An In Depth Look at Human Behaviour
... • Unconditioned Response (UR) – automatic response to a US • Neutral Stimulus (NS) – agent that initially has no effect • Conditioned Stimulus (CS) – a former NS that comes to elicit a given response after pairing it with an US • Conditioned Response (CR) – a learned response to CS * The NS always b ...
... • Unconditioned Response (UR) – automatic response to a US • Neutral Stimulus (NS) – agent that initially has no effect • Conditioned Stimulus (CS) – a former NS that comes to elicit a given response after pairing it with an US • Conditioned Response (CR) – a learned response to CS * The NS always b ...
• behavior modification • biofeedback • neurofeedback • latent
... 1. Describe Pavlov’s pioneering research on classical conditioning (CC). 2. How do you create a conditioned response (CR)? 3. Think about stimulus generalization and discrimination. Predict what would be the adaptive significance of both of these responses. 4. Explain the key factor in producing ext ...
... 1. Describe Pavlov’s pioneering research on classical conditioning (CC). 2. How do you create a conditioned response (CR)? 3. Think about stimulus generalization and discrimination. Predict what would be the adaptive significance of both of these responses. 4. Explain the key factor in producing ext ...
Learning - Kalyankaari
... dogs to salivate in response to the ringing of a bell. When he presented the dong with a piece of meat, the dog exhibited a noticeable increase in salivation. When he postponed the presentation of meat and only rang the bell, the dog did not salivate. Then Pavlov proceeded to link the meat and the r ...
... dogs to salivate in response to the ringing of a bell. When he presented the dong with a piece of meat, the dog exhibited a noticeable increase in salivation. When he postponed the presentation of meat and only rang the bell, the dog did not salivate. Then Pavlov proceeded to link the meat and the r ...
Behaviorism - pgt201e2009
... such people as Thorndike, Tolman, Guthrie, and Hull. What characterizes these investigators is their underlying assumptions about the process of learning. In essence, three basic assumptions are held to be true. First, learning is manifested by a change in behavior. Second, the environment shapes be ...
... such people as Thorndike, Tolman, Guthrie, and Hull. What characterizes these investigators is their underlying assumptions about the process of learning. In essence, three basic assumptions are held to be true. First, learning is manifested by a change in behavior. Second, the environment shapes be ...
2) Operant conditioning where there is reinforcement
... such people as Thorndike, Tolman, Guthrie, and Hull. What characterizes these investigators is their underlying assumptions about the process of learning. In essence, three basic assumptions are held to be true. First, learning is manifested by a change in behavior. Second, the environment shapes be ...
... such people as Thorndike, Tolman, Guthrie, and Hull. What characterizes these investigators is their underlying assumptions about the process of learning. In essence, three basic assumptions are held to be true. First, learning is manifested by a change in behavior. Second, the environment shapes be ...
student copy - learning - APPsychBCA
... sick, but not when it’s announced by a noise; so Pavlov was wrong in claiming that any stimulus could serve as a conditioned stimulus. -We are biologically prepared to learn certain associations and not others: we learn to fear snakes, but not flowers -Taste aversions result from biology. The smell ...
... sick, but not when it’s announced by a noise; so Pavlov was wrong in claiming that any stimulus could serve as a conditioned stimulus. -We are biologically prepared to learn certain associations and not others: we learn to fear snakes, but not flowers -Taste aversions result from biology. The smell ...
Convert - public.coe.edu
... Counterconditioning Pairing favorite food & rabbit Exposure therapy Gradually moved rabbit closer Peter watched another child play with rabbit ~ ...
... Counterconditioning Pairing favorite food & rabbit Exposure therapy Gradually moved rabbit closer Peter watched another child play with rabbit ~ ...
Applications of Operant Conditioning
... and the US (food) are paired, resulting in salivation (UR). After conditioning, the neutral stimulus (now Conditioned Stimulus, CS) elicits salivation (now Conditioned Response, CR) ...
... and the US (food) are paired, resulting in salivation (UR). After conditioning, the neutral stimulus (now Conditioned Stimulus, CS) elicits salivation (now Conditioned Response, CR) ...
Behavioral Perspective
... and the US (food) are paired, resulting in salivation (UR). After conditioning, the neutral stimulus (now Conditioned Stimulus, CS) elicits salivation (now Conditioned Response, CR) ...
... and the US (food) are paired, resulting in salivation (UR). After conditioning, the neutral stimulus (now Conditioned Stimulus, CS) elicits salivation (now Conditioned Response, CR) ...
Convert - public.coe.edu
... Counterconditioning Pairing favorite food & rabbit Exposure therapy Gradually moved rabbit closer Peter watched another child play with rabbit ~ ...
... Counterconditioning Pairing favorite food & rabbit Exposure therapy Gradually moved rabbit closer Peter watched another child play with rabbit ~ ...
Unit 6- Learning
... secretion in dogs, he knew that when he put food in a dog’s mouth the animal ...
... secretion in dogs, he knew that when he put food in a dog’s mouth the animal ...
learning.assign202-12 - King`s Psychology Network
... For the next class, please come prepared to present your assigned area. Read the textbook carefully and find any supplemental material that will help you explain your assigned concept to the class. Visit the course website and the related learning links on the subject that you find on the website. U ...
... For the next class, please come prepared to present your assigned area. Read the textbook carefully and find any supplemental material that will help you explain your assigned concept to the class. Visit the course website and the related learning links on the subject that you find on the website. U ...
Behaviorist Theory
... Watson's work was based on the experiments of Ivan Pavlov's model of classical conditioning based off one's personality and characteristics. (Schunk, 2012, p. 72) B.F. Skinner tested Watson's theories which he was able to associate with behaviorism. Skinner ...
... Watson's work was based on the experiments of Ivan Pavlov's model of classical conditioning based off one's personality and characteristics. (Schunk, 2012, p. 72) B.F. Skinner tested Watson's theories which he was able to associate with behaviorism. Skinner ...
learningmemory
... event that, through learning, elicits a given response after a period of training in which it has been paired with an unconditioned stimulus. The salivation that is caused by the tuning fork is called a conditioned response. Conditioned Response (CR): The learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus. ...
... event that, through learning, elicits a given response after a period of training in which it has been paired with an unconditioned stimulus. The salivation that is caused by the tuning fork is called a conditioned response. Conditioned Response (CR): The learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus. ...
Chapter 7 (Professor Powerpoint)
... – A response that is elicited by the conditioned stimulus. – Occurs after the CS is associated with the US. – Is usually similar to US Wade/Tavris, (c) 2006, Prentice Hall ...
... – A response that is elicited by the conditioned stimulus. – Occurs after the CS is associated with the US. – Is usually similar to US Wade/Tavris, (c) 2006, Prentice Hall ...
Behaviorism
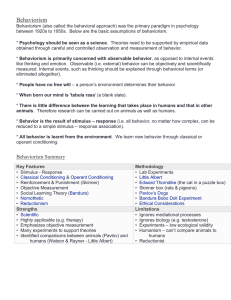
... eliminated altogether). * People have no free will – a person’s environment determines their behavior * When born our mind is 'tabula rasa' (a blank slate). * There is little difference between the learning that takes place in humans and that in other animals. Therefore research can be carried out o ...
... eliminated altogether). * People have no free will – a person’s environment determines their behavior * When born our mind is 'tabula rasa' (a blank slate). * There is little difference between the learning that takes place in humans and that in other animals. Therefore research can be carried out o ...
Learning and Motivation
... Unconditioned Stimulus (In this instance food) Neutral Stimulus: (Bell) Unconditioned/Natural response The automatic or unlearned ...
... Unconditioned Stimulus (In this instance food) Neutral Stimulus: (Bell) Unconditioned/Natural response The automatic or unlearned ...
Unit 6 FRQ
... 1. The police chief of New City publicly states that she sees a direct relationship between teenage arrests in New City for violent crimes and the popularity among New City teens of especially violent television shows and video games. Definitions without application do not score. a) Design a basic c ...
... 1. The police chief of New City publicly states that she sees a direct relationship between teenage arrests in New City for violent crimes and the popularity among New City teens of especially violent television shows and video games. Definitions without application do not score. a) Design a basic c ...
Learning Process PPT
... Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) stimulus that unconditionally--automatically and naturally--triggers a response ...
... Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) stimulus that unconditionally--automatically and naturally--triggers a response ...
Learning - Weber State University
... organism’s behavior resulting from an interaction with the environment. Who was Wundt? How long would it take you to “learn” the material for the first exam? ...
... organism’s behavior resulting from an interaction with the environment. Who was Wundt? How long would it take you to “learn” the material for the first exam? ...
What is learning? - Business Information Management
... originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response ...
... originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response ...
Programmed Learning Review Answers
... 43. __VARIABLE RATIO__ is the schedule of conditioning most resistant to extinction. If the animal is reinforced for the its correct response after a certain period of times has elapsed he is on a __FIXED INTERVAL__ schedule. If the time period randomly varies from reinforcement to reinforcement, it ...
... 43. __VARIABLE RATIO__ is the schedule of conditioning most resistant to extinction. If the animal is reinforced for the its correct response after a certain period of times has elapsed he is on a __FIXED INTERVAL__ schedule. If the time period randomly varies from reinforcement to reinforcement, it ...
Learning - ThaparNotes
... – Learn to associate a neutral event with another event or stimulus from the environment. ...
... – Learn to associate a neutral event with another event or stimulus from the environment. ...
Classical conditioning

Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.