Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning Chapter 7
... What if we could not distinguish between stimuli that were ...
... What if we could not distinguish between stimuli that were ...
PPT chapter 5
... paying attention to a model. In general, students pay attention to role models who are attractive, successful, interesting, and popular. Retention phase. Once teachers have students’ attention, it is time to model the behavior they want students to imitate and then give students a chance to practice ...
... paying attention to a model. In general, students pay attention to role models who are attractive, successful, interesting, and popular. Retention phase. Once teachers have students’ attention, it is time to model the behavior they want students to imitate and then give students a chance to practice ...
Behavior Therapy
... Russian physiologist, Ivan Pavlov. Pavlov was the first to show the process with dogs. Two stimuli are paired in classical conditioning. The first stimulus is a stimulus that is introduced that causes no response in an individual. This is called the conditioned stimulus. The second stimulus is an un ...
... Russian physiologist, Ivan Pavlov. Pavlov was the first to show the process with dogs. Two stimuli are paired in classical conditioning. The first stimulus is a stimulus that is introduced that causes no response in an individual. This is called the conditioned stimulus. The second stimulus is an un ...
learning by operant conditioning
... Continuous vs. Intermittent (Interval/Ratio; Fixed/Variable) = V-R Schedule is most effective ...
... Continuous vs. Intermittent (Interval/Ratio; Fixed/Variable) = V-R Schedule is most effective ...
Innate and Learned Behavior
... from their parents, and in determining behaviour later in life (such as courtship and mating) Imprinting occurs during a ...
... from their parents, and in determining behaviour later in life (such as courtship and mating) Imprinting occurs during a ...
Objective 5.3 - HCC Learning Web
... 1. (Pavlov, Watson, Skinner) discovered the principles of classical conditioning in conjunction with his research on the digestive system of dogs. 2. (Pavlov, Watson, Skinner) discovered the principles of operant conditioning in laboratory experiments with rats, pigeons, and other animals. 3. (Pavlo ...
... 1. (Pavlov, Watson, Skinner) discovered the principles of classical conditioning in conjunction with his research on the digestive system of dogs. 2. (Pavlov, Watson, Skinner) discovered the principles of operant conditioning in laboratory experiments with rats, pigeons, and other animals. 3. (Pavlo ...
AP Psychology Course Information
... AP Psychology Course Information – 2006/2007 Course Specific Standards Upon completion of this course students will be able to: ! Comprehend, articulate, and disseminate psychology as a science. ! Integrate natural and social sciences as they apply to psychology. ! Identify and define the principles ...
... AP Psychology Course Information – 2006/2007 Course Specific Standards Upon completion of this course students will be able to: ! Comprehend, articulate, and disseminate psychology as a science. ! Integrate natural and social sciences as they apply to psychology. ! Identify and define the principles ...
AP Psychology
... teacher gives her a sticker. _________________________ 4. If Thomas is late to practice, his coach makes him do extra push-ups. _________________________ 5. Margaret was given a standing ovation after singing karaoke. Now she goes to sing karaoke almost every other day. _________________________ 6. ...
... teacher gives her a sticker. _________________________ 4. If Thomas is late to practice, his coach makes him do extra push-ups. _________________________ 5. Margaret was given a standing ovation after singing karaoke. Now she goes to sing karaoke almost every other day. _________________________ 6. ...
Learning and Conditioning
... E. Stimulus Generalization: occurs when a new stimulus is similar to the original reinforced stimulus. The more similar the new stimulus is to the old, the more strongly the subject is likely to respond. ...
... E. Stimulus Generalization: occurs when a new stimulus is similar to the original reinforced stimulus. The more similar the new stimulus is to the old, the more strongly the subject is likely to respond. ...
Learning and Conditioning terms and concepts
... • Shaping- a process in which reinforcement is used to sculpt new responses out of old ones. • Response Chains- learned reactions that follow one another in sequence, each reaction producing the signal for the next. ...
... • Shaping- a process in which reinforcement is used to sculpt new responses out of old ones. • Response Chains- learned reactions that follow one another in sequence, each reaction producing the signal for the next. ...
AP Psychology Course Syllabus 2014 The AP Psychology course is
... associated with each of the major subfields within psychology. You will also learn about the ethics and methods psychologists use in their science and practice. Content Areas: I. History and Approaches (2-4% of AP Exam) Psychology has evolved markedly since its inception as a discipline in 1879. The ...
... associated with each of the major subfields within psychology. You will also learn about the ethics and methods psychologists use in their science and practice. Content Areas: I. History and Approaches (2-4% of AP Exam) Psychology has evolved markedly since its inception as a discipline in 1879. The ...
Mock Exam 2 - SI Psychology 101
... 12. Pavlov's research on classical conditioning was important because a. It highlighted the role of cognitive processes in learning. b. So many different species of animals, including humans, can be classically conditioned. c. It demonstrated an essential difference between animal and human learnin ...
... 12. Pavlov's research on classical conditioning was important because a. It highlighted the role of cognitive processes in learning. b. So many different species of animals, including humans, can be classically conditioned. c. It demonstrated an essential difference between animal and human learnin ...
LearningActivity answers
... often give rise to mental images of accidents. These mental images are already established CSs, providing the basis for the CS-CS pairing. 4. The sight of Donna (CS) elicits romantic excitement (CR). The response was extinguished when Donna failed to stimulate her partner (the US). The reaction one ...
... often give rise to mental images of accidents. These mental images are already established CSs, providing the basis for the CS-CS pairing. 4. The sight of Donna (CS) elicits romantic excitement (CR). The response was extinguished when Donna failed to stimulate her partner (the US). The reaction one ...
Applications of Operant Conditioning
... Pavlov and Watson believed that laws of learning were similar for all animals. Therefore, a pigeon and a person do not differ in their learning. However, behaviorists later suggested that learning is constrained by an animal’s biology. ...
... Pavlov and Watson believed that laws of learning were similar for all animals. Therefore, a pigeon and a person do not differ in their learning. However, behaviorists later suggested that learning is constrained by an animal’s biology. ...
Behavioral Perspective
... Pavlov and Watson believed that laws of learning were similar for all animals. Therefore, a pigeon and a person do not differ in their learning. However, behaviorists later suggested that learning is constrained by an animal’s biology. ...
... Pavlov and Watson believed that laws of learning were similar for all animals. Therefore, a pigeon and a person do not differ in their learning. However, behaviorists later suggested that learning is constrained by an animal’s biology. ...
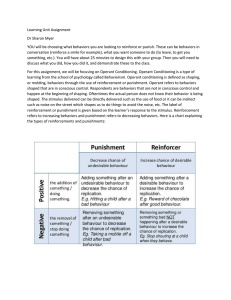
Learning Unit Assignment Dr Sharon Myer YOU will be choosing
... YOU will be choosing what behaviors you are looking to reinforce or punish. These can be behaviors in conversation (reinforce a smile for example), what you want someone to do (to leave, to get you something, etc.). You will have about 25 minutes to design this with your group. Then you will need to ...
... YOU will be choosing what behaviors you are looking to reinforce or punish. These can be behaviors in conversation (reinforce a smile for example), what you want someone to do (to leave, to get you something, etc.). You will have about 25 minutes to design this with your group. Then you will need to ...
A Behavior Analytic Paradigm for Adaptive Autonomous Agents
... number of interactions with the environment needed to learn through directly experienced environmental contingencies. Learning in humans is significantly more efficient than machine learning because, after infancy, much learning is mediated by language. A major innovation of the 7GT system is its ca ...
... number of interactions with the environment needed to learn through directly experienced environmental contingencies. Learning in humans is significantly more efficient than machine learning because, after infancy, much learning is mediated by language. A major innovation of the 7GT system is its ca ...
Consulting Course 18 Learning - Management Consulting Courses
... Analysis of B.F.Skinner Theory of Operant Conditioning: The theory of B.F. Skinner is based upon the idea that learning is a function of change in overt behavior. Changes in behavior are the result of an individual's response to events (stimuli) that occur in the environment. A response produces a ...
... Analysis of B.F.Skinner Theory of Operant Conditioning: The theory of B.F. Skinner is based upon the idea that learning is a function of change in overt behavior. Changes in behavior are the result of an individual's response to events (stimuli) that occur in the environment. A response produces a ...
PSYC 2500-01 LEARNING: QUIZ 2 NAME: Spring 2015 Read each
... Clark Hull's 1943 equation for learning was revised in 1952 to add K (incentive motivation). The addition of K was from the results of the Crespi-Zeaman Effect. Which of the following statements describes this effect accurately? a) Changing the number of reinforcements had an unexpected sudden effec ...
... Clark Hull's 1943 equation for learning was revised in 1952 to add K (incentive motivation). The addition of K was from the results of the Crespi-Zeaman Effect. Which of the following statements describes this effect accurately? a) Changing the number of reinforcements had an unexpected sudden effec ...
Learning
... Applications of Operant Conditioning • In school: use individualized shaping to reinforce students starting with their current level of performance. • At work: reinforce, even with a ‘good job’ for specific behaviors and achievements • At home: be careful not to reward ...
... Applications of Operant Conditioning • In school: use individualized shaping to reinforce students starting with their current level of performance. • At work: reinforce, even with a ‘good job’ for specific behaviors and achievements • At home: be careful not to reward ...
PSYC 2500-02 LEARNING: QUIZ 2 NAME: Spring 2017 Read each
... Clark Hull's 1943 equation for learning was revised in 1952 to add K (incentive motivation). The addition of K was from the results of the Crespi-Zeaman Effect. Which of the following statements describes this effect accurately? a) Changing the number of reinforcements had an unexpected sudden effec ...
... Clark Hull's 1943 equation for learning was revised in 1952 to add K (incentive motivation). The addition of K was from the results of the Crespi-Zeaman Effect. Which of the following statements describes this effect accurately? a) Changing the number of reinforcements had an unexpected sudden effec ...