterns (i.e. where more than one coupling constant is involved), we often use tree diagrams: ...
The Mole I
... we could say that 4NH3 molecules react with 5 O2 molecules to produce ____ NO molecules and ____ H2O molecules. One dozen represents ______ of something. We could also say that 4 dozen NH3 molecules react with 5 dozen O2 molecules to produce _____ dozen NO molecules and _____ dozen H2O molecules. In ...
... we could say that 4NH3 molecules react with 5 O2 molecules to produce ____ NO molecules and ____ H2O molecules. One dozen represents ______ of something. We could also say that 4 dozen NH3 molecules react with 5 dozen O2 molecules to produce _____ dozen NO molecules and _____ dozen H2O molecules. In ...
1 - GENCHEM
... (b) Which of the quantum numbers govern the shape and spatial orientation of an orbital? Write the full name of each quantum number for (a) and (b). (Answer) ...
... (b) Which of the quantum numbers govern the shape and spatial orientation of an orbital? Write the full name of each quantum number for (a) and (b). (Answer) ...
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding Theories
... Bonds form using shared electrons between overlapping orbitals on adjacent atoms. Orbitals arrange around central atom to avoid each other. Two types of bonds: sigma and pi. ...
... Bonds form using shared electrons between overlapping orbitals on adjacent atoms. Orbitals arrange around central atom to avoid each other. Two types of bonds: sigma and pi. ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I
... Exams will be given after every 2 or 3 chapters in the textbook. Laboratory activities will be held each week. Laboratory notebooks will be turned in and graded each week. A post test will be given at the end of the semester. ...
... Exams will be given after every 2 or 3 chapters in the textbook. Laboratory activities will be held each week. Laboratory notebooks will be turned in and graded each week. A post test will be given at the end of the semester. ...
Aromaticity

In organic chemistry, the term aromaticity is formally used to describe an unusually stable nature of some flat rings of atoms. These structures contain a number of double bonds that interact with each other according to certain rules. As a result of their being so stable, such rings tend to form easily, and once formed, tend to be difficult to break in chemical reactions. Since one of the most commonly encountered aromatic system of compounds in organic chemistry is based on derivatives of the prototypical aromatic compound benzene (common in petroleum), the word “aromatic” is occasionally used to refer informally to benzene derivatives, and this is how it was first defined. Nevertheless, many non-benzene aromatic compounds exist. In living organisms, for example, the most common aromatic rings are the double-ringed bases in RNA and DNA.The earliest use of the term “aromatic” was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. Hofmann used the term for a class of benzene compounds, many of which do have odors (unlike pure saturated hydrocarbons). Today, there is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds, although in 1855, before the structure of benzene or organic compounds was understood, chemists like Hofmann were beginning to understand that odiferous molecules from plants, such as terpenes, had chemical properties we recognize today are similar to unsaturated petroleum hydrocarbons like benzene.In terms of the electronic nature of the molecule, aromaticity describes the way a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs of electrons, or empty molecular orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. Aromaticity can be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double-bonded to one another. These bonds may be seen as a hybrid of a single bond and a double bond, each bond in the ring identical to every other. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by August Kekulé (see History section below). The model for benzene consists of two resonance forms, which corresponds to the double and single bonds superimposing to produce six one-and-a-half bonds. Benzene is a more stable molecule than would be expected without accounting for charge delocalization.