Chapter 7: the Nervous System
... • Cells of the central nervous system have a very limited ability to regenerate themselves • The cells themselves are soft and easily damaged (your brain has the consistency of tofu) • The blood-brain barrier refers to the fact that capillaries in the brain are less permeable than those in other par ...
... • Cells of the central nervous system have a very limited ability to regenerate themselves • The cells themselves are soft and easily damaged (your brain has the consistency of tofu) • The blood-brain barrier refers to the fact that capillaries in the brain are less permeable than those in other par ...
Ch 2 neurotrans and nervous sys
... – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizure ...
... – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizure ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Thick axons are myelinated Thin axons are unmyelinated, conduct impulses more slowly Myelin Sheaths in the PNS Myalin sheaths formed by Schwann cells (neurolemmacytes) Develop during fetal period and in the first year of postnatal life Schwann cells wrap in concentric layers around the axon, cover t ...
... Thick axons are myelinated Thin axons are unmyelinated, conduct impulses more slowly Myelin Sheaths in the PNS Myalin sheaths formed by Schwann cells (neurolemmacytes) Develop during fetal period and in the first year of postnatal life Schwann cells wrap in concentric layers around the axon, cover t ...
So it is the number of action potentials per second
... 1. There is a great tendency for K+ to diffuse out of the cell. 2. As this occurs, there is a greater and greater negative charge within the cell due to the loss of K+ and the anions left inside. 3. This buildup of negative charge creates a charge gradient for cations (potassium) to flow back in. 4. ...
... 1. There is a great tendency for K+ to diffuse out of the cell. 2. As this occurs, there is a greater and greater negative charge within the cell due to the loss of K+ and the anions left inside. 3. This buildup of negative charge creates a charge gradient for cations (potassium) to flow back in. 4. ...
Chapter 1: Concepts and Methods in Biology - Rose
... 1. Dendrites of a single neuron receive information from thousands of neurons (fig. 48.13) a. Changes in Vm reflect a weighting of all of the EPSPs and IPSPs that dendrites receive i. EPSPs and IPSPs cause waves of electrical activity starting from site of stimulation ii. EPSPs and IPSPs decay with ...
... 1. Dendrites of a single neuron receive information from thousands of neurons (fig. 48.13) a. Changes in Vm reflect a weighting of all of the EPSPs and IPSPs that dendrites receive i. EPSPs and IPSPs cause waves of electrical activity starting from site of stimulation ii. EPSPs and IPSPs decay with ...
T 2.0
... The connecting point is called a synapse - a space gap - across which electrochemical signals travel. Learning is believed to exist at these connections. ...
... The connecting point is called a synapse - a space gap - across which electrochemical signals travel. Learning is believed to exist at these connections. ...
Two Point Discrimination Lab
... 1. Identify the three different types of neurons and describe their functions. ...
... 1. Identify the three different types of neurons and describe their functions. ...
Biological roots of Behavioral Sciences
... medulla which monitor and control vital body functions , the pons which contains important groups of sensory and motor neurons ,and the cerebellum ,which is concerned with motor co-ordination. The mid brain contains important sensory and motor neurons and tracts connecting higher and lower parts of ...
... medulla which monitor and control vital body functions , the pons which contains important groups of sensory and motor neurons ,and the cerebellum ,which is concerned with motor co-ordination. The mid brain contains important sensory and motor neurons and tracts connecting higher and lower parts of ...
NEUROCHEMISTRY & NEUROTRANSMITTERS
... A REFERENCE WAS MADE TO PROTEINS THAT ARE PROMPTED BY Ca+2 IONS TO CAUSE FUSION OF VESICLES & PRE-SYN. MEMBRANES. THIS IS ACCOMPLISHED WITH A PROTEIN COMPLEX OF SYNTAXINSYNAPTOBREVIN-SNAP25 MOLECULES. THESE MOLECULES HAVE BEEN PROPOSED TO ALSO CONTINUE IN THE FORMATION OF PORES IN THE FUSED MEMBRANE ...
... A REFERENCE WAS MADE TO PROTEINS THAT ARE PROMPTED BY Ca+2 IONS TO CAUSE FUSION OF VESICLES & PRE-SYN. MEMBRANES. THIS IS ACCOMPLISHED WITH A PROTEIN COMPLEX OF SYNTAXINSYNAPTOBREVIN-SNAP25 MOLECULES. THESE MOLECULES HAVE BEEN PROPOSED TO ALSO CONTINUE IN THE FORMATION OF PORES IN THE FUSED MEMBRANE ...
Chapter 13: Peripheral Nervous System
... Parasympathetic Responses Enhance “rest-and-digest” activities Mechanisms that help conserve and restore body energy during times of rest Normally dominate over sympathetic impulses SLUDD type responses = salivation, lacrimation, urination, digestion ...
... Parasympathetic Responses Enhance “rest-and-digest” activities Mechanisms that help conserve and restore body energy during times of rest Normally dominate over sympathetic impulses SLUDD type responses = salivation, lacrimation, urination, digestion ...
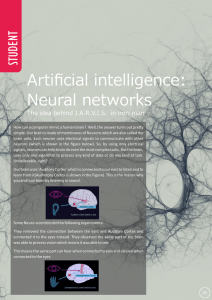
Artificial intelligence: Neural networks
... brain uses to process any kind of data. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. In machine learning and deep learning problems, a neural network is one of the most widely used algorithms which is used to process data that helps a machine learn different things (like a hu ...
... brain uses to process any kind of data. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. In machine learning and deep learning problems, a neural network is one of the most widely used algorithms which is used to process data that helps a machine learn different things (like a hu ...
Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... technique, the researchers discovered distinct pattern of dopamine cell activation that seemed to be able to disrupt alcohol-drinking behavior. Scientists at the California Institute of Technology found a neural circuit that connects the lateral septum (LS) with other brain structures in a manner th ...
... technique, the researchers discovered distinct pattern of dopamine cell activation that seemed to be able to disrupt alcohol-drinking behavior. Scientists at the California Institute of Technology found a neural circuit that connects the lateral septum (LS) with other brain structures in a manner th ...
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue (Chapter 12) Lecture Materials for
... -amount of depolarization or hyperpolarization ! ! depends on intensity of stimulus: ! ...
... -amount of depolarization or hyperpolarization ! ! depends on intensity of stimulus: ! ...
The Nervous System
... take information to the brain, descending tracts in the ventral part carry information down from the brain. THE BRAIN The brain itself contains parts which function in the coordination of movement, sensing, & consciousness (and all that entails), as well as areas that are below the level of consciou ...
... take information to the brain, descending tracts in the ventral part carry information down from the brain. THE BRAIN The brain itself contains parts which function in the coordination of movement, sensing, & consciousness (and all that entails), as well as areas that are below the level of consciou ...
Olfactory tubercle neurons exhibit slowphasic firing patterns during
... both the structures have been implicated in the rewarding properties of drugs, the OT has not been as thoroughly investigated with regard to reward processing. Anatomical and cellular studies have revealed that both the NAcc and OT share continuous stretches of medium spiny neurons. Moreover, projec ...
... both the structures have been implicated in the rewarding properties of drugs, the OT has not been as thoroughly investigated with regard to reward processing. Anatomical and cellular studies have revealed that both the NAcc and OT share continuous stretches of medium spiny neurons. Moreover, projec ...
Lecture 9 Unsupervis..
... All the nodes present in this subnet are fully interconnected and there exist symmetrical weights in all these weighted interconnections. ...
... All the nodes present in this subnet are fully interconnected and there exist symmetrical weights in all these weighted interconnections. ...
Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Resting state: Voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels (not shown). ...
... Resting state: Voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels (not shown). ...
Neuroglia - wsscience
... Acetylcholine binds to receptors and depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane Initiates action potential Acetylcholine is removed through acetyl ...
... Acetylcholine binds to receptors and depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane Initiates action potential Acetylcholine is removed through acetyl ...
Neural Basis of Emotion
... central • Afferents from all lobes of neocortex & hippocampus and cingulate gyrus ...
... central • Afferents from all lobes of neocortex & hippocampus and cingulate gyrus ...
Document
... – Integrate the absolute value of the synaptic activity over 50msec – Convolve with a hemodynamic response function (e.g., Boynton model) – Downsample every TR to get fMRI data MEG – Local MEG signal is proportional to the difference between the excitatory and inhibitory synaptic activity on the exc ...
... – Integrate the absolute value of the synaptic activity over 50msec – Convolve with a hemodynamic response function (e.g., Boynton model) – Downsample every TR to get fMRI data MEG – Local MEG signal is proportional to the difference between the excitatory and inhibitory synaptic activity on the exc ...
Neural Cell Assemblies for Practical
... CA is a short-term or working memory. CAs represent both short and long-term memories. The brain does not have concepts when it is created and thus concepts and therefore CAs must be learned. A CA is learned by adjusting synaptic weights between neurons in the CA. This is done in an unsupervised man ...
... CA is a short-term or working memory. CAs represent both short and long-term memories. The brain does not have concepts when it is created and thus concepts and therefore CAs must be learned. A CA is learned by adjusting synaptic weights between neurons in the CA. This is done in an unsupervised man ...
L20- Brain neurotran..
... • (B) Mesocortical System : • Arises from the Ventral Tegmental Area ( VTA) , and projects to Nucleus Accumbens and Limbic System . • The Mesocortical System is involved in behaviors of Pleasure , Reward , and Addiction • Mesocortical System overstimulation can lead to (1) Schizophrenia-like sympt ...
... • (B) Mesocortical System : • Arises from the Ventral Tegmental Area ( VTA) , and projects to Nucleus Accumbens and Limbic System . • The Mesocortical System is involved in behaviors of Pleasure , Reward , and Addiction • Mesocortical System overstimulation can lead to (1) Schizophrenia-like sympt ...
test - Scioly.org
... 6. A drug that causes potassium to leak out of a neuron, increasing the positive charge on the outside, would ______. a. Make it easier to trigger action potentials in the neuron b. Cause the cell to release its neurotransmitter c. Speed up nerve signals traveling the length of the cell d. Act as a ...
... 6. A drug that causes potassium to leak out of a neuron, increasing the positive charge on the outside, would ______. a. Make it easier to trigger action potentials in the neuron b. Cause the cell to release its neurotransmitter c. Speed up nerve signals traveling the length of the cell d. Act as a ...
BIOPSYCHOLOGY notes
... “endogenous morphine” natural opiates that are released in response to pain and vigorous exercise; an inhibitory NT resulting in pain reduction and pleasurable feelings Plays a role in learning and memory. Messenger between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle. Allows for the contraction of muscles. ...
... “endogenous morphine” natural opiates that are released in response to pain and vigorous exercise; an inhibitory NT resulting in pain reduction and pleasurable feelings Plays a role in learning and memory. Messenger between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle. Allows for the contraction of muscles. ...
nervous system - Doctor Jade Main
... degree of depolarization decreases with distance from opened channel local currents produce changes that cannot spread far from area of stimulation cytosol resists ion movement & some entering Na can move back across ...
... degree of depolarization decreases with distance from opened channel local currents produce changes that cannot spread far from area of stimulation cytosol resists ion movement & some entering Na can move back across ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.