Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can't find answers in the text. 1. What does it mean for behavior to be elicited? 2. What are eliciting stimuli? 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be invol ...
... Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can't find answers in the text. 1. What does it mean for behavior to be elicited? 2. What are eliciting stimuli? 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be invol ...
Unit 6 Review (Modules 26-30, Pages 262-315)
... ● Generalization ● Discrimination ● John B. Watson: Human emotions and behaviors are mainly a bundle of conditioned responses ○ Created “Little Albert” experiment Module 27 ● B.F. Skinner: Modern behaviorism’s most influential and controversial figure ○ Elaborated on Edward L. Thorndike’s law of eff ...
... ● Generalization ● Discrimination ● John B. Watson: Human emotions and behaviors are mainly a bundle of conditioned responses ○ Created “Little Albert” experiment Module 27 ● B.F. Skinner: Modern behaviorism’s most influential and controversial figure ○ Elaborated on Edward L. Thorndike’s law of eff ...
chapter5
... • Explain how goals contribute to performance management • Describe how feedback can provide information for improved performance • Define types of rewards, and summarize their relationship to performance • Describe how the effects and consequences of behaviors can influence future behaviors ...
... • Explain how goals contribute to performance management • Describe how feedback can provide information for improved performance • Define types of rewards, and summarize their relationship to performance • Describe how the effects and consequences of behaviors can influence future behaviors ...
Chapter Outline Learning
... Operant Conditioning: Learning by associating a behavior with its consequences Reinforcement- strengthens behavior it follows ...
... Operant Conditioning: Learning by associating a behavior with its consequences Reinforcement- strengthens behavior it follows ...
Chapter 1 ppt - s3.amazonaws.com
... applied laboratory techniques to study of the mind Edward Titchener (1867–1927) Wundt’s student, professor at Cornell University developed approach called structuralism—emphasized studying the most basic components, or structures, of conscious experiences Objective sensations: sight and taste. ...
... applied laboratory techniques to study of the mind Edward Titchener (1867–1927) Wundt’s student, professor at Cornell University developed approach called structuralism—emphasized studying the most basic components, or structures, of conscious experiences Objective sensations: sight and taste. ...
Document
... 2. Under the conscious control of the individual 3. Although classically conditioned behaviors are elicited by stimuli that occur before the response, operant behaviors are emitted because of the consequences that occur after the behavior 4. Operant conditioning has occurred when the response hierar ...
... 2. Under the conscious control of the individual 3. Although classically conditioned behaviors are elicited by stimuli that occur before the response, operant behaviors are emitted because of the consequences that occur after the behavior 4. Operant conditioning has occurred when the response hierar ...
Chapter 6 No Media
... ¡Pavlov’s e xperiment : §Attached tube to dog’s salivary gland §Rang a bell, then presented food (repeated pairings) §Dogs soon began to salivate when bell rang – even when food wasn’t presented! ...
... ¡Pavlov’s e xperiment : §Attached tube to dog’s salivary gland §Rang a bell, then presented food (repeated pairings) §Dogs soon began to salivate when bell rang – even when food wasn’t presented! ...
Can you answer these questions about classical and operant
... 9. Learning may be defined as a ______ change in behavior that occurs as the result of experience. ...
... 9. Learning may be defined as a ______ change in behavior that occurs as the result of experience. ...
Chapter Outline - Cengage Learning
... called the unconditioned response. After repeated pairing, the conditioned stimulus alone can produce a weakened version of the response, call the conditioned response. Classical conditioning in psychopathology. These concepts can be said to explain the development of phobias and deviant sexual beha ...
... called the unconditioned response. After repeated pairing, the conditioned stimulus alone can produce a weakened version of the response, call the conditioned response. Classical conditioning in psychopathology. These concepts can be said to explain the development of phobias and deviant sexual beha ...
Addenda to Print for Class
... Steps for Developing a Behavior Modification Plan Step 1--Identify a reinforcer. It is important to establish rather than assume that a consequence has reinforcing effects. To do this, one must first record a baseline or operant level of responding for some commonly occurring behavior (e.g., eye co ...
... Steps for Developing a Behavior Modification Plan Step 1--Identify a reinforcer. It is important to establish rather than assume that a consequence has reinforcing effects. To do this, one must first record a baseline or operant level of responding for some commonly occurring behavior (e.g., eye co ...
Therapy
... conditions and at all times, perform well (or outstandingly well) and win the approval (or complete love) of significant others. If I fail in these important—and sacred—respects, that is awful and I am a bad, incompetent, unworthy person, who will probably always fail and deserves to suffer." ...
... conditions and at all times, perform well (or outstandingly well) and win the approval (or complete love) of significant others. If I fail in these important—and sacred—respects, that is awful and I am a bad, incompetent, unworthy person, who will probably always fail and deserves to suffer." ...
File - SSHS AP Psychology
... knowledge important to create new ideas--language, culture and social interactions important) 2) Theory of Knowledge: how is knowledge different from belief? (intellectual abilities are specific to the culture in which the child was reared) ...
... knowledge important to create new ideas--language, culture and social interactions important) 2) Theory of Knowledge: how is knowledge different from belief? (intellectual abilities are specific to the culture in which the child was reared) ...
A View on Behaviorist Learning Theory Introduction
... behaviorism is that of classical condition, due to Pavlov. His researched drew conclusions that a response is given due to an association with the environment. In relating this to learning, a stimulus or event that happens in the learning process can be used to predict how the learner will respond ...
... behaviorism is that of classical condition, due to Pavlov. His researched drew conclusions that a response is given due to an association with the environment. In relating this to learning, a stimulus or event that happens in the learning process can be used to predict how the learner will respond ...
leadership
... If we are the same then we could study human behaviors and human learnings by studying non-human organisms ...
... If we are the same then we could study human behaviors and human learnings by studying non-human organisms ...
Reinforcement_Learned Helplessness
... A technique in which a desired behavior is molded first by rewarding any act similar to that behavior, then requiring closer and closer approximations to the desired behavior before giving the reward A real-life example: Trainers sometimes use shaping to teach animals how to ...
... A technique in which a desired behavior is molded first by rewarding any act similar to that behavior, then requiring closer and closer approximations to the desired behavior before giving the reward A real-life example: Trainers sometimes use shaping to teach animals how to ...
Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since
... John Broadus Watson (1878-1958) • The move to Johns Hopkins • Instinct as a set of reflexes activated by heredity • Conditioned responses • Conditioned fear: Little Albert • Scandal • The move to advertising work • Origins of the behaviorist movement ...
... John Broadus Watson (1878-1958) • The move to Johns Hopkins • Instinct as a set of reflexes activated by heredity • Conditioned responses • Conditioned fear: Little Albert • Scandal • The move to advertising work • Origins of the behaviorist movement ...
Behaviorism Study Guide Spring 2013
... Task analysis Positive practice Notes from Guidelines: Encouraging Positive Behaviors (pg. 288): Response cost Group consequences Contingency contract Token Economy (token reinforcement system) Fading (not in text) Self-management ...
... Task analysis Positive practice Notes from Guidelines: Encouraging Positive Behaviors (pg. 288): Response cost Group consequences Contingency contract Token Economy (token reinforcement system) Fading (not in text) Self-management ...
KleinCh6aTEMP
... Animal is reinforced for withholding its behavior for a time, then showing it at the end of the period. If a period goes by without a response then the response is shown, the reward is given. ...
... Animal is reinforced for withholding its behavior for a time, then showing it at the end of the period. If a period goes by without a response then the response is shown, the reward is given. ...
PSY402 Theories of Learning
... Animal is reinforced for withholding its behavior for a time, then showing it at the end of the period. If a period goes by without a response then the response is shown, the reward is given. ...
... Animal is reinforced for withholding its behavior for a time, then showing it at the end of the period. If a period goes by without a response then the response is shown, the reward is given. ...
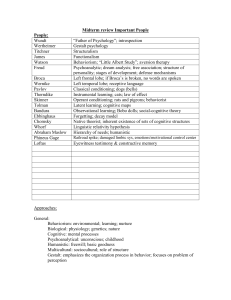
AP Psychology Crib Notes
... Cognitive: mental processes Psychoanalytical: unconscious; childhood Humanistic: freewill; basic goodness Multicultural: sociocultural; role of structure Gestalt: emphasizes the organization process in behavior; focuses on problem of perception ...
... Cognitive: mental processes Psychoanalytical: unconscious; childhood Humanistic: freewill; basic goodness Multicultural: sociocultural; role of structure Gestalt: emphasizes the organization process in behavior; focuses on problem of perception ...