Your Child`s Brain
... advance scouts breaking trail: within a week of conception they march out of the embryo's "neural tube;' a cylinder of cells extending from head to tail. Multiplying as they go (the brain adds an astonishing 250,000 neurons per minute during gestation), the neurons clump into the brain stem which co ...
... advance scouts breaking trail: within a week of conception they march out of the embryo's "neural tube;' a cylinder of cells extending from head to tail. Multiplying as they go (the brain adds an astonishing 250,000 neurons per minute during gestation), the neurons clump into the brain stem which co ...
Biological_Bases
... A neuron either fires or it does not When it does fire, it will always produce an impulse of the same strength Intensity of a stimulus is seen by the frequency of action potentials ...
... A neuron either fires or it does not When it does fire, it will always produce an impulse of the same strength Intensity of a stimulus is seen by the frequency of action potentials ...
Structure and Function of Neurons - Assets
... Another anatomical zone is that of the axon hillock, also called the axon’s initial segment (Figure 1-8). Its job is to serve as an “electrical integrator” of all the incoming electrical information and decide whether or not to “fire” the neuron. Directly connected to the axon hillock is the axon its ...
... Another anatomical zone is that of the axon hillock, also called the axon’s initial segment (Figure 1-8). Its job is to serve as an “electrical integrator” of all the incoming electrical information and decide whether or not to “fire” the neuron. Directly connected to the axon hillock is the axon its ...
Results Introduction! Conclusions!
... real counterparts in terms of their shape, size, and genetic expression levels. Furthermore, it is interesting to explore differences between IPSC cell lines because expression levels are different between the lines. It is important to note the changes that occur in expression levels between control ...
... real counterparts in terms of their shape, size, and genetic expression levels. Furthermore, it is interesting to explore differences between IPSC cell lines because expression levels are different between the lines. It is important to note the changes that occur in expression levels between control ...
Large-scale projects to build artificial brains: review
... • Understanding emergent properties of neural systems: how high-level cognition arises from low-level interactions between neurons. • Removing all but a few areas of the brain will to lead to functional system, therefore even crude simulation that includes all major areas can teach us something. • B ...
... • Understanding emergent properties of neural systems: how high-level cognition arises from low-level interactions between neurons. • Removing all but a few areas of the brain will to lead to functional system, therefore even crude simulation that includes all major areas can teach us something. • B ...
File
... 4) The motor nerve transmits the signal to the muscles and makes it react. This reaction can be voluntary or involuntary ...
... 4) The motor nerve transmits the signal to the muscles and makes it react. This reaction can be voluntary or involuntary ...
CENTENNIAL HONORS COLLEGE Western Illinois University Undergraduate Research Day 2015
... Characterizing an Abnormal Action Potential Pattern in Ion-Channel-Mutant Drosophila Mariah Maiman Faculty Mentor: Jeffrey Engel Biology Repetitive activities such as flight are organized by neural networks called central pattern generators and the patterns of action potentials they produce is thoug ...
... Characterizing an Abnormal Action Potential Pattern in Ion-Channel-Mutant Drosophila Mariah Maiman Faculty Mentor: Jeffrey Engel Biology Repetitive activities such as flight are organized by neural networks called central pattern generators and the patterns of action potentials they produce is thoug ...
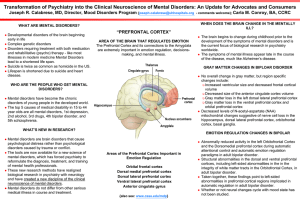
Transformation of Psychiatry into the Clinical Neuroscience of
... psychological distress rather than psychological disorders caused by trauma or conflict. The tools are now available for a new science of mental disorders, which has forced psychiatry to reformulate the diagnosis, treatment, and training of mental health professionals. These new research methods ...
... psychological distress rather than psychological disorders caused by trauma or conflict. The tools are now available for a new science of mental disorders, which has forced psychiatry to reformulate the diagnosis, treatment, and training of mental health professionals. These new research methods ...
Nervous System
... out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another ...
... out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another ...
PDF
... Stay tuned for more information and the launch announcement. Announcing the CereStage 96 channel Headstage This is exciting news for all Plexon OmniPlex® or MAP Data Acquisition System customers using the Utah Array in their research. We have just launched the CereStage 96 channel unity, gain headst ...
... Stay tuned for more information and the launch announcement. Announcing the CereStage 96 channel Headstage This is exciting news for all Plexon OmniPlex® or MAP Data Acquisition System customers using the Utah Array in their research. We have just launched the CereStage 96 channel unity, gain headst ...
The Nervous System - Marblehead High School
... Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
... Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
chapter nervous system i: basig strugture and function
... Continuous stimulation ofa neuron on the distal side ofthisjunction is prevented by ...
... Continuous stimulation ofa neuron on the distal side ofthisjunction is prevented by ...
Introduction to Psychology - John Marshall High School
... Sensory Neurons neurons that carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the central nervous ...
... Sensory Neurons neurons that carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the central nervous ...
Lecture 9
... • Joined by specific protein structures called gap junctions (specialized ionic channels that connect the cytoplasm of both cells) • Action potential comes to gap junction depolarizes or hyperpolarizes the membrane induces opening of the channels diffusion of ions from one neuron to the other ...
... • Joined by specific protein structures called gap junctions (specialized ionic channels that connect the cytoplasm of both cells) • Action potential comes to gap junction depolarizes or hyperpolarizes the membrane induces opening of the channels diffusion of ions from one neuron to the other ...
Diverse Origins of Network Rhythms in Local Cortical Circuits
... synaptic connections alone may be insufficient for explaining cortical dynamics. In entorhinal cortex, a sparse pyramidal neuronal network enables signaling between cells mediated by slow glutamate receptors (GluR5-mediated kainate responses). Postsynaptic events using this communication strategy ha ...
... synaptic connections alone may be insufficient for explaining cortical dynamics. In entorhinal cortex, a sparse pyramidal neuronal network enables signaling between cells mediated by slow glutamate receptors (GluR5-mediated kainate responses). Postsynaptic events using this communication strategy ha ...
WHY STUDY THE BRAIN IN PSYCHOLOGY?
... • Acts as a relay station to send incoming and outgoing messages to and from various parts of brain. – Ex. If you want to move your big toe, the brain sends a message to the thalamus, which then sends it to the correct place on the motor strip. ...
... • Acts as a relay station to send incoming and outgoing messages to and from various parts of brain. – Ex. If you want to move your big toe, the brain sends a message to the thalamus, which then sends it to the correct place on the motor strip. ...
Unit: Regulation Notes
... • Attached at the base of the brain is the spinal cord • The spinal cord carries messages from the nerves in the body to the brain • Damage to the spinal cord can result in paralysis (loss of muscle control) Ex. Paraplegic (cannot walk) ...
... • Attached at the base of the brain is the spinal cord • The spinal cord carries messages from the nerves in the body to the brain • Damage to the spinal cord can result in paralysis (loss of muscle control) Ex. Paraplegic (cannot walk) ...
1. Biophysics of the Nervous System
... In 1930s, there have been various arguments on the synaptic transmission mechanisms between physiologists and ...
... In 1930s, there have been various arguments on the synaptic transmission mechanisms between physiologists and ...
Pontine Respiratory Center
... the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve then inhibits the apneustic centre thus switching off the inspiration . • This is a protective mechanism preventing excess inflation of the lungs. The threshold for this reflex is tidal volume more than 1.5 litres(T.V.≥1.5l) ...
... the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve then inhibits the apneustic centre thus switching off the inspiration . • This is a protective mechanism preventing excess inflation of the lungs. The threshold for this reflex is tidal volume more than 1.5 litres(T.V.≥1.5l) ...
Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System
... Spatial summation takes place when EPSPs from different synapses occur in postsynaptic cell at _____________ time Temporal Summation Temporal summation occurs because EPSPs that occur closely in time can sum before they fade Synaptic Plasticity Repeated use of a synapse can increase or decreas ...
... Spatial summation takes place when EPSPs from different synapses occur in postsynaptic cell at _____________ time Temporal Summation Temporal summation occurs because EPSPs that occur closely in time can sum before they fade Synaptic Plasticity Repeated use of a synapse can increase or decreas ...
Heroin - WordPress.com
... • Many of the drugs of abuse affect either glutamate or GABA or both to exert tranquilizing or stimulating effects on the brain. ...
... • Many of the drugs of abuse affect either glutamate or GABA or both to exert tranquilizing or stimulating effects on the brain. ...
PDF
... excitation [15,16] of neuronal activity associated with contralateral acoustic stimulation. The facilitation of neuronal activity observed in previous studies could be related to the complex nature and relatively long duration of sound stimuli, compared with single shock electrical stimulation of th ...
... excitation [15,16] of neuronal activity associated with contralateral acoustic stimulation. The facilitation of neuronal activity observed in previous studies could be related to the complex nature and relatively long duration of sound stimuli, compared with single shock electrical stimulation of th ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.