Binaural Interaction in the Nucleus Laminaris of the Barn Owl: A
... In the auditory system of the barn owl, ITD is analyzed in a separate, hierarchically organized network, the ’time pathway’. The anatomical and physiological features of the first two stations of this pathway, the cochlear nucleus magnocellularis (NM) and the nucleus laminaris (NL), the first locus ...
... In the auditory system of the barn owl, ITD is analyzed in a separate, hierarchically organized network, the ’time pathway’. The anatomical and physiological features of the first two stations of this pathway, the cochlear nucleus magnocellularis (NM) and the nucleus laminaris (NL), the first locus ...
ganglion trigeminale – large light pseudounipolar neurons
... Wei F., 2006), there are yet omissions in cytological aspect. Generally results of our investigation are in accordance with results of number of authors, working with different animal and human samples. Trigeminal system is displayed by two populations of afferent neurons. Essential difference of bi ...
... Wei F., 2006), there are yet omissions in cytological aspect. Generally results of our investigation are in accordance with results of number of authors, working with different animal and human samples. Trigeminal system is displayed by two populations of afferent neurons. Essential difference of bi ...
Slide ()
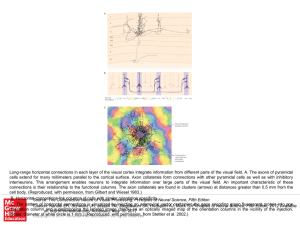
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS
... gyrus of anesthetized monkeys. All were placed within 1 mm of the plane marked A on the inset drawing, which show the cytoarchitectonic areas. Penetrations perpendicular to the cortical surface and passing down parallel to its radial axis encountered neurons all of the same modality (Powell and Moun ...
... gyrus of anesthetized monkeys. All were placed within 1 mm of the plane marked A on the inset drawing, which show the cytoarchitectonic areas. Penetrations perpendicular to the cortical surface and passing down parallel to its radial axis encountered neurons all of the same modality (Powell and Moun ...
The Human Brain
... Messages are sent through these neurons by incredibly quick electrical charges which are caused by incredibly quick chemical reactions. Different neurons can have different types of chemical transmitters which allow the messages to be passed from neuron to neuron. You may have heard of some of these ...
... Messages are sent through these neurons by incredibly quick electrical charges which are caused by incredibly quick chemical reactions. Different neurons can have different types of chemical transmitters which allow the messages to be passed from neuron to neuron. You may have heard of some of these ...
Bio_246_files/Motor Control
... – Direct pathways (pyramidal): tracts which originate in the cerebral cortex. • Initiate movement from premotor and prefrontal areas that are receiving sensory information ( Multimodal) from many areas of the brain. • controls contra lateral side of body. – Indirect pathways, (extra pyramidal) origi ...
... – Direct pathways (pyramidal): tracts which originate in the cerebral cortex. • Initiate movement from premotor and prefrontal areas that are receiving sensory information ( Multimodal) from many areas of the brain. • controls contra lateral side of body. – Indirect pathways, (extra pyramidal) origi ...
NEUROSCIENCE FACTS
... granule cell surface (Han et al. , Eur. J. Neurosci., in press; Halasy and Somogyi, ibid., in press): (i) Hilar cells whose cell bodies and dendrites are restricted to the hilus and which have ascending axons to the outer two-thirds of the molecular layer terminate in conjunction with the perforant ...
... granule cell surface (Han et al. , Eur. J. Neurosci., in press; Halasy and Somogyi, ibid., in press): (i) Hilar cells whose cell bodies and dendrites are restricted to the hilus and which have ascending axons to the outer two-thirds of the molecular layer terminate in conjunction with the perforant ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... Abstract: C-Mantec is a new neural network algorithm that adds competition between neurons with thermal perceptron learning rule. The neuron learning is ruled by the thermal perceptron rule that guarantees the stability of the learnt information while the architecture increases and while the neurons ...
... Abstract: C-Mantec is a new neural network algorithm that adds competition between neurons with thermal perceptron learning rule. The neuron learning is ruled by the thermal perceptron rule that guarantees the stability of the learnt information while the architecture increases and while the neurons ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... postganglionic neurons (4-15 pre to one post) • A single synaptic event is not sufficient to initiate an action potential in the postganglionic neurons, but the summation of multiple events is required to initiate it • Divergence: relatively few preganglionic neurons synapse with many postganglion ...
... postganglionic neurons (4-15 pre to one post) • A single synaptic event is not sufficient to initiate an action potential in the postganglionic neurons, but the summation of multiple events is required to initiate it • Divergence: relatively few preganglionic neurons synapse with many postganglion ...
The cells of the nervous system
... proteins (e.g. enzymes) for the synthesis of neurotransmitters. • Dendrites – these fibres receive nerve impulses and carry them towards the cell body • Axon – this fibre carries nerve impulses away from the cell body. • A neuron in a newly-born child has fewer dendrites and synaptic knobs • The axo ...
... proteins (e.g. enzymes) for the synthesis of neurotransmitters. • Dendrites – these fibres receive nerve impulses and carry them towards the cell body • Axon – this fibre carries nerve impulses away from the cell body. • A neuron in a newly-born child has fewer dendrites and synaptic knobs • The axo ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-05
... Middle (MCP) Input: Motor info from cortex for coordination, forms transverse fibers that give pons its shape Superior (SCP) Output: TO red nucleus and thalamus to correct motor actions Cerebellar Peduncles Inferior peduncle, can’t be labeled Only one blood vessel – gives blood supply to both sides ...
... Middle (MCP) Input: Motor info from cortex for coordination, forms transverse fibers that give pons its shape Superior (SCP) Output: TO red nucleus and thalamus to correct motor actions Cerebellar Peduncles Inferior peduncle, can’t be labeled Only one blood vessel – gives blood supply to both sides ...
Understanding the Gifted Learner`s Brain
... Attention is important for moving sensory memories to working memory. How do we get the brain to “pay attention”? There are many factors that influence attention, however the two over which we have the most control are: • Meaning – Whether or not the student can make sense of the information (Does ...
... Attention is important for moving sensory memories to working memory. How do we get the brain to “pay attention”? There are many factors that influence attention, however the two over which we have the most control are: • Meaning – Whether or not the student can make sense of the information (Does ...
1 - U-System
... - NMDA receptor binds glutamate (and with depolarization to remove the Mg2+) produces a prolonged facilitation of transmission - Once Mg2+ block removed and glutamate is bound to the NMDA receptor calcium flows into the postsynapse activates NOS (nitrous oxide synthase) NO to presynapse more ...
... - NMDA receptor binds glutamate (and with depolarization to remove the Mg2+) produces a prolonged facilitation of transmission - Once Mg2+ block removed and glutamate is bound to the NMDA receptor calcium flows into the postsynapse activates NOS (nitrous oxide synthase) NO to presynapse more ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW
... The ____________ nervous system is responsible for increasing the output of energy during emotion and stress (pumping you up!) ...
... The ____________ nervous system is responsible for increasing the output of energy during emotion and stress (pumping you up!) ...
leadership
... The brain has various localized parts Every student sitting here, is thinking about something else, so different parts of your brain is active right now, even when you are sitting in the same class. ...
... The brain has various localized parts Every student sitting here, is thinking about something else, so different parts of your brain is active right now, even when you are sitting in the same class. ...
New Title
... The outside of the cell has a net positive charge. This charge difference across the cell membrane is called the resting potential of the neuron. When a resting neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment, an impulse starts. Positive ions flow into the neuron making the inside of th ...
... The outside of the cell has a net positive charge. This charge difference across the cell membrane is called the resting potential of the neuron. When a resting neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment, an impulse starts. Positive ions flow into the neuron making the inside of th ...
Chapter 15 - FacultyWeb
... sensory neurons. Excitatory neurons in the basal nuclei become more active, leading to faulty control of voluntary movements. Axons that synapse in the thalamus no longer convey messages to the motor cortex. GABA is released by neurons in excessive amounts. ...
... sensory neurons. Excitatory neurons in the basal nuclei become more active, leading to faulty control of voluntary movements. Axons that synapse in the thalamus no longer convey messages to the motor cortex. GABA is released by neurons in excessive amounts. ...
glossary of terms
... Communication that conveys meaning without the use of spoken language and in which effectiveness is dependent on specific and shared cultural contexts. It includes but is not limited to facial expressions, ...
... Communication that conveys meaning without the use of spoken language and in which effectiveness is dependent on specific and shared cultural contexts. It includes but is not limited to facial expressions, ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Existence of distinct agnosias for aspects of perception suggests that these abilities are localized to areas selectively damaged. Achromatopsia – good perception of form despite inability to distinguish hues. Prosopagnosia – inability to recognize faces as particular people (identity). Can recogniz ...
... Existence of distinct agnosias for aspects of perception suggests that these abilities are localized to areas selectively damaged. Achromatopsia – good perception of form despite inability to distinguish hues. Prosopagnosia – inability to recognize faces as particular people (identity). Can recogniz ...
Autism and Computational Simulations
... Detailed models of pyramidal neurons and interneurons in the CA3 area of hippocampus elucidated synchronization processes and showed the influence of various chemicals. Very high 200-600 Hz (phi) frequencies observed in some form of epilepsy cannot be generated by “normal” chemical synapses. Fast el ...
... Detailed models of pyramidal neurons and interneurons in the CA3 area of hippocampus elucidated synchronization processes and showed the influence of various chemicals. Very high 200-600 Hz (phi) frequencies observed in some form of epilepsy cannot be generated by “normal” chemical synapses. Fast el ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.