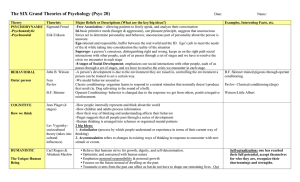
Printer-Friendly Version
... Although most therapists do not subscribe to behaviorism as the only way to impact behavior, they may certainly feel shaping behavior can be useful. "Dr. Phil," a current talk show host, often provides advice based on reward and punishment i.e. an individual will repeat behavior if he or she is rewa ...
... Although most therapists do not subscribe to behaviorism as the only way to impact behavior, they may certainly feel shaping behavior can be useful. "Dr. Phil," a current talk show host, often provides advice based on reward and punishment i.e. an individual will repeat behavior if he or she is rewa ...
1.1 History and Perspective
... behavior among animals is learned rather than instinctive (Classical Conditioning) • Watson – applied Pavlov’s reasoning to humans / believed humans could be socialized in any direction through learning • Skinner – organisms repeat responses that lead to positive responses and do not repeat behavior ...
... behavior among animals is learned rather than instinctive (Classical Conditioning) • Watson – applied Pavlov’s reasoning to humans / believed humans could be socialized in any direction through learning • Skinner – organisms repeat responses that lead to positive responses and do not repeat behavior ...
Behaviorism
... Examples of the application of operant conditioning: Punishment – applying an aversive stimulus after a (undesired) behavior Avoidance conditioning – exhibiting a behavior that prevents an undesired stimulus from occurring, e.g. going to counseling to avoid going to jail Escape conditioning – termin ...
... Examples of the application of operant conditioning: Punishment – applying an aversive stimulus after a (undesired) behavior Avoidance conditioning – exhibiting a behavior that prevents an undesired stimulus from occurring, e.g. going to counseling to avoid going to jail Escape conditioning – termin ...
Social facilitation
... diminishes when we are not good at that task… – Should students schedule when they take tests so that can take them when they are ready? Why or why not? – Should students be allowed to give oral presentations in front of just the teacher if they believe their project isn’t good, or if they are uncom ...
... diminishes when we are not good at that task… – Should students schedule when they take tests so that can take them when they are ready? Why or why not? – Should students be allowed to give oral presentations in front of just the teacher if they believe their project isn’t good, or if they are uncom ...
Observational Learning
... imitated the very acts they had observed and used the words they heard. ...
... imitated the very acts they had observed and used the words they heard. ...
Chapter 1
... Hypothesis—tentative statement about the relationship between variables Variables—factors that can vary in ways that can be observed, measured, and verified (independent versus dependent) Operational definition—precise description of how the variables will be measured ...
... Hypothesis—tentative statement about the relationship between variables Variables—factors that can vary in ways that can be observed, measured, and verified (independent versus dependent) Operational definition—precise description of how the variables will be measured ...
Why do we use ABA? - Hope Center for Autism
... scientific research aspect, and applied behavior analysis, which puts those research findings into application. ABA-based approaches to therapy are evidence-based, which means they have undergone rigorous scrutiny and are scientifically supported by valid research. Because of the evidence backing th ...
... scientific research aspect, and applied behavior analysis, which puts those research findings into application. ABA-based approaches to therapy are evidence-based, which means they have undergone rigorous scrutiny and are scientifically supported by valid research. Because of the evidence backing th ...
BHC The Shaping Police
... Train one aspect of any particular behavior at a time. Don't try to shape for two criteria simultaneously. ...
... Train one aspect of any particular behavior at a time. Don't try to shape for two criteria simultaneously. ...
Working definition of Social Psychology
... – relatively stable change in a person’s behavior attributed to observation of other people. • Imitative behavior, vicarious reinforcement ...
... – relatively stable change in a person’s behavior attributed to observation of other people. • Imitative behavior, vicarious reinforcement ...
File - Ms. Thresher
... rewarding someone when they acted in a favorable manner that was close to the desired act could shape behavior. A way to achieve this is through positive reinforcers and punishment. A positive reinforcer would be telling someone thank you or perhaps a hug or kiss when a child does a desirable behavi ...
... rewarding someone when they acted in a favorable manner that was close to the desired act could shape behavior. A way to achieve this is through positive reinforcers and punishment. A positive reinforcer would be telling someone thank you or perhaps a hug or kiss when a child does a desirable behavi ...
chapter 17
... – observers who watch models being rewarded for certain behaviors tend to repeat them, whereas observers who watch models being punished for their actions tend not to repeat those actions. – observers are more likely to imitate aggressive models who receive no punishment for their behavior. • even w ...
... – observers who watch models being rewarded for certain behaviors tend to repeat them, whereas observers who watch models being punished for their actions tend not to repeat those actions. – observers are more likely to imitate aggressive models who receive no punishment for their behavior. • even w ...
Self Instructional: Cognitive Behavioral
... The Theory of Observational Learning Attentional Processes – seeing is not enough; one must perceive accurately by attending at varying degrees Retention Processes – imaginal & verbal coding (self-talk) describe subvocal events for remembering Motor Reproduction Process – translating observed pheno ...
... The Theory of Observational Learning Attentional Processes – seeing is not enough; one must perceive accurately by attending at varying degrees Retention Processes – imaginal & verbal coding (self-talk) describe subvocal events for remembering Motor Reproduction Process – translating observed pheno ...
Explaining Behavior with Learning Theory – The Behaviorists What
... Regarding issues like domestic violence, drug use, etc., our learning is not limited to just classical and operant conditioning or observational learning because we think about the things that we learn. For example, we could all have the same experience and each learn something completely different ...
... Regarding issues like domestic violence, drug use, etc., our learning is not limited to just classical and operant conditioning or observational learning because we think about the things that we learn. For example, we could all have the same experience and each learn something completely different ...
Reinforcements from the environment ∙Operant conditioning: a type of
... -Food, shelter, comfort, and warmth are examples of primary reinforcers, because they help satisfy biological needs. ∙The vast majority of reinforcers (or punishers) have little to do with biology. -Secondary reinforcers derive their effectiveness from their association with the primary reinforcers. ...
... -Food, shelter, comfort, and warmth are examples of primary reinforcers, because they help satisfy biological needs. ∙The vast majority of reinforcers (or punishers) have little to do with biology. -Secondary reinforcers derive their effectiveness from their association with the primary reinforcers. ...
Psychology 155: Personality Study Guide 2 Chapter 5: Biological
... 3. Alzheimer's Disease, Pick's Disease, Strokes, etc. 4. Biological Determinism: The belief that an individual's personality is completely determined by biological factors (and especially by genetic factors). 5. Drugs: tranquilizers, sleeping pills, antidepressants, cocaine can have both short and l ...
... 3. Alzheimer's Disease, Pick's Disease, Strokes, etc. 4. Biological Determinism: The belief that an individual's personality is completely determined by biological factors (and especially by genetic factors). 5. Drugs: tranquilizers, sleeping pills, antidepressants, cocaine can have both short and l ...
Psychoanalytic Theory
... Social Learning Theory- Albert Bandura (b. 1925) An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to cha ...
... Social Learning Theory- Albert Bandura (b. 1925) An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to cha ...
The SIX Grand Theories of Psychology (Psyc 20)
... -Human thinking is arranged into schemes or organized mental patterns 2 big Ideas: 1. Assimilation (process by which people understand or experience in terms of their current way of thinking) 2. Accommodation refers to changes in existing ways of thinking in response to encounter with new stimuli or ...
... -Human thinking is arranged into schemes or organized mental patterns 2 big Ideas: 1. Assimilation (process by which people understand or experience in terms of their current way of thinking) 2. Accommodation refers to changes in existing ways of thinking in response to encounter with new stimuli or ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... Mesosystem – relationships within the miscrosystem, such as family and school experiences. Exosystem – the influences of factors over which one has no control, such as divorce, parents’ work stress. Macrosystem – the culture in which one lives, its beliefs and value systems. Chronosystem – the seque ...
... Mesosystem – relationships within the miscrosystem, such as family and school experiences. Exosystem – the influences of factors over which one has no control, such as divorce, parents’ work stress. Macrosystem – the culture in which one lives, its beliefs and value systems. Chronosystem – the seque ...
Behavior Therapy - Mypage Web Server
... reflection, clarification, and open-ended questions. They focus on specifics, systematically getting information about specific antecedents, the dimensions of the problem behavior, and the consequences of the problem. (Goldried & Davison, 1976) ...
... reflection, clarification, and open-ended questions. They focus on specifics, systematically getting information about specific antecedents, the dimensions of the problem behavior, and the consequences of the problem. (Goldried & Davison, 1976) ...
Review for Quiz 2 Fixed Action Pattern Types of neurons Anatomy of
... Define and know examples of the following types of rhythms Ultradian Infradian Circadian Circannual Exogenous vs. Endogenous rhythms Free running rhythms Entrainment & Zeitgeiber What is the SCN and where ...
... Define and know examples of the following types of rhythms Ultradian Infradian Circadian Circannual Exogenous vs. Endogenous rhythms Free running rhythms Entrainment & Zeitgeiber What is the SCN and where ...
ANIMAL BEHAVIORS
... – Animal learns to repeat behaviors that result in reward, and avoid those that end in punishment – “trial-and-error” learning – This learning begins with “random behavior” – Many animals use this type of learning to identify sources of food ...
... – Animal learns to repeat behaviors that result in reward, and avoid those that end in punishment – “trial-and-error” learning – This learning begins with “random behavior” – Many animals use this type of learning to identify sources of food ...
This is Where You Type the Slide Title
... - lack of awareness for free assn info an unconscious mind exists that produces deviant behavior when it struggles with conflicts & drives. revealing these conflicts is cathartic. ...
... - lack of awareness for free assn info an unconscious mind exists that produces deviant behavior when it struggles with conflicts & drives. revealing these conflicts is cathartic. ...