Neural coding of behavioral relevance in parietal cortex
... Task-switching signals may be localized to the lateral portion of the IPS [39]. Attentional processes in the IPS appear to extend to other stimulus modalities beyond vision. For example, a positron-emission tomography (PET) study found signals in the IPS when subjects attended to either contralatera ...
... Task-switching signals may be localized to the lateral portion of the IPS [39]. Attentional processes in the IPS appear to extend to other stimulus modalities beyond vision. For example, a positron-emission tomography (PET) study found signals in the IPS when subjects attended to either contralatera ...
Acetylcholine - American College of Neuropsychopharmacology
... transmission (45,46). While a significant proportion of the PPT neurons that project to the tegmental dopamine neurons are noncholinergic (44), the cholinergic input per se appears to stimulate dopamine neurons (47). Thus, ascending projections from the PPT to the dopamine cells may regulate the abi ...
... transmission (45,46). While a significant proportion of the PPT neurons that project to the tegmental dopamine neurons are noncholinergic (44), the cholinergic input per se appears to stimulate dopamine neurons (47). Thus, ascending projections from the PPT to the dopamine cells may regulate the abi ...
Review Questions
... 1. Define the following terms: A. Amygdaloid nucleus B. Anterior medullary velum C. Cerebral aqueduct D. Corona radiata E. Inferior cerebellar peduncle (restiform body) ...
... 1. Define the following terms: A. Amygdaloid nucleus B. Anterior medullary velum C. Cerebral aqueduct D. Corona radiata E. Inferior cerebellar peduncle (restiform body) ...
Different levels of Ih determine distinct temporal integration in
... The subiculum functions as the main output structure of the hippocampus proper and gets its main inputs from the CA1 area and the entorhinal cortex as well as from other subcortical and cortical areas. Functionally, the subiculum plays a role in certain forms of spatial memory and in mnemonic proces ...
... The subiculum functions as the main output structure of the hippocampus proper and gets its main inputs from the CA1 area and the entorhinal cortex as well as from other subcortical and cortical areas. Functionally, the subiculum plays a role in certain forms of spatial memory and in mnemonic proces ...
Parallel Evolution of Cortical Areas Involved in Skilled Hand Use
... sulcus of the cebus was mapped in detail using electrophysiological methods. Our primary goal was to examine the organization of the cortex in the expected location of cortical fields 2 and 5. The organization of areas 3b and 1 have been documented previously in cebus monkeys (Felleman et al., 1983) ...
... sulcus of the cebus was mapped in detail using electrophysiological methods. Our primary goal was to examine the organization of the cortex in the expected location of cortical fields 2 and 5. The organization of areas 3b and 1 have been documented previously in cebus monkeys (Felleman et al., 1983) ...
Izabella Battonyai
... processes in the CNS. The center of odor processing is the procerebrum (olfactory lobe, PC), which is located in the cerebral ganglion and is a characteristic unit in Stylommatophora (Pulmonata) snails (Van Mol 1974). There are also a number of morphological and physiological data proving that the P ...
... processes in the CNS. The center of odor processing is the procerebrum (olfactory lobe, PC), which is located in the cerebral ganglion and is a characteristic unit in Stylommatophora (Pulmonata) snails (Van Mol 1974). There are also a number of morphological and physiological data proving that the P ...
vocabulary - anatomy and physiology one
... Explain how afterpotential occurs and its importance. Describe the relative and absolute refractory period and discuss their importance. Discuss how the absolute and relative refractory periods relate to depolarization and repolarization of the cell membrane. Define the term action potential frequen ...
... Explain how afterpotential occurs and its importance. Describe the relative and absolute refractory period and discuss their importance. Discuss how the absolute and relative refractory periods relate to depolarization and repolarization of the cell membrane. Define the term action potential frequen ...
Visual Field and the Human Visual System
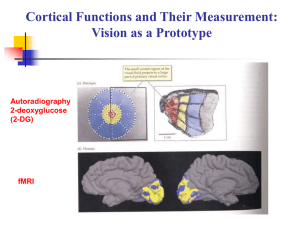
... Brain shows much greater activation as subjects look at visual words (2nd row) than when they view a static fixation point (top row). ...
... Brain shows much greater activation as subjects look at visual words (2nd row) than when they view a static fixation point (top row). ...
Development of the Nervous System
... basal plates is that they are lateral to them rather than dorsal to them. Cranial nerves are associated with various cranial nerve nuclei, which lie in the floor of the fourth ventricle in the brainstem. Some of them are motor, some have a sensory function. The sensory nuclei are more lateral, and t ...
... basal plates is that they are lateral to them rather than dorsal to them. Cranial nerves are associated with various cranial nerve nuclei, which lie in the floor of the fourth ventricle in the brainstem. Some of them are motor, some have a sensory function. The sensory nuclei are more lateral, and t ...
No Slide Title
... Figure 19-19 Hemiballismus. A, A 65-year-old HIV-positive man developed, over the course of several months, "unintentional, forceful flinging movements of his right arm and leg ...
... Figure 19-19 Hemiballismus. A, A 65-year-old HIV-positive man developed, over the course of several months, "unintentional, forceful flinging movements of his right arm and leg ...
Multilayer perceptrons
... All neurons in one layer are connected to all neurons in the next layer The network is a feedforward network, so all data flows from the input to the output The architecture of the network shown is described as 3:4:2 All neurons in the hidden and output layers have a bias connection ...
... All neurons in one layer are connected to all neurons in the next layer The network is a feedforward network, so all data flows from the input to the output The architecture of the network shown is described as 3:4:2 All neurons in the hidden and output layers have a bias connection ...
Full text
... common localization of GnRH and NPY containg neurons especially in IN and ME was shown [2, 14]. This neuroanatomical colocalization implicates some physiological interactions which are associated with hormone release. Recently, Advis et al. [1] showed, using the push-pull technique, that NPY release ...
... common localization of GnRH and NPY containg neurons especially in IN and ME was shown [2, 14]. This neuroanatomical colocalization implicates some physiological interactions which are associated with hormone release. Recently, Advis et al. [1] showed, using the push-pull technique, that NPY release ...
Document
... I am interested in the molecular mechanisms of axon guidance and synaptic target recognition – the proper wiring of all nervous systems depends on these mechanisms. A mammal’s brain is very complex, so we studied this problem using identified neurons in the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. The cerc ...
... I am interested in the molecular mechanisms of axon guidance and synaptic target recognition – the proper wiring of all nervous systems depends on these mechanisms. A mammal’s brain is very complex, so we studied this problem using identified neurons in the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. The cerc ...
敌獳湯⌠ⴷ8
... mainly of cellular processes, of which the majority are granule cell axons—parallel fibers, see below— and Purkinje cell dendrites. A few neurons are found among the fibers (stellate cells, basket cells, Golgi cells), which function as inhibitory interneurons. Pukinje cell layer (stratum ganglionare ...
... mainly of cellular processes, of which the majority are granule cell axons—parallel fibers, see below— and Purkinje cell dendrites. A few neurons are found among the fibers (stellate cells, basket cells, Golgi cells), which function as inhibitory interneurons. Pukinje cell layer (stratum ganglionare ...
invariant face and object recognition in the visual system
... generalization to similar stimuli (in the Hamming distance sense, see Rolls and Treves, 1997), graceful degradation (fault tolerance), and some locality to the representation, so that some single neurons which receive inputs from such a representation can obtain sufficient information without requir ...
... generalization to similar stimuli (in the Hamming distance sense, see Rolls and Treves, 1997), graceful degradation (fault tolerance), and some locality to the representation, so that some single neurons which receive inputs from such a representation can obtain sufficient information without requir ...
Striate cortex increases contrast gain of macaque LGN neurons
... Recurrent projections comprise a universal feature of cerebral organization. Here, we show that the corticofugal projections from the striate cortex (V1) to the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) robustly and multiplicatively enhance the responses of parvocellular neurons, stimulated by gratings restr ...
... Recurrent projections comprise a universal feature of cerebral organization. Here, we show that the corticofugal projections from the striate cortex (V1) to the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) robustly and multiplicatively enhance the responses of parvocellular neurons, stimulated by gratings restr ...
2605_lect9
... between cells – Prevalent in brain development – May play a role in aggregation and other processes ...
... between cells – Prevalent in brain development – May play a role in aggregation and other processes ...
Intention, Action Planning, and Decision Making in Parietal
... the dorsal premotor cortex (PMd), and other areas within the PPC, such as area 5. In the final section, we will show examples of ‘‘proof of concept’’ in which the action-related activity in the PPC and PMd cortex can be decoded and used to provide control signals for neural prosthetic applications. ...
... the dorsal premotor cortex (PMd), and other areas within the PPC, such as area 5. In the final section, we will show examples of ‘‘proof of concept’’ in which the action-related activity in the PPC and PMd cortex can be decoded and used to provide control signals for neural prosthetic applications. ...
Two Kinds of Reverse Inference in Cognitive Neuroscience
... However, this article shows that it is crucial two distinguish between two different types of reverse inference. In the first kind, cognitive processes are inferred from the particular locations of neural activation observed in particular tasks. We examine these location-based inferences through a c ...
... However, this article shows that it is crucial two distinguish between two different types of reverse inference. In the first kind, cognitive processes are inferred from the particular locations of neural activation observed in particular tasks. We examine these location-based inferences through a c ...
Neuroscience Information Framework Standard Ontologies
... • Multiple participants can edit the ontology contents instantly • Control of content is done after edits are made based on the merit of the content • Semantics are limited to what is convenient for the domain • Not a replacement for top-down construction; sometimes necessary to increase flexibility ...
... • Multiple participants can edit the ontology contents instantly • Control of content is done after edits are made based on the merit of the content • Semantics are limited to what is convenient for the domain • Not a replacement for top-down construction; sometimes necessary to increase flexibility ...
Molecular basis of learning in the hippocampus and the amygdala
... conditioning learning is impaired in both situations of blocking the amygdala: before and after an experiment (Campeau et al., 1995). So we can assume that this structure is involved not only in detection of stimuli coexistence but also in storage of some of engrams. Synaptic plasticity is an adapti ...
... conditioning learning is impaired in both situations of blocking the amygdala: before and after an experiment (Campeau et al., 1995). So we can assume that this structure is involved not only in detection of stimuli coexistence but also in storage of some of engrams. Synaptic plasticity is an adapti ...
Physiology of the Striate Cortex
... • Retinal ganglion cells: Center-surround structure, Sensitive to contrast, and wavelength of light • Striate cortex: Orientation selectivity, direction selectivity, and binocularity • Extrastriate cortical areas: Selective responsive to complex shapes; e.g., ...
... • Retinal ganglion cells: Center-surround structure, Sensitive to contrast, and wavelength of light • Striate cortex: Orientation selectivity, direction selectivity, and binocularity • Extrastriate cortical areas: Selective responsive to complex shapes; e.g., ...
Gluck_OutlinePPT_Ch08 short
... Instrumental conditioning = learning a threeway association (S → R → C) between: Discriminative stimulus (S) Response (R) ...
... Instrumental conditioning = learning a threeway association (S → R → C) between: Discriminative stimulus (S) Response (R) ...
Visual Properties of Neurons in a Polysensory Area in Superior
... responsive, and over half responded to more than one sensory modality; 21% responded to visual and auditory stimuli, 17% responded to visual and somesthetic stimuli, 17% were trimodal, and 41% were exclusively visual. 3. Almost all the visual receptive fields extended into both visual half-fields, a ...
... responsive, and over half responded to more than one sensory modality; 21% responded to visual and auditory stimuli, 17% responded to visual and somesthetic stimuli, 17% were trimodal, and 41% were exclusively visual. 3. Almost all the visual receptive fields extended into both visual half-fields, a ...
Bad Fish
... • When this threshold is reached, the voltagegated Na+ channels open, allowing more Na+ to diffuse rapidly into the cell. ...
... • When this threshold is reached, the voltagegated Na+ channels open, allowing more Na+ to diffuse rapidly into the cell. ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.