Neurons, Neural Networks, and Learning
... membership is recognized correctly. If so, no action is required. If not, a learning rule must be applied to adjust the weights. • This iterative process has to continue either until for all vectors from the learning set their membership will be recognized correctly or it will not be recognized just ...
... membership is recognized correctly. If so, no action is required. If not, a learning rule must be applied to adjust the weights. • This iterative process has to continue either until for all vectors from the learning set their membership will be recognized correctly or it will not be recognized just ...
Abstract View ; The Salk Inst, San Diego, CA, USA
... visual system of Manduca sexta (Sphingidae, Lepidoptera) reveal two cell classes that are sensitive to the retreat or approach of an object. Stimulation with different looming stimuli and illusions (such as a rotating spiral) reveals that these cell types use different visual cues to determine direc ...
... visual system of Manduca sexta (Sphingidae, Lepidoptera) reveal two cell classes that are sensitive to the retreat or approach of an object. Stimulation with different looming stimuli and illusions (such as a rotating spiral) reveals that these cell types use different visual cues to determine direc ...
[j26]Chapter 7#
... ___ 30. Although all cells have a membrane potential only a few types of cells, such as neurons and muscle cells, demonstrate the ability to respond to stimulation - a property called excitability or irritability. ___ 31. Following stimulation of a neuron, positive charges flow into the cell causing ...
... ___ 30. Although all cells have a membrane potential only a few types of cells, such as neurons and muscle cells, demonstrate the ability to respond to stimulation - a property called excitability or irritability. ___ 31. Following stimulation of a neuron, positive charges flow into the cell causing ...
Chapter 17 Part A
... - inhibitory: postsynaptic membrane hyperpolarizes (lowers resting potential) - potassium gates open (in addition to channels) - resting potential driven more negative - more difficult for an impulse to surpass threshold level into an action potential ...
... - inhibitory: postsynaptic membrane hyperpolarizes (lowers resting potential) - potassium gates open (in addition to channels) - resting potential driven more negative - more difficult for an impulse to surpass threshold level into an action potential ...
Slide ()
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
endocrine system
... axon like a wave Just as “the wave” can flow to the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
... axon like a wave Just as “the wave” can flow to the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
Chapter 11 Marieb
... concentrated outside the cell, it rushes in so cell becomes more negative! o With either of these you get hyperpolarization! INTEGRATION Individual postsynaptic potentials are not enough to effect axon hillock and push it to threshold. They are either too weak or too far away from the axon hillock. ...
... concentrated outside the cell, it rushes in so cell becomes more negative! o With either of these you get hyperpolarization! INTEGRATION Individual postsynaptic potentials are not enough to effect axon hillock and push it to threshold. They are either too weak or too far away from the axon hillock. ...
lecture 20
... • right hemisphere will have other distinct functions – recognition of faces, patterns, spatial relationships and non-verbal thinking ...
... • right hemisphere will have other distinct functions – recognition of faces, patterns, spatial relationships and non-verbal thinking ...
Chapter 2 The Neural Impulse
... A) Neurons in the central nervous system have myelin sheaths, while those in the peripheral nervous system do not. B) Some neurons have axons that are several feet long. C) The nerve impulse involves the exchange of electrically charged ions across the cell membrane. D) Within a neuron, information ...
... A) Neurons in the central nervous system have myelin sheaths, while those in the peripheral nervous system do not. B) Some neurons have axons that are several feet long. C) The nerve impulse involves the exchange of electrically charged ions across the cell membrane. D) Within a neuron, information ...
ANIMAL RESPONSES TO ENVIRONMENT
... Dagga is a hallucinogen. It is dried parts of a plant called Cannabis. It contains at least 60 different chemicals that affect the working of the brain. THC, the most powerful chemical, attaches to the receptors of neurons that are used for short term memory, thought, concentration, and time and dis ...
... Dagga is a hallucinogen. It is dried parts of a plant called Cannabis. It contains at least 60 different chemicals that affect the working of the brain. THC, the most powerful chemical, attaches to the receptors of neurons that are used for short term memory, thought, concentration, and time and dis ...
Visual Brain
... The Map on the Striate Cortex • Cortex shows retinotopic map. – Electrodes that recorded activation from a cat’s visual cortex show: • Receptive fields on the retina that overlap also overlap in the cortex. ...
... The Map on the Striate Cortex • Cortex shows retinotopic map. – Electrodes that recorded activation from a cat’s visual cortex show: • Receptive fields on the retina that overlap also overlap in the cortex. ...
Self-Organization in the Nervous System
... cortical maps is the way of processing visual information. The nerve fibers from ganglion cells in the retina project via the thalamus to the primary visual cortex. They do that as said in a topographic manner, such that nearby locations in the retina project onto neighboring locations in the cortex ...
... cortical maps is the way of processing visual information. The nerve fibers from ganglion cells in the retina project via the thalamus to the primary visual cortex. They do that as said in a topographic manner, such that nearby locations in the retina project onto neighboring locations in the cortex ...
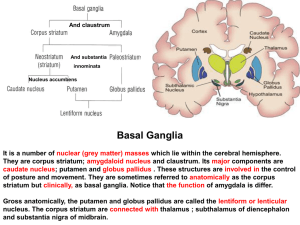
17-Basal ganglion
... Originates from the pars compacta of the ipsilateral substantia nigra of the midbrain tegmentum to caudate nucleus and putamen. The neurons of pars compacta contain the dark pigment neuromelanin. Their transmitter is the monoamine dopamine which has both excitatory and inhibitory effects upon striat ...
... Originates from the pars compacta of the ipsilateral substantia nigra of the midbrain tegmentum to caudate nucleus and putamen. The neurons of pars compacta contain the dark pigment neuromelanin. Their transmitter is the monoamine dopamine which has both excitatory and inhibitory effects upon striat ...
Chapter 16: Autonomic Nervous System
... 2. Which type of receptor is found on the membranes of all postganglionic neurons? ______________________________ 3. Which type of receptor is found on the membranes of effector cells that respond to acetylcholine? ______________________________ 4. When acetylcholine binds to nicotinic receptors it ...
... 2. Which type of receptor is found on the membranes of all postganglionic neurons? ______________________________ 3. Which type of receptor is found on the membranes of effector cells that respond to acetylcholine? ______________________________ 4. When acetylcholine binds to nicotinic receptors it ...
Document
... represented in the mind by a single unit, we consider the possibility that it could be represented by a pattern of activation a over population of units. • The elements of the pattern may represent (approximately) some feature or sensible combination of features but they need not. • What is crucial ...
... represented in the mind by a single unit, we consider the possibility that it could be represented by a pattern of activation a over population of units. • The elements of the pattern may represent (approximately) some feature or sensible combination of features but they need not. • What is crucial ...
Neural Axis Representing Target Range in the Auditory
... the frequency-modulated-signal processing area of the auditory cortex of the mustache bat (Pteronotus parnellii rubiginosus), neurons respond poorly or not at all to synthesized orientation sounds or echoes alone but respond vigorously to echoes following the emitted sound with a specific delay from ...
... the frequency-modulated-signal processing area of the auditory cortex of the mustache bat (Pteronotus parnellii rubiginosus), neurons respond poorly or not at all to synthesized orientation sounds or echoes alone but respond vigorously to echoes following the emitted sound with a specific delay from ...
Deroche-Gamonet
... nucleus accumbens, a form of synaptic plasticity, i.e. the NMDA receptordependent long-term depression (NMDAR-LTD), is suppressed in all subjects, after early drug use. Rats shifting to addiction maintain a permanent impairment of NMDAR-LTD, while rats keeping control on drug use recover it. In para ...
... nucleus accumbens, a form of synaptic plasticity, i.e. the NMDA receptordependent long-term depression (NMDAR-LTD), is suppressed in all subjects, after early drug use. Rats shifting to addiction maintain a permanent impairment of NMDAR-LTD, while rats keeping control on drug use recover it. In para ...
doc Chapter 8
... Motor nuclei includes the caudate nucleus, the putamen and globus pallidus. Caudate nucleus-a telencephalic nucleus, one of input nuclei of basal ganglia, involved in voluntary movement Putamen-telencephalic nucleus, one of the input nuclei of the basal ganglia, involved with control of voluntary mo ...
... Motor nuclei includes the caudate nucleus, the putamen and globus pallidus. Caudate nucleus-a telencephalic nucleus, one of input nuclei of basal ganglia, involved in voluntary movement Putamen-telencephalic nucleus, one of the input nuclei of the basal ganglia, involved with control of voluntary mo ...
Nervous System
... • Action potential triggers an influx of calcium • Synaptic vesicles fuse with presynaptic membrane • Neurotransmitter released into synaptic cleft • Neurotransmitters bind to receptors and open ion channels on postsynaptic membrane which sets off new action potential • Neurotransmitters are degrade ...
... • Action potential triggers an influx of calcium • Synaptic vesicles fuse with presynaptic membrane • Neurotransmitter released into synaptic cleft • Neurotransmitters bind to receptors and open ion channels on postsynaptic membrane which sets off new action potential • Neurotransmitters are degrade ...
Electrochemical Impulse
... There are many things that can cause a change in membrane potential of a neuron. Specialized receptors exist in your skin and organs that can change membrane potential due to environmental changes. These receptors will open channels allowing cations like sodium into the cell body. ...
... There are many things that can cause a change in membrane potential of a neuron. Specialized receptors exist in your skin and organs that can change membrane potential due to environmental changes. These receptors will open channels allowing cations like sodium into the cell body. ...
Spinal Cord Reflexes
... stretch reflex in flexors and extensors of limb, and FRA reflex with crossed extension component. Others suggested tactile initiated reflexes were important. •Graham Brown: central rhythmogenesis by balanced antagonist half centers—it is the interaction of the two centers that generates the rhythm. ...
... stretch reflex in flexors and extensors of limb, and FRA reflex with crossed extension component. Others suggested tactile initiated reflexes were important. •Graham Brown: central rhythmogenesis by balanced antagonist half centers—it is the interaction of the two centers that generates the rhythm. ...
Mechanism for Understanding and Imitating Actions
... “Consciousness and subjective experience cannot be reduce to brain activity.” ...
... “Consciousness and subjective experience cannot be reduce to brain activity.” ...
Major Parts of the Brain:
... 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved in motor control 12. _____ regulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and ...
... 9. _____ balance and coordination 10. _____ processes visual and auditory information, generates involuntary motor responses, maintains consciousness 11. _____ connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved in motor control 12. _____ regulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and ...
2015 SCSB FALL POSTER SESSION ABSTRACTS
... places a brain specific promoter (gnb5), in frame with the exons for the cargo binding domain of the factin motor protein Myosin Va. Myosin Va normally transports the scaffolds for glutamate receptors to spine synapses. Whole body mutations of myo5a cause early death in rodents (Mercer et al., 1991) ...
... places a brain specific promoter (gnb5), in frame with the exons for the cargo binding domain of the factin motor protein Myosin Va. Myosin Va normally transports the scaffolds for glutamate receptors to spine synapses. Whole body mutations of myo5a cause early death in rodents (Mercer et al., 1991) ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... Spinal Reflexes In a reflex arc, a sensory neuron connects with a motor neuron, allowing the sensory stimulation to trigger a movement. The knee-jerk reflex, where you extend your leg after the doctor taps your knee with a hammer, is an example of this. ...
... Spinal Reflexes In a reflex arc, a sensory neuron connects with a motor neuron, allowing the sensory stimulation to trigger a movement. The knee-jerk reflex, where you extend your leg after the doctor taps your knee with a hammer, is an example of this. ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.

![[j26]Chapter 7#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009746692_1-cea296eaa3596328a1d6ed73629d44e9-300x300.png)