Consumer Behavior
... who buy goods and services for their own use and organizational buyers who purchase business products • Consumer behavior: the process through which the ultimate buyer makes purchase decisions ...
... who buy goods and services for their own use and organizational buyers who purchase business products • Consumer behavior: the process through which the ultimate buyer makes purchase decisions ...
PSY402 Theories of Learning
... Suppressive effects may generalize from an undesirable behavior to other desirable behaviors. ...
... Suppressive effects may generalize from an undesirable behavior to other desirable behaviors. ...
lifesmart-1st-edition-fiore-solution-manual
... In operant conditioning, behavior is controlled by its consequences. When a student prepares well and performs well on an exam, he/she gets a good grade; when an adolescent cuts classes, she has to stay after school; when a driver parks illegally, he gets fined; when a cardholder returns overdue lib ...
... In operant conditioning, behavior is controlled by its consequences. When a student prepares well and performs well on an exam, he/she gets a good grade; when an adolescent cuts classes, she has to stay after school; when a driver parks illegally, he gets fined; when a cardholder returns overdue lib ...
SI: September 19, 2011 Chapter 7: Part 2 Part I: Warm
... True/False: Delayed reinforcers are effective. True/False: Negative reinforcement punishes an individual and reinforces that behavior to not happen again. Continuous reinforcement reinforces the action how many times? a. Every other time b. Never c. Every time it occurs d. Whenever you feel like it ...
... True/False: Delayed reinforcers are effective. True/False: Negative reinforcement punishes an individual and reinforces that behavior to not happen again. Continuous reinforcement reinforces the action how many times? a. Every other time b. Never c. Every time it occurs d. Whenever you feel like it ...
UNIT VI Notes
... Behaviorist learning doesn’t allow us to generalize from one response to another, nor from one species to another Cognitive processes 1. Rescorla and Wagner (1972): animals learn to “expect” an unconditioned stimulus; this shows cognition at work: the animal learns the predictability of a second ass ...
... Behaviorist learning doesn’t allow us to generalize from one response to another, nor from one species to another Cognitive processes 1. Rescorla and Wagner (1972): animals learn to “expect” an unconditioned stimulus; this shows cognition at work: the animal learns the predictability of a second ass ...
Operant Conditioning 001
... Whether we are likely to continue producing given behaviors depends on the consequences of our actions. Consequences that increase the frequency of a behavior, are referred to as ―reinforcers,‖ whereas events that decrease the frequency of behavior are called ―punishments.‖ Most operant behavior is ...
... Whether we are likely to continue producing given behaviors depends on the consequences of our actions. Consequences that increase the frequency of a behavior, are referred to as ―reinforcers,‖ whereas events that decrease the frequency of behavior are called ―punishments.‖ Most operant behavior is ...
File
... Operant Conditioning began with Thorndike’s Law of Effect: a response followed by a pleasant consequence will probably be repeated and a response followed by an unpleasant consequence will probably be diminished BF Skinner furthered this idea by applying it strictly to behavior, by way of his Operan ...
... Operant Conditioning began with Thorndike’s Law of Effect: a response followed by a pleasant consequence will probably be repeated and a response followed by an unpleasant consequence will probably be diminished BF Skinner furthered this idea by applying it strictly to behavior, by way of his Operan ...
Behaviorism: Its all in the action
... Click here to read information about John Watson, Who is believed to be the “Father of Behaviorism” ...
... Click here to read information about John Watson, Who is believed to be the “Father of Behaviorism” ...
Operant Conditioning
... brief period of time when the undesired behavior may occur with greater intensity, frequency, and variability. This is called the extinction burst. So Sandy may tantrum for even longer and harder next time, in the hope that she will be reinforced. As long as she is not reinforced in the future for t ...
... brief period of time when the undesired behavior may occur with greater intensity, frequency, and variability. This is called the extinction burst. So Sandy may tantrum for even longer and harder next time, in the hope that she will be reinforced. As long as she is not reinforced in the future for t ...
Myers Module Twenty One
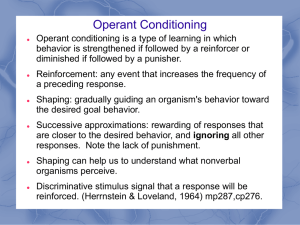
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
behaviourist theories
... another, via observation, imitation, and modeling. The theory has often been called a bridge between behaviorist and cognitive learning theories because it encompasses attention, memory, and motivation. Originator: Albert Bandura Social Learning Theory (Bandura) People learn through observing others ...
... another, via observation, imitation, and modeling. The theory has often been called a bridge between behaviorist and cognitive learning theories because it encompasses attention, memory, and motivation. Originator: Albert Bandura Social Learning Theory (Bandura) People learn through observing others ...
Reinforcement - Eagan High School
... Ex. Dogs in individual chambers received shocks Some dogs could jump over barriers, others were restrained to prevent escape. Restrained dogs learned to be helpless… Depression happens when people have no control ...
... Ex. Dogs in individual chambers received shocks Some dogs could jump over barriers, others were restrained to prevent escape. Restrained dogs learned to be helpless… Depression happens when people have no control ...
Module 27 notes - Bremerton School District
... reinforcer that gets its reinforcing power through association with the primary reinforcer. Money is a conditioned reinforcer (desire for money is derived from the desire for food and other necessities). ...
... reinforcer that gets its reinforcing power through association with the primary reinforcer. Money is a conditioned reinforcer (desire for money is derived from the desire for food and other necessities). ...
Chapter 1 The Science of Psychology Learning Objectives: These
... childhood sexuality/ little lab or research testing of theories. b. Modern psychodynamic theories downplay hidden sexual and aggressive motives but focus on early family relationships, social factors and sense of self. Object relations theory focuses on how early experiences with caregivers shape ou ...
... childhood sexuality/ little lab or research testing of theories. b. Modern psychodynamic theories downplay hidden sexual and aggressive motives but focus on early family relationships, social factors and sense of self. Object relations theory focuses on how early experiences with caregivers shape ou ...
Chapter Outline Learning
... Observational Learning: Learning by observing and imitating others Key Factors in Observational Learning ...
... Observational Learning: Learning by observing and imitating others Key Factors in Observational Learning ...
Skinner
... We believe that positively reinforcing the behavior within the 2nd graders will yield more of the expected results. We believe that by reinforcing their behavior with a physical gift, their motives are rather extrinsic, not intrinsic. We believe that that may not be the case for the 8th graders beca ...
... We believe that positively reinforcing the behavior within the 2nd graders will yield more of the expected results. We believe that by reinforcing their behavior with a physical gift, their motives are rather extrinsic, not intrinsic. We believe that that may not be the case for the 8th graders beca ...
Unit III: Learning
... – These instincts differ from species to species. – Some responses cannot be trained into an animal regardless of conditioning. ...
... – These instincts differ from species to species. – Some responses cannot be trained into an animal regardless of conditioning. ...
Unit 6 - Crossword Labs
... 23. A stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer 24. A relatively permanent change in an organism's behavior due to experience ...
... 23. A stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer 24. A relatively permanent change in an organism's behavior due to experience ...
Module 19 Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning
... punishing consequences from actions such as reaching into a fire. In that case, operant conditioning helps us to avoid dangers. Punishment is less effective when we try to artificially create punishing consequences for other’s choices; Severity of punishments is not as helpful as making the pu ...
... punishing consequences from actions such as reaching into a fire. In that case, operant conditioning helps us to avoid dangers. Punishment is less effective when we try to artificially create punishing consequences for other’s choices; Severity of punishments is not as helpful as making the pu ...
Intro to Animal Behavior
... forR allele is more active than that encoded by fors. PKG is activated by a molecule called cyclic GMP (cGMP). She and her colleagues have succeeded in inserting forR DNA into sitters who promptly become rovers. Why should alleles for two such different behaviors be maintained at such high frequency ...
... forR allele is more active than that encoded by fors. PKG is activated by a molecule called cyclic GMP (cGMP). She and her colleagues have succeeded in inserting forR DNA into sitters who promptly become rovers. Why should alleles for two such different behaviors be maintained at such high frequency ...
Learning and Cognition
... •Deductive reasoning and learning to consider possibilities also occurs in this stage. Some Adults Post-Formal •Individuals are able to think on many different Operational Stage levels, building on formal operational thought. •Individuals are able to mentally manipulate even complex, abstract ideas. ...
... •Deductive reasoning and learning to consider possibilities also occurs in this stage. Some Adults Post-Formal •Individuals are able to think on many different Operational Stage levels, building on formal operational thought. •Individuals are able to mentally manipulate even complex, abstract ideas. ...
Paradigms in Personality Psychology
... “why people do what they do”? “The disposition a person brings to the experiment is probably less important a cause of his behavior than most readers assume….. Often, it is not so much the kind of person a man is as the kind of situation in which he finds himself that determines how he will act.” (M ...
... “why people do what they do”? “The disposition a person brings to the experiment is probably less important a cause of his behavior than most readers assume….. Often, it is not so much the kind of person a man is as the kind of situation in which he finds himself that determines how he will act.” (M ...
CHAPTER 3
... training manuals, lectures, role playing • Many believe this form is most successful when external rewards are provided ...
... training manuals, lectures, role playing • Many believe this form is most successful when external rewards are provided ...