Innate/Learned Behavior Powerpoint
... Innate vs. Learned Behaviors http://www.sparknotes. com/biology/animalbeh avior/learning/problem s_1.html ...
... Innate vs. Learned Behaviors http://www.sparknotes. com/biology/animalbeh avior/learning/problem s_1.html ...
Chapter 6 - Learning
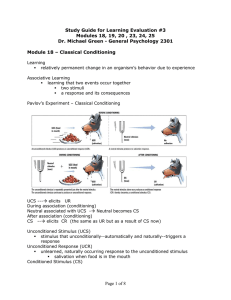
... • UR – Unconditioned Response- salivation in response to meat is not learned it is natural. • CR – Conditioned Response- learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral. ...
... • UR – Unconditioned Response- salivation in response to meat is not learned it is natural. • CR – Conditioned Response- learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral. ...
Classical and Operant Conditioning
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
B. F. Skinner - Kelley Kline
... conditioning: classical (Pavlovian) & operant (instrumental) conditioning ...
... conditioning: classical (Pavlovian) & operant (instrumental) conditioning ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... • A) aggressive children will imitate aggressive behavior. • B) children will imitate aggressive behavior just by observing it. • C) children who are non-aggressive will not imitate aggressive behavior. • D) children will imitate aggressive behavior is reinforced with candy. ...
... • A) aggressive children will imitate aggressive behavior. • B) children will imitate aggressive behavior just by observing it. • C) children who are non-aggressive will not imitate aggressive behavior. • D) children will imitate aggressive behavior is reinforced with candy. ...
Motivation - Flow in Sports
... • Escape conditioning occurs when the aversive stimulus has already begun, and the behavior terminates it. Examples include scratching an itch or hitting the snooze button on an alarm clock. • Avoidance conditioning occurs when the behavior allows an aversive stimulus to be avoided before it starts. ...
... • Escape conditioning occurs when the aversive stimulus has already begun, and the behavior terminates it. Examples include scratching an itch or hitting the snooze button on an alarm clock. • Avoidance conditioning occurs when the behavior allows an aversive stimulus to be avoided before it starts. ...
Sports Psychology
... • Escape conditioning occurs when the aversive stimulus has already begun, and the behavior terminates it. Examples include scratching an itch or hitting the snooze button on an alarm clock. • Avoidance conditioning occurs when the behavior allows an aversive stimulus to be avoided before it starts. ...
... • Escape conditioning occurs when the aversive stimulus has already begun, and the behavior terminates it. Examples include scratching an itch or hitting the snooze button on an alarm clock. • Avoidance conditioning occurs when the behavior allows an aversive stimulus to be avoided before it starts. ...
Inglês
... Abstract: The explanatory system developed by Skinner culminated in the formulation of an explanatory mechanism that should address the behavior as an analogy between natural selection of Darwin and operant conditioning. Skinner believed that this analogy would be enough to sort the behavioral disci ...
... Abstract: The explanatory system developed by Skinner culminated in the formulation of an explanatory mechanism that should address the behavior as an analogy between natural selection of Darwin and operant conditioning. Skinner believed that this analogy would be enough to sort the behavioral disci ...
Study Guide for Learning Evaluation #4
... type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment operates (acts) on environment produces consequences Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors ...
... type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment operates (acts) on environment produces consequences Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors ...
6. Learning2
... modification (also known as operant conditioning theory) -Takes the rather extreme view that learning is completely dependent on the environment • Behavior modification does not question the notion that thinking is part of learning process-but views human thoughts as unimportant intermediate stages ...
... modification (also known as operant conditioning theory) -Takes the rather extreme view that learning is completely dependent on the environment • Behavior modification does not question the notion that thinking is part of learning process-but views human thoughts as unimportant intermediate stages ...
Conditioning - WordPress.com
... Classical Conditioning Classical conditioning occurs gradually. The more frequently the tuning fork was paired with food the stronger the salivation response was. ...
... Classical Conditioning Classical conditioning occurs gradually. The more frequently the tuning fork was paired with food the stronger the salivation response was. ...
1 4.0 learning - eduNEPAL.info
... Whenever, the bell was the artificial stimulus or conditioned stimulus the reaction took place. While it was originally neutral, when the bell was paired with the meat (an unconditioned stimulus), if eventually produced a response when presented alone. It is the conditioned response. This describes ...
... Whenever, the bell was the artificial stimulus or conditioned stimulus the reaction took place. While it was originally neutral, when the bell was paired with the meat (an unconditioned stimulus), if eventually produced a response when presented alone. It is the conditioned response. This describes ...
Running head: BEHAVIOR MODIFICATION THROUGH OPERANT
... the cat took less and less time to escape after each trial. This shows that the cat was able to learn a task faster when reinforced as opposed to no reinforcement because it had something to work for. Therefore, learning and accomplishing the new task will result in a desirable reward. (Kazdin, 1989 ...
... the cat took less and less time to escape after each trial. This shows that the cat was able to learn a task faster when reinforced as opposed to no reinforcement because it had something to work for. Therefore, learning and accomplishing the new task will result in a desirable reward. (Kazdin, 1989 ...
Psychology Unit 1 - spetersopsych
... You groups will need to develop a skit to demonstrate the approach. **You can read more about each approach in the textbook (Chapter 1 section 2) **Everyone in the group must be involved in the skit! ...
... You groups will need to develop a skit to demonstrate the approach. **You can read more about each approach in the textbook (Chapter 1 section 2) **Everyone in the group must be involved in the skit! ...
Shaping (psychology)
... A lot of research is done with mice involving autoshaping as well. Since mice and humans share approximately 90% of the same genes, a lot of research is done to try to discover which genes do what in humans by using mice first. If successful, the field of medicine can be further progressed. Autoshap ...
... A lot of research is done with mice involving autoshaping as well. Since mice and humans share approximately 90% of the same genes, a lot of research is done to try to discover which genes do what in humans by using mice first. If successful, the field of medicine can be further progressed. Autoshap ...
Corrigendum: Auditory and cognitive factors underlying
... Auditory and cognitive factors underlying individual differences in aided speechunderstanding among older adults by Humes, L. E., Kidd, G. R., and Lentz, J. J. (2013). Front. Syst. Neurosci. 7:55. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2013.00055 Reason for Corrigendum: There is an error in the reporting of the Text Re ...
... Auditory and cognitive factors underlying individual differences in aided speechunderstanding among older adults by Humes, L. E., Kidd, G. R., and Lentz, J. J. (2013). Front. Syst. Neurosci. 7:55. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2013.00055 Reason for Corrigendum: There is an error in the reporting of the Text Re ...
Chapter Seven Part Two - K-Dub
... Positive punishment: “You’re playing video games instead of practicing the piano, so I am justified in YELLING at you.” Negative punishment: “You’re ...
... Positive punishment: “You’re playing video games instead of practicing the piano, so I am justified in YELLING at you.” Negative punishment: “You’re ...
Final Review Guide ( Due on May 2-counts toward
... Abraham Maslow suggested that “A person who is lacking food, love, and self-esteem would most likely hunger for food more strongly than anything else.” Conversely, the novelist Dostoyevski wrote, “Without a firm idea of himself and the purpose of his life, man cannot live even if surrounded with bre ...
... Abraham Maslow suggested that “A person who is lacking food, love, and self-esteem would most likely hunger for food more strongly than anything else.” Conversely, the novelist Dostoyevski wrote, “Without a firm idea of himself and the purpose of his life, man cannot live even if surrounded with bre ...
Lecture9-OperantCond..
... The test starts today…if you take it before Friday I will give you 20 extra credit points on that test. If you are caught texting in class, you will lose 20 points off your final grade. If you spend more time studying the material in PsychPortal, you will earn all the possible points. ...
... The test starts today…if you take it before Friday I will give you 20 extra credit points on that test. If you are caught texting in class, you will lose 20 points off your final grade. If you spend more time studying the material in PsychPortal, you will earn all the possible points. ...
Chapter 6 No Media
... ¡Ivan P avlov §Scientist who studied digestion by measuring the saliva of dogs §Discovered that dogs “predicted” the arrival of food; led to salivation ...
... ¡Ivan P avlov §Scientist who studied digestion by measuring the saliva of dogs §Discovered that dogs “predicted” the arrival of food; led to salivation ...