Bad Fish
... • When this threshold is reached, the voltagegated Na+ channels open, allowing more Na+ to diffuse rapidly into the cell. ...
... • When this threshold is reached, the voltagegated Na+ channels open, allowing more Na+ to diffuse rapidly into the cell. ...
B42010712
... projections given new situations of interest and answer "what if" questions. so in this paper we tried to introduce a brief overview of ANN to help researchers in their way throw ANN. ...
... projections given new situations of interest and answer "what if" questions. so in this paper we tried to introduce a brief overview of ANN to help researchers in their way throw ANN. ...
Neural Networks
... It is a fixed weight network that can be used to implement boolean functions. Its characteristics are: Binary activation (1 ON, 0 OFF). i.e. it either fires with an activation 1 or does not fire with an activation of 0. Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. If w > 0, excitatory, else inh ...
... It is a fixed weight network that can be used to implement boolean functions. Its characteristics are: Binary activation (1 ON, 0 OFF). i.e. it either fires with an activation 1 or does not fire with an activation of 0. Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. If w > 0, excitatory, else inh ...
PII: S0006-8993(97) - UCSD Cognitive Science
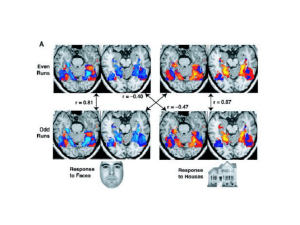
... In adult monkeys with dorsal rhizotomies extending from the second cervical ŽC 2 . to the fifth thoracic ŽT5 . vertebrae, cortex deprived of its normal inputs regained responsiveness to inputs conveyed by intact peripheral afferents from the face wT.P. Pons, P.E. Garraghty, A.K. Ommaya, J.H. Kaas, E ...
... In adult monkeys with dorsal rhizotomies extending from the second cervical ŽC 2 . to the fifth thoracic ŽT5 . vertebrae, cortex deprived of its normal inputs regained responsiveness to inputs conveyed by intact peripheral afferents from the face wT.P. Pons, P.E. Garraghty, A.K. Ommaya, J.H. Kaas, E ...
Emergence of Mirror Neurons in a Model of Gaze Following
... unclear, however, is how mirror neurons arrive at their specific response properties. We find it very unlikely that a sophisticated mirror system could be innate, in the sense of a detailed pre-specified connection pattern for every neuron. Rather, we believe that learning processes must play an imp ...
... unclear, however, is how mirror neurons arrive at their specific response properties. We find it very unlikely that a sophisticated mirror system could be innate, in the sense of a detailed pre-specified connection pattern for every neuron. Rather, we believe that learning processes must play an imp ...
The Nervous System
... • Somatic: motor neurons that carry electrical impulses to voluntary muscles (muscle that can be moved at will) • Autonomic: the division with motor neurons that take impulses to glands and to involuntary muscles in the heart, organs, and blood vessels ...
... • Somatic: motor neurons that carry electrical impulses to voluntary muscles (muscle that can be moved at will) • Autonomic: the division with motor neurons that take impulses to glands and to involuntary muscles in the heart, organs, and blood vessels ...
from discrete neuronal ensembles to serial order
... language is primarily based on lesion studies. Lesions in certain areas of the left hemisphere cause language deficits, or aphasias, in most individuals. However, this does not allow one to conclude that only the left hemisphere contributes to language. It was already pointed out by the English neur ...
... language is primarily based on lesion studies. Lesions in certain areas of the left hemisphere cause language deficits, or aphasias, in most individuals. However, this does not allow one to conclude that only the left hemisphere contributes to language. It was already pointed out by the English neur ...
A visual motion detection circuit suggested by Drosophila
... term ultraperiodic. We do not include infraperiodic tangential or local amacrine-like cells even if they have arborizations in every column because this cannot be determined unambiguously from our electron microscopy reconstruction (Supplementary Table 2). We used the existence of multiple represent ...
... term ultraperiodic. We do not include infraperiodic tangential or local amacrine-like cells even if they have arborizations in every column because this cannot be determined unambiguously from our electron microscopy reconstruction (Supplementary Table 2). We used the existence of multiple represent ...
More Mind Bogglers!
... Neurons communicate with one another and with other cells such as muscles through a special junction known as a synapse. At the synapse, the axon of one neuron usually is separated from the next cell by a narrow gap (20 to 40 nanometers wide) known as the synaptic cleft. Messages traveling from neur ...
... Neurons communicate with one another and with other cells such as muscles through a special junction known as a synapse. At the synapse, the axon of one neuron usually is separated from the next cell by a narrow gap (20 to 40 nanometers wide) known as the synaptic cleft. Messages traveling from neur ...
somatic sensory system
... lie lateral to the fibers of the medial lemniscus make synapses in the reticular formation have arisen from cells in the dorsal column nuclei have arisen from cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord decussate (cross the midline) ...
... lie lateral to the fibers of the medial lemniscus make synapses in the reticular formation have arisen from cells in the dorsal column nuclei have arisen from cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord decussate (cross the midline) ...
Somatic Sensation - PROFESSOR AC BROWN
... 2. These action potentials are conducted into the Central Nervous System (spinal cord and brain), where they excite adjacent nerve cells (2nd order, 3rd order, etc. neurons) 3. By this mechanism, excitation eventually reaches specialized regions of the cerebral cortex where conscious sensation occur ...
... 2. These action potentials are conducted into the Central Nervous System (spinal cord and brain), where they excite adjacent nerve cells (2nd order, 3rd order, etc. neurons) 3. By this mechanism, excitation eventually reaches specialized regions of the cerebral cortex where conscious sensation occur ...
Control of Movement
... thalamus-motor cortex) Loss of output from the indirect circuit (which is overall an excitatory circuit for motor behavior) ...
... thalamus-motor cortex) Loss of output from the indirect circuit (which is overall an excitatory circuit for motor behavior) ...
Neural computations associated with goal
... assigned to the charities. Moreover, functional connectivity analyses suggest that the OFC value signal integrated inputs from anterior insula and pSTC, areas that are thought to be critical for social cognit ...
... assigned to the charities. Moreover, functional connectivity analyses suggest that the OFC value signal integrated inputs from anterior insula and pSTC, areas that are thought to be critical for social cognit ...
Nicotinic Receptors in Addiction Pathways
... by a rich dendritic arbor from striatal cholinergic interneurons (Zhou et al., 2002). Although cholinergic and dopamine neurons were once thought to have opposing actions, a complex interrelationship has now been revealed (Surmeier and Graybiel, 2012). In both dorsal and ventral striatum, presynapti ...
... by a rich dendritic arbor from striatal cholinergic interneurons (Zhou et al., 2002). Although cholinergic and dopamine neurons were once thought to have opposing actions, a complex interrelationship has now been revealed (Surmeier and Graybiel, 2012). In both dorsal and ventral striatum, presynapti ...
ppt - BIAC – Duke
... In this period of intense research in the neurosciences, nothing is more promising than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) methods, which localize brain activities. These functional imaging methodologies map neurophysiological responses to cognitive, ...
... In this period of intense research in the neurosciences, nothing is more promising than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) methods, which localize brain activities. These functional imaging methodologies map neurophysiological responses to cognitive, ...
Serotonin release from the neuronal cell body and its long
... which vesicles fuse with the membrane; and the plateau of the fluorescence increase is reached when the last vesicles in the cluster fuse and exocytosis finishes. Since exo/endocytosis from each vesicle contributes to the FM1-fluorescence with a small stepwise increase, with appropriate optics, the ...
... which vesicles fuse with the membrane; and the plateau of the fluorescence increase is reached when the last vesicles in the cluster fuse and exocytosis finishes. Since exo/endocytosis from each vesicle contributes to the FM1-fluorescence with a small stepwise increase, with appropriate optics, the ...
Developmental biology 2008 Fates of the ectoderm: The neural tube
... Neurotrophins promote survival of specific neuronal and glial populations by locally counteracting the apoptotic cell death that would occur in their absence. Survival depends on competition for a limited supply of neurotrophins. ...
... Neurotrophins promote survival of specific neuronal and glial populations by locally counteracting the apoptotic cell death that would occur in their absence. Survival depends on competition for a limited supply of neurotrophins. ...
Zoran Đogaš
... and larger neurons will fire later (larger twitch tension). • V = IR: Small neurons have a higher resistance, which means they will show a stronger depolarization (V) for the same current (I). • That's why they fire first. This is the opposite of external stimulation, ...
... and larger neurons will fire later (larger twitch tension). • V = IR: Small neurons have a higher resistance, which means they will show a stronger depolarization (V) for the same current (I). • That's why they fire first. This is the opposite of external stimulation, ...
Lecture 14
... you want (the Target), since all the weights are random. We then calculate the Error of each neuron, which is essentially: Target Actual Output (i.e., What you want - What you actually get). This error is then used mathematically to change the weights in such a way that the error will get smaller. I ...
... you want (the Target), since all the weights are random. We then calculate the Error of each neuron, which is essentially: Target Actual Output (i.e., What you want - What you actually get). This error is then used mathematically to change the weights in such a way that the error will get smaller. I ...
Amygdala oscillations and the consolidation of
... emotionally charged learning tasks [c]. However, the memory modulating effects of these manipulations do not result from alterations of memory storage in the but in other structures that represent the storage site of particular forms of memories [e]. The modulation of memory by the BL amygdala can a ...
... emotionally charged learning tasks [c]. However, the memory modulating effects of these manipulations do not result from alterations of memory storage in the but in other structures that represent the storage site of particular forms of memories [e]. The modulation of memory by the BL amygdala can a ...
The neuronal structure of the medial geniculate body in the pig
... pear-shaped neurons, the smallest cells of the pig MGB that have similar arborisation of the dendrites to the multipolar and triangular neurons were not reported in MGB of other mammals. Small neurons were described as Golgi type II neurons in the cat [9, 11, 31], rat [27], and in the opossum [34]. ...
... pear-shaped neurons, the smallest cells of the pig MGB that have similar arborisation of the dendrites to the multipolar and triangular neurons were not reported in MGB of other mammals. Small neurons were described as Golgi type II neurons in the cat [9, 11, 31], rat [27], and in the opossum [34]. ...
3. NEURAL NETWORK MODELS 3.1 Early Approaches
... cases of (3.1); therefore, any other logical function can be constructed from these. The model of McCulloch and Pitts for the first time suggested how neurons might be able to carry out logical operations. Their idea of the neuron as a logical threshold element was a fundamental contribution to the ...
... cases of (3.1); therefore, any other logical function can be constructed from these. The model of McCulloch and Pitts for the first time suggested how neurons might be able to carry out logical operations. Their idea of the neuron as a logical threshold element was a fundamental contribution to the ...
Reflex action and Reflex arc
... It is a common observation that when a dog sees food it salivates. He rang a bell when the dog was given food. After doing this for few days he noticed that the dog started salivating when it heard the bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed t ...
... It is a common observation that when a dog sees food it salivates. He rang a bell when the dog was given food. After doing this for few days he noticed that the dog started salivating when it heard the bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed t ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Lesson I-11: Structure of the Vertebrate Nervous System (Part 1) Objectives: ...
... Lesson I-11: Structure of the Vertebrate Nervous System (Part 1) Objectives: ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.