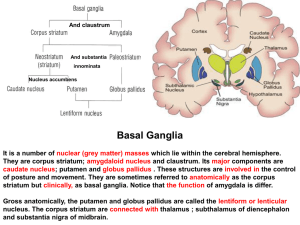
21. Basal ganglion
... plallidal neurons which becomes disinhibited to subthalamus causes activation of medial pallidal and nigral neurons and inhibition of thalamus and cortical cells. This pathway has the effect of inhibiting unwanted movements. ...
... plallidal neurons which becomes disinhibited to subthalamus causes activation of medial pallidal and nigral neurons and inhibition of thalamus and cortical cells. This pathway has the effect of inhibiting unwanted movements. ...
File - Perkins Science
... the axons of CNS neurons b.Microglia: migrate around CNS tissue and phagocytize foreign and degenerated material c.Astrocytes: regulate the external environment of the neurons d.Ependymal cells: line the ventricles and secrete ...
... the axons of CNS neurons b.Microglia: migrate around CNS tissue and phagocytize foreign and degenerated material c.Astrocytes: regulate the external environment of the neurons d.Ependymal cells: line the ventricles and secrete ...
Axon - Perkins Science
... the axons of CNS neurons b.Microglia: migrate around CNS tissue and phagocytize foreign and degenerated material c.Astrocytes: regulate the external environment of the neurons d.Ependymal cells: line the ventricles and secrete ...
... the axons of CNS neurons b.Microglia: migrate around CNS tissue and phagocytize foreign and degenerated material c.Astrocytes: regulate the external environment of the neurons d.Ependymal cells: line the ventricles and secrete ...
How do we manage to remember smells despite the fact
... Olfactory sensory neurons, which sit in the mucus in the back of the nose and relay data into the brain via axons (fingerlike projections that transmit information out from the cell body), do not live forever. In fact, they are one of the increasingly large number of neuron types that are known to d ...
... Olfactory sensory neurons, which sit in the mucus in the back of the nose and relay data into the brain via axons (fingerlike projections that transmit information out from the cell body), do not live forever. In fact, they are one of the increasingly large number of neuron types that are known to d ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Series of rapidly occurring events that change and then restore the membrane potential of a cell to its resting state • Ion channels open, Na+ rushes in (depolarization), K+ rushes out (repolarization) • All-or-none principal = with stimulation, either happens one specific way or not at all (lasts ...
... • Series of rapidly occurring events that change and then restore the membrane potential of a cell to its resting state • Ion channels open, Na+ rushes in (depolarization), K+ rushes out (repolarization) • All-or-none principal = with stimulation, either happens one specific way or not at all (lasts ...
Text - Department of Physiology, UCLA
... Work in our lab spans many levels of analysis, from the molecular to the behavioral. We are studying how voltage controls the activity of K+ channels, how changes in channel function or expression affect the firing patterns of neurons and the emergent properties of neuronal circuits, and how alterin ...
... Work in our lab spans many levels of analysis, from the molecular to the behavioral. We are studying how voltage controls the activity of K+ channels, how changes in channel function or expression affect the firing patterns of neurons and the emergent properties of neuronal circuits, and how alterin ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... excitation, thus they are either inhibitory (make the firing of the receiving neuron LESS likely) or excitatory (make the firing of the receiving neuron MORE likely). ...
... excitation, thus they are either inhibitory (make the firing of the receiving neuron LESS likely) or excitatory (make the firing of the receiving neuron MORE likely). ...
Nerve tissue
... ① nerve cells ( neurons) -- structural and functional unit. ②glial cells ( neuroglia )-- supporting, protecting and nourishing neurons. B. Neurons have unique processes and contact with each other via synapses forming neural network and circuit. C. Nervous tissue makes up nervous system. The central ...
... ① nerve cells ( neurons) -- structural and functional unit. ②glial cells ( neuroglia )-- supporting, protecting and nourishing neurons. B. Neurons have unique processes and contact with each other via synapses forming neural network and circuit. C. Nervous tissue makes up nervous system. The central ...
action potential
... b. norepinephrine (noradrenaline) [NE,NAd] c. dopamine [DA] d. serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) [5-HT] e. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) ...
... b. norepinephrine (noradrenaline) [NE,NAd] c. dopamine [DA] d. serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) [5-HT] e. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) ...
lecture 13 - McLoon Lab - University of Minnesota
... The reticular nucleus inhibits the output of other thalamic nuclei. Gating is an important way to attenuate the flow of information when it is not needed such as during sleep or when concentrating on one thing for which other information would be distracting ...
... The reticular nucleus inhibits the output of other thalamic nuclei. Gating is an important way to attenuate the flow of information when it is not needed such as during sleep or when concentrating on one thing for which other information would be distracting ...
Kein Folientitel - Institut für Grundlagen der Informationsverarbeitung
... • Inclusion of results, models, and problems of cognitive neuroscience (memory, top-level-control) • Discussion of work in related EU-research projects (in which students could become involved) ...
... • Inclusion of results, models, and problems of cognitive neuroscience (memory, top-level-control) • Discussion of work in related EU-research projects (in which students could become involved) ...
Neurotransmitters
... Neurotransmitters • Language of nervous system • 50 or more neurotransmitters have been identified • Most neurons make two or more neurotransmitters – Neurons can exert several influences ...
... Neurotransmitters • Language of nervous system • 50 or more neurotransmitters have been identified • Most neurons make two or more neurotransmitters – Neurons can exert several influences ...
The Nervous System - Gordon State College
... Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
... Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
Key Transmitters - Sinauer Associates
... activates two types of postsynaptic ionotropic receptors: fast-opening α-amino-3-hydroxy5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors and slower-opening N-methyl-Daspartate (NMDA) receptors (see Figure 11.12) The AMPA receptors are responsible for normal fast transmission. They are made up of ...
... activates two types of postsynaptic ionotropic receptors: fast-opening α-amino-3-hydroxy5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors and slower-opening N-methyl-Daspartate (NMDA) receptors (see Figure 11.12) The AMPA receptors are responsible for normal fast transmission. They are made up of ...
Bioinspired Computing Lecture 5
... Circuitry depends on neural code Temporal codes rely on a noise-free signal transmission. Thus, we would expect to find very few ‘redundant’ neurons with co-varying outputs in that network. Accordingly, an optimal temporal coding circuit might tend to eliminate redundancy in the pattern of inputs t ...
... Circuitry depends on neural code Temporal codes rely on a noise-free signal transmission. Thus, we would expect to find very few ‘redundant’ neurons with co-varying outputs in that network. Accordingly, an optimal temporal coding circuit might tend to eliminate redundancy in the pattern of inputs t ...
Biopsychology and the Foundations of
... Then answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper. After you are done, we will discuss and debate. 1. If you could select 3 genetic traits for your child, what would they be? 2. If you knew you were a possible carrier for a genetic disorder, would you want to be tested before having children? ...
... Then answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper. After you are done, we will discuss and debate. 1. If you could select 3 genetic traits for your child, what would they be? 2. If you knew you were a possible carrier for a genetic disorder, would you want to be tested before having children? ...
The Nervous System
... found in the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system stimulates the heart, blood vessels, sweat glands, the large internal organs, and the adrenal medulla in the brain. GABA GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the most important and the abundant inhibitory neurotransmitter in the br ...
... found in the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system stimulates the heart, blood vessels, sweat glands, the large internal organs, and the adrenal medulla in the brain. GABA GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the most important and the abundant inhibitory neurotransmitter in the br ...
Presentation
... Then answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper. After you are done, we will discuss and debate. 1. If you could select 3 genetic traits for your child, what would they be? 2. If you knew you were a possible carrier for a genetic disorder, would you want to be tested before having children? ...
... Then answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper. After you are done, we will discuss and debate. 1. If you could select 3 genetic traits for your child, what would they be? 2. If you knew you were a possible carrier for a genetic disorder, would you want to be tested before having children? ...
Overview of the Reticular Formation (RF)
... The neurons of the diffuse modulatory system located around the border of the Reticular Formation and have long projections covering wide areas of the brain (e.g. entire cerebral cortex, cerebellum). Neurons of nuclei within these groups play a role in modulating our level of arousal, sleep, learnin ...
... The neurons of the diffuse modulatory system located around the border of the Reticular Formation and have long projections covering wide areas of the brain (e.g. entire cerebral cortex, cerebellum). Neurons of nuclei within these groups play a role in modulating our level of arousal, sleep, learnin ...
A Neuron - Gordon State College
... After locking into receptor sites, neurotransmitters either excite or inhibit firing of the receiving neuron. Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
... After locking into receptor sites, neurotransmitters either excite or inhibit firing of the receiving neuron. Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
Introduction_to_nerv..
... • These membranes contain phospholipid molecules that have long fatty acids. • These prevent the movement of charged water soluble ions ...
... • These membranes contain phospholipid molecules that have long fatty acids. • These prevent the movement of charged water soluble ions ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.