
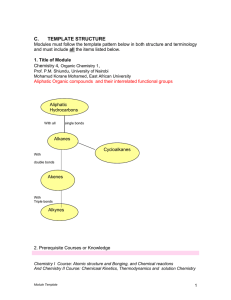
IB2 SL CHEMISTRY Name: …………………………… Topic 10
... in CO2(g) both bonds are double bonds and would have a value around 0.137 nm; Ester; Arene/benzene ring; Alcohol; Award 2 for any three correct, award [1] for any two correct. Do not accept alkane as a type of functional group in this molecule. ...
... in CO2(g) both bonds are double bonds and would have a value around 0.137 nm; Ester; Arene/benzene ring; Alcohol; Award 2 for any three correct, award [1] for any two correct. Do not accept alkane as a type of functional group in this molecule. ...
-23- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY A. STRUCTURE AND ISOMERISM 1
... see 1 (a) (ii) (hydrogenation of aldehyde or ketone) (b) active metal plus alcohol to the corresponding salt O ...
... see 1 (a) (ii) (hydrogenation of aldehyde or ketone) (b) active metal plus alcohol to the corresponding salt O ...
Organic Chemistry
... More Complex Splitting Patterns • Because the angle between C-H bond determines the extent of coupling, bond rotation is a key parameter. • In molecules with relatively free rotation about C-C sigma bonds, H atoms bonded to the same carbon in CH3 and CH2 groups generally are equivalent. • If there ...
... More Complex Splitting Patterns • Because the angle between C-H bond determines the extent of coupling, bond rotation is a key parameter. • In molecules with relatively free rotation about C-C sigma bonds, H atoms bonded to the same carbon in CH3 and CH2 groups generally are equivalent. • If there ...
Chemistry - Kendriya Vidyalaya Raigarh
... Hydrogen bonds are stronger than Van der Walls forces since hydrogen bonds are regarded as an extreme form of dipole-dipole interaction. Q.2. Write the favourable factors for the formation of ionic bond. Ans-(i) Low ionization enthalpy of metal atom. (ii) High electron gain enthalpy (Δeg H) of a non ...
... Hydrogen bonds are stronger than Van der Walls forces since hydrogen bonds are regarded as an extreme form of dipole-dipole interaction. Q.2. Write the favourable factors for the formation of ionic bond. Ans-(i) Low ionization enthalpy of metal atom. (ii) High electron gain enthalpy (Δeg H) of a non ...
Ultimate Analysis - Cheresources.com
... corrosion of copper & brass in the presence of air & also affect lead* susceptibility & color stability. Free sulfur is also corrosive, as are sulfides, disulfides, & thiophenes, which are detrimental to the octane number response to tetraethyl lead*. In diesel fuels, sulfur compounds increase wear ...
... corrosion of copper & brass in the presence of air & also affect lead* susceptibility & color stability. Free sulfur is also corrosive, as are sulfides, disulfides, & thiophenes, which are detrimental to the octane number response to tetraethyl lead*. In diesel fuels, sulfur compounds increase wear ...
4 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: STRUCTURE AND NOMENCLATURE
... effect of your diet on the level of cholesterol in your blood, which brings up the questions, “What is cholesterol?” and “Why do so many people worry about it?” Answers to each of these questions fall within the realm of a field known as organic chemistry. For more than 200 years, chemists have divi ...
... effect of your diet on the level of cholesterol in your blood, which brings up the questions, “What is cholesterol?” and “Why do so many people worry about it?” Answers to each of these questions fall within the realm of a field known as organic chemistry. For more than 200 years, chemists have divi ...
Chapter 24. Amines - Houston Community College System
... Amides (RCONH2) in general are not proton acceptors except in ...
... Amides (RCONH2) in general are not proton acceptors except in ...
Unit 4 - INTEC Chemistry Blog
... recognise oxidation, reduction, condensation, nucleophilic substitution or nucleophilic addition Redox (reduction oxidation reaction) describes / all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation number/state changed Oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all ...
... recognise oxidation, reduction, condensation, nucleophilic substitution or nucleophilic addition Redox (reduction oxidation reaction) describes / all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation number/state changed Oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all ...
CHM 3200 - Miami Dade College
... substitutions, and carbonyl condensations). Competency 10: The student will demonstrate knowledge of the chemical behavior of carboxylic acids and their derivatives by: a. Identifying properties of carboxylic acids and their derivatives. b. Illustrating methodologies for the synthesis of carboxylic ...
... substitutions, and carbonyl condensations). Competency 10: The student will demonstrate knowledge of the chemical behavior of carboxylic acids and their derivatives by: a. Identifying properties of carboxylic acids and their derivatives. b. Illustrating methodologies for the synthesis of carboxylic ...
Chpt2 - Dr. Erdal ONURHAN
... o All atoms of the same element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. o Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of numbers of atoms pf any of the two ...
... o All atoms of the same element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. o Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of numbers of atoms pf any of the two ...
2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
... If you get 6 items or more correct you can consider that you are doing fine, but if you get less than 4 items correct then you have to work very hard to pass the course. ...
... If you get 6 items or more correct you can consider that you are doing fine, but if you get less than 4 items correct then you have to work very hard to pass the course. ...
amine
... groups bonded to the nitrogen and attach the suffix –amine so the name is one word. • Use di- or tri- prefixes for identical alkyl groups. Examples: ...
... groups bonded to the nitrogen and attach the suffix –amine so the name is one word. • Use di- or tri- prefixes for identical alkyl groups. Examples: ...
Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of [Zn(2-qmpe)Cl ] containing diethyl (quinolin-2-ylmethyl)phosphonate ligand (2-qmpe)
... the appropriate hydrated zinc nitrate (1 mmol) in ethanol (10 cm3) and adding it to a solution of the ligand (1 mmol) in ethanol (15 cm3). The resulting solution was filtered and left to evaporate slowly at room temperature. Pale yellow monocrystals of the Zn(II) compound, suitable for X-ray determi ...
... the appropriate hydrated zinc nitrate (1 mmol) in ethanol (10 cm3) and adding it to a solution of the ligand (1 mmol) in ethanol (15 cm3). The resulting solution was filtered and left to evaporate slowly at room temperature. Pale yellow monocrystals of the Zn(II) compound, suitable for X-ray determi ...
PPT
... groups bonded to the nitrogen and attach the suffix –amine so the name is one word. • Use di- or tri- prefixes for identical alkyl groups. Examples: ...
... groups bonded to the nitrogen and attach the suffix –amine so the name is one word. • Use di- or tri- prefixes for identical alkyl groups. Examples: ...
1.4 Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols Answers
... ethanol. Another test is to perform a dehydration reaction using sulfuric acid as a catalyst on each alcohol to change it to an alkene. The dehydration of ethanol, which is a primary alcohol, will produce only one alkene—ethene. For the dehydration of heptan-2-ol, which is a secondary alcohol, a mix ...
... ethanol. Another test is to perform a dehydration reaction using sulfuric acid as a catalyst on each alcohol to change it to an alkene. The dehydration of ethanol, which is a primary alcohol, will produce only one alkene—ethene. For the dehydration of heptan-2-ol, which is a secondary alcohol, a mix ...
Cycloalkanes - faculty at Chemeketa
... The favored conformer of the 1,3-isomer is more stable than that of the 1,2-isomer. The favored conformer of the 1,3-isomer and that of the 1,2isomer are equal in energy. The relative stability of the two molecules cannot be ...
... The favored conformer of the 1,3-isomer is more stable than that of the 1,2-isomer. The favored conformer of the 1,3-isomer and that of the 1,2isomer are equal in energy. The relative stability of the two molecules cannot be ...
organic revision nots
... substitution reaction easily at ortho and para positions. 2. In Phenol, the –OH group activates the benzene ring towards elecrophilic substitution and directs the substituents to Ortho and para positions in benzene ring. 3. The –OH group in phenols is more strongly held as compared to –OH group in a ...
... substitution reaction easily at ortho and para positions. 2. In Phenol, the –OH group activates the benzene ring towards elecrophilic substitution and directs the substituents to Ortho and para positions in benzene ring. 3. The –OH group in phenols is more strongly held as compared to –OH group in a ...
Aromaticity

In organic chemistry, the term aromaticity is formally used to describe an unusually stable nature of some flat rings of atoms. These structures contain a number of double bonds that interact with each other according to certain rules. As a result of their being so stable, such rings tend to form easily, and once formed, tend to be difficult to break in chemical reactions. Since one of the most commonly encountered aromatic system of compounds in organic chemistry is based on derivatives of the prototypical aromatic compound benzene (common in petroleum), the word “aromatic” is occasionally used to refer informally to benzene derivatives, and this is how it was first defined. Nevertheless, many non-benzene aromatic compounds exist. In living organisms, for example, the most common aromatic rings are the double-ringed bases in RNA and DNA.The earliest use of the term “aromatic” was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. Hofmann used the term for a class of benzene compounds, many of which do have odors (unlike pure saturated hydrocarbons). Today, there is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds, although in 1855, before the structure of benzene or organic compounds was understood, chemists like Hofmann were beginning to understand that odiferous molecules from plants, such as terpenes, had chemical properties we recognize today are similar to unsaturated petroleum hydrocarbons like benzene.In terms of the electronic nature of the molecule, aromaticity describes the way a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs of electrons, or empty molecular orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. Aromaticity can be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double-bonded to one another. These bonds may be seen as a hybrid of a single bond and a double bond, each bond in the ring identical to every other. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by August Kekulé (see History section below). The model for benzene consists of two resonance forms, which corresponds to the double and single bonds superimposing to produce six one-and-a-half bonds. Benzene is a more stable molecule than would be expected without accounting for charge delocalization.
















![Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of [Zn(2-qmpe)Cl ] containing diethyl (quinolin-2-ylmethyl)phosphonate ligand (2-qmpe)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008844838_1-bf4cef9539c1ba0a885c25bcd900772d-300x300.png)





