Neuroimaging Tutorial
... Psy 531 Affects and Emotions A brief tutorial on neurimaging techniques fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its st ...
... Psy 531 Affects and Emotions A brief tutorial on neurimaging techniques fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its st ...
Signaling in large-scale neural networks
... and function at the network level is one of the hard problems in neuroscience. Nevertheless, there is much to be said about synaptic transduction in individual neurons. Intercalated between the synaptic currents and spike generation are active non-linear filters provided by current generating voltag ...
... and function at the network level is one of the hard problems in neuroscience. Nevertheless, there is much to be said about synaptic transduction in individual neurons. Intercalated between the synaptic currents and spike generation are active non-linear filters provided by current generating voltag ...
RESEARCH LETTERS 3 Marwood RP. Disappearance of
... filamentous projections. 39.9% of the DAT* neurons were found in the putamen, 11.6% in the caudate nucleus, 16.3% in the globus pallidus externa, 6.2% in the globus pallidus interna, and 25.9% in the adjacent internal capsule and in particular the ansa lenticularis. In eight of the ten brains from p ...
... filamentous projections. 39.9% of the DAT* neurons were found in the putamen, 11.6% in the caudate nucleus, 16.3% in the globus pallidus externa, 6.2% in the globus pallidus interna, and 25.9% in the adjacent internal capsule and in particular the ansa lenticularis. In eight of the ten brains from p ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... - midbrain reticular formation ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) promotes wakefulness by affecting thalamus and cortex - ARAS thalamic relay and association nuclei (tonic mode) - ARAS projects to midline and intralaminar nuclei of thalamus these project to cortical areas activat ...
... - midbrain reticular formation ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) promotes wakefulness by affecting thalamus and cortex - ARAS thalamic relay and association nuclei (tonic mode) - ARAS projects to midline and intralaminar nuclei of thalamus these project to cortical areas activat ...
Chapter Two
... B. Neurotransmitters are chemical molecules released at the synapse that, in general, will either excite or inhibit a reaction in the cell on the other side of the synapse. C. Receptor sites are places on a neuron where neurotransmitters can be received. 1. It is the interaction of neurotransmitter ...
... B. Neurotransmitters are chemical molecules released at the synapse that, in general, will either excite or inhibit a reaction in the cell on the other side of the synapse. C. Receptor sites are places on a neuron where neurotransmitters can be received. 1. It is the interaction of neurotransmitter ...
Cerebral cortex and thalamus lecture
... Integrating sensory input language and speech production memory ...
... Integrating sensory input language and speech production memory ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
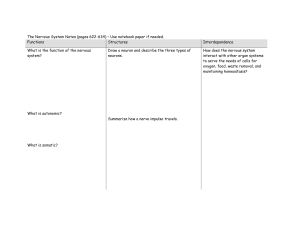
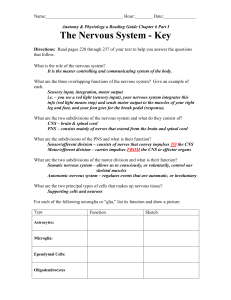
The Nervous System – Use notebook paper if
... The Nervous System Notes (pages 622-634) – Use notebook paper if needed. Functions Structures What is the function of the nervous system? ...
... The Nervous System Notes (pages 622-634) – Use notebook paper if needed. Functions Structures What is the function of the nervous system? ...
Somatosensory system
... Dorsal root ganglia - spinal nerve - limb and trunk Trigeminal ganglia - cranial nerve - head and face ...
... Dorsal root ganglia - spinal nerve - limb and trunk Trigeminal ganglia - cranial nerve - head and face ...
Paralys
... Neurotrophins 3, 4, and 6 (NT-3, NT4, and NT-6) regulate survival and growth like NGF, but these central neurotrophins also have a role in the long-term neural changes in the brain that underlie learning and memory. The mechanisms of neurotrophins on cell machinery are the subject of vigorous resear ...
... Neurotrophins 3, 4, and 6 (NT-3, NT4, and NT-6) regulate survival and growth like NGF, but these central neurotrophins also have a role in the long-term neural changes in the brain that underlie learning and memory. The mechanisms of neurotrophins on cell machinery are the subject of vigorous resear ...
begin
... axon terminal The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter An action potential is started in the dendrite Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... axon terminal The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter An action potential is started in the dendrite Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Types of Neurons of ANS
... To review the different types of neurons associated with the ANS. To clearly identify the position and role of the sympathetic trunk & collateral ganglia. To address the two different types of receptors for neurotransmitters of the sympathetic ANS: - Cholinergic Receptors - Adrenergic Receptors To r ...
... To review the different types of neurons associated with the ANS. To clearly identify the position and role of the sympathetic trunk & collateral ganglia. To address the two different types of receptors for neurotransmitters of the sympathetic ANS: - Cholinergic Receptors - Adrenergic Receptors To r ...
brain - Austin Community College
... - Somatic nervous system – provides conscious control of skeletal muscles - Autonomic nervous system – regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands 3. All other neurons are termed as association neurons or interneurons responsible for integrating afferent information and formulating an effere ...
... - Somatic nervous system – provides conscious control of skeletal muscles - Autonomic nervous system – regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands 3. All other neurons are termed as association neurons or interneurons responsible for integrating afferent information and formulating an effere ...
Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural networks
... indicate that a combinatorial neural code, based on rapid associations of groups of neurons co-ordinating their activity at the single spike level, is possible within a cortical-like network. Evidence is accumulating that cortical neurons in vivo are capable of producing action potentials with high ...
... indicate that a combinatorial neural code, based on rapid associations of groups of neurons co-ordinating their activity at the single spike level, is possible within a cortical-like network. Evidence is accumulating that cortical neurons in vivo are capable of producing action potentials with high ...
Parieto-prefrontal pathway
... focused on navigation and relating ourselves to our environment. •The hippocampus creates cognitive maps, which reduce the cognitive load required for navigation, as well as allow us to acquire, code, decode, store, and recall information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in o ...
... focused on navigation and relating ourselves to our environment. •The hippocampus creates cognitive maps, which reduce the cognitive load required for navigation, as well as allow us to acquire, code, decode, store, and recall information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in o ...
Neurotransmitters - Shifa College of Medicine
... Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: autoimmune disorder also characterized by muscle weakness. Due to autoantibodies against the presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels ...
... Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: autoimmune disorder also characterized by muscle weakness. Due to autoantibodies against the presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels ...
File
... What is the function of a neuron? They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better unders ...
... What is the function of a neuron? They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better unders ...
Modeling large cortical networks with growing self
... the GLISSOM starting size is sufficiently large [7]. Scaling equations similar to those in section 2 can also be developed for other similar models, and then smooth interpolation can be used to scale them up during self-organization. Essentially, the GLISSOM method allows a fixed model to be adapted ...
... the GLISSOM starting size is sufficiently large [7]. Scaling equations similar to those in section 2 can also be developed for other similar models, and then smooth interpolation can be used to scale them up during self-organization. Essentially, the GLISSOM method allows a fixed model to be adapted ...
ángeles garcía pardo
... in axogenesis, axon branching and presynaptic function, Franck Polleux The developmental mechanisms underlying axon morphogenesis of specific populations of mammalian neurons in vivo are still poorly understood at the cellular and molecular levels. Operationally, axon development can be divided in t ...
... in axogenesis, axon branching and presynaptic function, Franck Polleux The developmental mechanisms underlying axon morphogenesis of specific populations of mammalian neurons in vivo are still poorly understood at the cellular and molecular levels. Operationally, axon development can be divided in t ...
Resting potential
... A. Neurons 1. The long, thin cells of nerve tissue along which messages travel to & from the brain – About 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) in the human brain ...
... A. Neurons 1. The long, thin cells of nerve tissue along which messages travel to & from the brain – About 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) in the human brain ...
Neuron_glia interaction
... through release of cytokine leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). - Nervous system repair: upon injury to nerve cells within the central nervous system, astrocytes become phagocytic to ingest the injured nerve cells. The astrocytes then fill up the space to form a glial scar, repairing the area and repl ...
... through release of cytokine leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). - Nervous system repair: upon injury to nerve cells within the central nervous system, astrocytes become phagocytic to ingest the injured nerve cells. The astrocytes then fill up the space to form a glial scar, repairing the area and repl ...
Which Model to Use for the Liquid State Machine?
... work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational performance for various neuron models. The integrate-and-fire, resonate-and-fire, FitzHugh-Nagumo, Morris-Lecar, both versions of Hindmarsh-Rose and Izikevich’s neural models are examined and assessed. Beata J. Grzyb and Eris ...
... work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational performance for various neuron models. The integrate-and-fire, resonate-and-fire, FitzHugh-Nagumo, Morris-Lecar, both versions of Hindmarsh-Rose and Izikevich’s neural models are examined and assessed. Beata J. Grzyb and Eris ...
Melting the Iceberg
... sharp transitions as they emerge from the floor. To find the solution to these two problems, Finn et al. (2007) took the final step and measured the impact of noise fluctuations in membrane potential (Figures 1G–1I). Previous work from the Ferster laboratory had demonstrated that these fluctuations ...
... sharp transitions as they emerge from the floor. To find the solution to these two problems, Finn et al. (2007) took the final step and measured the impact of noise fluctuations in membrane potential (Figures 1G–1I). Previous work from the Ferster laboratory had demonstrated that these fluctuations ...
Resonate-and-fire neurons
... similar eigenfrequencies, and non-resonant for others. This provides an effective tool for selective communication, see Fig. 10. In particular, the network can multiplex: send many message via a single transmission line, as we illustrate in Fig. 11. In Figs. 10 and 11 we implicitly assume that axona ...
... similar eigenfrequencies, and non-resonant for others. This provides an effective tool for selective communication, see Fig. 10. In particular, the network can multiplex: send many message via a single transmission line, as we illustrate in Fig. 11. In Figs. 10 and 11 we implicitly assume that axona ...
Regents Biology - Baldwinsville Central School District
... immune system (T cells) attacks myelin coating loss of signal ...
... immune system (T cells) attacks myelin coating loss of signal ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.