Prac T12 - studylib.net
... The ependymal cells line the blood vessels that supply the neural tissues of the brain, thereby forming the blood-brain barrier True False Neurotransmitters that depress the resting potential are called excitatory. ...
... The ependymal cells line the blood vessels that supply the neural tissues of the brain, thereby forming the blood-brain barrier True False Neurotransmitters that depress the resting potential are called excitatory. ...
Slide ()
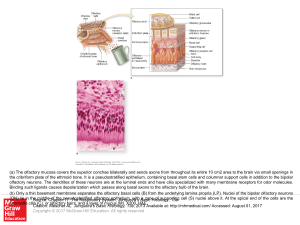
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
Motor Systems I Cortex
... Given an intent to move, the DLPFAC, with input from other frontal lobe areas (in particular the ventrolateral PFC; the endpoint of the ventral streams), anticipates the consequences of various movements and forms a plan of action Outputs to secondary motor cortex, primary motor cortex, and ...
... Given an intent to move, the DLPFAC, with input from other frontal lobe areas (in particular the ventrolateral PFC; the endpoint of the ventral streams), anticipates the consequences of various movements and forms a plan of action Outputs to secondary motor cortex, primary motor cortex, and ...
Nervous System III – Reflexes and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... Transmit information from the ...
... Transmit information from the ...
brain
... – Patient video – Patient video • Neglect Syndrome: complete inattentiveness to stimuli on one side of the body – Patient video • Akinetopsia: inability to perceive movement – “I see the world in snapshots – like frames of a move but most of the frames are missing” ...
... – Patient video – Patient video • Neglect Syndrome: complete inattentiveness to stimuli on one side of the body – Patient video • Akinetopsia: inability to perceive movement – “I see the world in snapshots – like frames of a move but most of the frames are missing” ...
Frontal Lobe
... (Failure to inhibit irrelevant information) and show perseveration in the: WCST test (Failure to flexible shifting of goals). It is now clear that the basal ganglia are not only the recipient of PFC inputs but also project to the PFC. In view of the strong inhibitory nature of the basal ganglia proj ...
... (Failure to inhibit irrelevant information) and show perseveration in the: WCST test (Failure to flexible shifting of goals). It is now clear that the basal ganglia are not only the recipient of PFC inputs but also project to the PFC. In view of the strong inhibitory nature of the basal ganglia proj ...
File
... 6. Your brain is about the size of a cantaloupe and is wrinkled like a walnut. 7. Your brain feels like a ripe avocado and looks pink because of the blood running through it. 8. The baby’s brain grows 3x in size during its first year. 9. At birth, the human brain weighs 4/5 of a pound, while an adu ...
... 6. Your brain is about the size of a cantaloupe and is wrinkled like a walnut. 7. Your brain feels like a ripe avocado and looks pink because of the blood running through it. 8. The baby’s brain grows 3x in size during its first year. 9. At birth, the human brain weighs 4/5 of a pound, while an adu ...
brain
... – Patient video – Patient video • Neglect Syndrome: complete inattentiveness to stimuli on one side of the body – Patient video • Akinetopsia: inability to perceive movement – “I see the world in snapshots – like frames of a move but most of the frames are missing” ...
... – Patient video – Patient video • Neglect Syndrome: complete inattentiveness to stimuli on one side of the body – Patient video • Akinetopsia: inability to perceive movement – “I see the world in snapshots – like frames of a move but most of the frames are missing” ...
Students know
... (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the synapses. ...
... (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the synapses. ...
Decision Making: Hitting an uncertain target | eLife
... monkeys were now performing a target estimation task. When the degree of uncertainty in the visual information supplied to the monkeys was high they tended to move the cursor to a location that was the average of the target locations in the previous trials: this approach makes sense when relatively ...
... monkeys were now performing a target estimation task. When the degree of uncertainty in the visual information supplied to the monkeys was high they tended to move the cursor to a location that was the average of the target locations in the previous trials: this approach makes sense when relatively ...
Printable version
... 2. the potential is due to the difference in the sodium and potassium ion concentrations inside & outside of the cell C. membrane potentials that act as signals 1. a graded potential is a small, brief potential change that acts as a short-distance signal 2. an action potential, or nerve impulse, is ...
... 2. the potential is due to the difference in the sodium and potassium ion concentrations inside & outside of the cell C. membrane potentials that act as signals 1. a graded potential is a small, brief potential change that acts as a short-distance signal 2. an action potential, or nerve impulse, is ...
the human brain
... cortex spends most of its time talking to itself. Each of the cortical hemispheres have four principal lobes (see upper diagram, right). The frontal lobes house the neural circuits for thinking and planning, and are also thought to be responsible for our individual personalities. The occipital and t ...
... cortex spends most of its time talking to itself. Each of the cortical hemispheres have four principal lobes (see upper diagram, right). The frontal lobes house the neural circuits for thinking and planning, and are also thought to be responsible for our individual personalities. The occipital and t ...
acetylcholine
... Although dopamine is synthesized by only several hundred thousand cells, it fulfils an exceedingly important role in the higher parts of the CNS. These dopaminergic neurons can be divided into three subgroups with different functions. The first group regulates movements: a deficit of dopamine in thi ...
... Although dopamine is synthesized by only several hundred thousand cells, it fulfils an exceedingly important role in the higher parts of the CNS. These dopaminergic neurons can be divided into three subgroups with different functions. The first group regulates movements: a deficit of dopamine in thi ...
lgn - cinpla
... surprising because the LGN does not only receive input from the ganglion cells of the retina alone. About 80 % of the excitatory input to the LGN is feedback from the visual cortex. One would therefore expect the LGN to be more heavily influenced by visual cortex and the response not so similar to t ...
... surprising because the LGN does not only receive input from the ganglion cells of the retina alone. About 80 % of the excitatory input to the LGN is feedback from the visual cortex. One would therefore expect the LGN to be more heavily influenced by visual cortex and the response not so similar to t ...
Neuroscience
... dendrite of another neuron 1. Vesicle – bubble like containers that hold chemical molecules called neurotransmitters ...
... dendrite of another neuron 1. Vesicle – bubble like containers that hold chemical molecules called neurotransmitters ...
Neurons and Networks. An Introduction to Behavioral Neuroscience, Second Edition Brochure
... solid foundation of understanding and knowledge required for further study. The new edition retains the features that made the first edition so attractive: consistent emphasis on results and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanati ...
... solid foundation of understanding and knowledge required for further study. The new edition retains the features that made the first edition so attractive: consistent emphasis on results and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanati ...
Can the ophthalmologist repair the Brain in Infantile ET
... average prevalence for all the infants. Data from more than 100 consecutive infants, replotted from Birch et al ...
... average prevalence for all the infants. Data from more than 100 consecutive infants, replotted from Birch et al ...
Midterm 1 - studyfruit
... Synaptic Integration ■ EPSP ● (excitatory post synaptic potential) ● Every time NT released, some ions can enter post synaptic cell and raise membrane potential. (positive contribution) ● If enough of these happen close together, threshold can be reached ● Always one nerve, but either three signals ...
... Synaptic Integration ■ EPSP ● (excitatory post synaptic potential) ● Every time NT released, some ions can enter post synaptic cell and raise membrane potential. (positive contribution) ● If enough of these happen close together, threshold can be reached ● Always one nerve, but either three signals ...
Chapter_03_4E
... Hyperpolarization occurs when inside of cell becomes more negative relative to outside (<–70 mV) Graded potentials are localized changes in membrane potential (either depolarization or hyperpolarization) ...
... Hyperpolarization occurs when inside of cell becomes more negative relative to outside (<–70 mV) Graded potentials are localized changes in membrane potential (either depolarization or hyperpolarization) ...
Acetylcholine
... ending from releasing acetylcholine, causing paralysis. The botulin derivative botox is used by many people to temporarily eliminate wrinkles - a sad commentary on our times, I would say. On a more serious note, there is a link between acetylcholine and Alzheimer's disease: There is something on the ...
... ending from releasing acetylcholine, causing paralysis. The botulin derivative botox is used by many people to temporarily eliminate wrinkles - a sad commentary on our times, I would say. On a more serious note, there is a link between acetylcholine and Alzheimer's disease: There is something on the ...
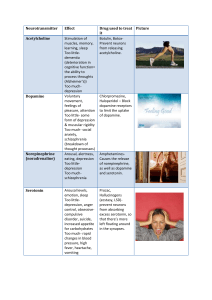
Neurotransmitter - Pamoja Education Blogs
... Too little- some form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
... Too little- some form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.