Telencephalon
... amygdala, entorhinal and perirhinal cortices (areas 28 and 35), anterior cingulate cortex (area 24), medial orbitofrontal cortex, and widespread sources within the temporal lobe) Projects to ventral pallidum ...
... amygdala, entorhinal and perirhinal cortices (areas 28 and 35), anterior cingulate cortex (area 24), medial orbitofrontal cortex, and widespread sources within the temporal lobe) Projects to ventral pallidum ...
source1
... mode, the neuron can be trained to fire (or not), for particular input patterns. In the using mode, when a taught input pattern is detected at the input, its associated output becomes the current output. If the input pattern does not belong in the taught list of input patterns, the firing rule is us ...
... mode, the neuron can be trained to fire (or not), for particular input patterns. In the using mode, when a taught input pattern is detected at the input, its associated output becomes the current output. If the input pattern does not belong in the taught list of input patterns, the firing rule is us ...
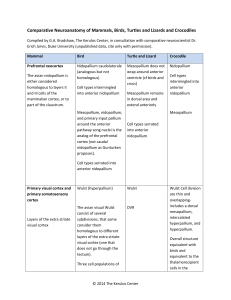
Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards
... Wulst Cell division are thin and overlappingincludes a dorsal mesopallium, intercalated hyperpallium, and hyperpallium. Overall structure equivalent with birds and equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the ...
... Wulst Cell division are thin and overlappingincludes a dorsal mesopallium, intercalated hyperpallium, and hyperpallium. Overall structure equivalent with birds and equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the ...
Reward system - Basic Knowledge 101
... perception of reward and the phenomenon of positive reinforcement are a set of interconnected forebrain structures called brain reward pathways; these include the nucleus accumbens (NAc; the major component of the ventral striatum), the basal forebrain (components of which have been termed the exten ...
... perception of reward and the phenomenon of positive reinforcement are a set of interconnected forebrain structures called brain reward pathways; these include the nucleus accumbens (NAc; the major component of the ventral striatum), the basal forebrain (components of which have been termed the exten ...
How does the Teenage Brain Work? (Teacher Version)
... 1. Do you feel teenagers have a lack of control over their impulses? truthfulness of Why or why not? arguments set forth in (Student’s answers will vary.) public documents; their 2. According to researchers, why are teenagers not able to make appeal to both friendly decisions the same way adults do? ...
... 1. Do you feel teenagers have a lack of control over their impulses? truthfulness of Why or why not? arguments set forth in (Student’s answers will vary.) public documents; their 2. According to researchers, why are teenagers not able to make appeal to both friendly decisions the same way adults do? ...
CHAPTER 48 NEURONS, SYNAPSES, AND SIGNALING I. Student
... These students do not realize the small number of ions that are involved, and they assume that Na+ entry into the axon during depolarization reverses the Na+ gradient across the membrane. ...
... These students do not realize the small number of ions that are involved, and they assume that Na+ entry into the axon during depolarization reverses the Na+ gradient across the membrane. ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 The Central Nervous
... branch is found a terminal knob. Synaptic vesicles (bundles of neurotransmitters) are located within each terminal knob. That portion of the terminal knob that faces the synaptic cleft is thickened and is called the presynaptic membrane. This is the membrane through that neurotransmitters pass to en ...
... branch is found a terminal knob. Synaptic vesicles (bundles of neurotransmitters) are located within each terminal knob. That portion of the terminal knob that faces the synaptic cleft is thickened and is called the presynaptic membrane. This is the membrane through that neurotransmitters pass to en ...
Chapter 2: The synapse – regulating communication and
... The neuromuscular junction and other excitatory synapses depolarize the postsynaptic membrane above the threshold required to elicit a postsynaptic action potential. In contrast an inhibitory synapse suppresses the action potential. As you might imagine, inhibitory neurotransmission is somewhat diff ...
... The neuromuscular junction and other excitatory synapses depolarize the postsynaptic membrane above the threshold required to elicit a postsynaptic action potential. In contrast an inhibitory synapse suppresses the action potential. As you might imagine, inhibitory neurotransmission is somewhat diff ...
... 5. Describe how synapses can ‘filter out’ weak stimuli. When the stimulus is weak, the synapse acts as a gap which the impulse cannot cross and the stimulus is ‘filtered out’ due to insufficient secretion of neurotransmitters. 6. Describe the what is meant by ‘summation’ The cumulative effect of a s ...
Lecture 07 Part A - Artificial Neural Networks
... The Structure of Neurons • A neuron only fires if its input signal exceeds a certain amount (the threshold) in a short time period. • Synapses play role in formation of memory – Two neurons are strengthened when both neurons are active at the same time – The strength of connection is thought to res ...
... The Structure of Neurons • A neuron only fires if its input signal exceeds a certain amount (the threshold) in a short time period. • Synapses play role in formation of memory – Two neurons are strengthened when both neurons are active at the same time – The strength of connection is thought to res ...
Anatomy Questions 3/2/16 1. The dorsal gray horns of the spinal
... i. It is part of the limbic system ii. It plays a role in controlling circadian rhythms iii. It regulates body temperature iv. It controls specific involuntary somatic motor activities a. 1 and 3 b. 2 and 4 c. 1, 2, and 3 d. All of the above e. None of the above 4. Non-fluent aphasia is a condition ...
... i. It is part of the limbic system ii. It plays a role in controlling circadian rhythms iii. It regulates body temperature iv. It controls specific involuntary somatic motor activities a. 1 and 3 b. 2 and 4 c. 1, 2, and 3 d. All of the above e. None of the above 4. Non-fluent aphasia is a condition ...
Feedback and feedforward control of blood flow
... of blood vessels, such as arterioles. It has long been known that larger cortical arteries are surrounded by intertwining processes arising from neurons, raising the possibility that some aspects of blood flow may be controlled by neurons themselves. For example, surface arteries receive extrinsic p ...
... of blood vessels, such as arterioles. It has long been known that larger cortical arteries are surrounded by intertwining processes arising from neurons, raising the possibility that some aspects of blood flow may be controlled by neurons themselves. For example, surface arteries receive extrinsic p ...
Neurons - E-Learning/An-Najah National University
... the cell body (Figure 7.8). If there are several, the neuron is a multipolar neuron. Since all motor and association neurons are multipolar, this is the most common structural type. Neurons with two processes—an axon and a dendrite—are called bipolar neurons. Bipolar neurons are rare in adults, foun ...
... the cell body (Figure 7.8). If there are several, the neuron is a multipolar neuron. Since all motor and association neurons are multipolar, this is the most common structural type. Neurons with two processes—an axon and a dendrite—are called bipolar neurons. Bipolar neurons are rare in adults, foun ...
Chapter 22 Thalamus
... Receptors have a characteristic pattern of position and density Orderly arrangement of receptors exists along skin, basilar membrane, and retina Differences in peripheral innervation density are tightly correlated w/ spatial acuity Receptors; sites of convergence and divergence A single gangli ...
... Receptors have a characteristic pattern of position and density Orderly arrangement of receptors exists along skin, basilar membrane, and retina Differences in peripheral innervation density are tightly correlated w/ spatial acuity Receptors; sites of convergence and divergence A single gangli ...
Towards an Empirically Grounded Predictive Coding Account of
... the predictive coding account of action understanding. Kilner et al. (2004), using event-related brain potentials, found that during action observation, the human brain generated a motor-preparation-like negative potential when the action was in a predictable context; no such potential was found whe ...
... the predictive coding account of action understanding. Kilner et al. (2004), using event-related brain potentials, found that during action observation, the human brain generated a motor-preparation-like negative potential when the action was in a predictable context; no such potential was found whe ...
Structures and Functions Lecture 2
... fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
... fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
Nervous System - Serrano High School AP Biology
... Neural impulses are transmitted both chemically and electrically. This can happen because the cell membrane has the ability to pump out certain molecules that have an electrical charge and allow other charged particles in. There is a great diversity of neuron shapes and functions. There are three ty ...
... Neural impulses are transmitted both chemically and electrically. This can happen because the cell membrane has the ability to pump out certain molecules that have an electrical charge and allow other charged particles in. There is a great diversity of neuron shapes and functions. There are three ty ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System and Brain Complete
... outside through the K+ channels; so you get a positive +++ charge outside again - then shortly after this, the Na+-K+ pump restores the ions to the correct side of the membrane (i.e., with Na+ outside, K+ inside) ...
... outside through the K+ channels; so you get a positive +++ charge outside again - then shortly after this, the Na+-K+ pump restores the ions to the correct side of the membrane (i.e., with Na+ outside, K+ inside) ...
File
... Receive impulses from the entire cerebral cortex, including the motor, sensory, and association cortical areas, as well as input from the limbic system. Most of the output goes to the primary motor cortex. Do not exert direct control over lower motor neurons. Provide the patterned background movemen ...
... Receive impulses from the entire cerebral cortex, including the motor, sensory, and association cortical areas, as well as input from the limbic system. Most of the output goes to the primary motor cortex. Do not exert direct control over lower motor neurons. Provide the patterned background movemen ...
Spinal Cord - Northside Middle School
... and developing well into our 80’s (current research states 80’s but it could be longer). Just because your biological hand may have dealt you a certain brain style doesn’t mean you can’t change, build, and reconstruct your brain. If you communicate indirectly you can practice communicating directly ...
... and developing well into our 80’s (current research states 80’s but it could be longer). Just because your biological hand may have dealt you a certain brain style doesn’t mean you can’t change, build, and reconstruct your brain. If you communicate indirectly you can practice communicating directly ...
What is Your Reaction Time?
... in the brain so far, each with specific, often complex roles in brain function and human behavior. Receptors: Molecules on the surfaces of neurons whose structures precisely match those of chemical messengers (such as neurotransmitters or hormones) released during synaptic transmission. The chemical ...
... in the brain so far, each with specific, often complex roles in brain function and human behavior. Receptors: Molecules on the surfaces of neurons whose structures precisely match those of chemical messengers (such as neurotransmitters or hormones) released during synaptic transmission. The chemical ...
Chapter 6 - TeacherWeb
... something that your body does automatically occurs rapidly without conscious control a good example of a response some are controlled by spinal cord only, not brain ...
... something that your body does automatically occurs rapidly without conscious control a good example of a response some are controlled by spinal cord only, not brain ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.