What Is Motivation Motivation Motivation Theories Maslow`s
... tighten the bolts with my electric wrench. Thirty cars and 220 bolts an hour, eight hours a day. I didn’t care that they were paying me $17 and hour. I was going crazy. I did it for almost a year and a half. Finally, I just said to my wife that this isn’t going to be the way that I spend the rest of ...
... tighten the bolts with my electric wrench. Thirty cars and 220 bolts an hour, eight hours a day. I didn’t care that they were paying me $17 and hour. I was going crazy. I did it for almost a year and a half. Finally, I just said to my wife that this isn’t going to be the way that I spend the rest of ...
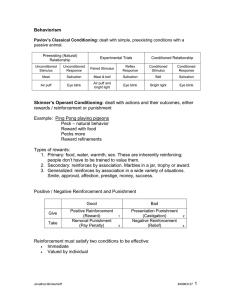
BehaviorPrinciples
... system elicited unconditioned reflexes such as gastric secretions and saliva discovered that these responses could be stimulated when certain stimuli associated with the presentation of food were also present in the environment identified "conditioned response" food food + bell bell ...
... system elicited unconditioned reflexes such as gastric secretions and saliva discovered that these responses could be stimulated when certain stimuli associated with the presentation of food were also present in the environment identified "conditioned response" food food + bell bell ...
Learning 1
... 5. Involves feelings or expectancies 6. Change is mainly in effectiveness of a S 7. S-S learning -- S predicts other S ...
... 5. Involves feelings or expectancies 6. Change is mainly in effectiveness of a S 7. S-S learning -- S predicts other S ...
ELEMENTS OF CHANGE 6. BEHAVIORAL THERAPY 6.1
... measures how long the client can tolerate an anxiety-inducing stimulus. The BAT falls under the exposure-based methods of Behavior Therapy. Exposure-based methods of behavioral therapy are well suited to the treatment of phobias, which include intense and unreasonable fears (e.g., of spiders, blood, ...
... measures how long the client can tolerate an anxiety-inducing stimulus. The BAT falls under the exposure-based methods of Behavior Therapy. Exposure-based methods of behavioral therapy are well suited to the treatment of phobias, which include intense and unreasonable fears (e.g., of spiders, blood, ...
Behaviorism
... 1. Punishment suppresses rather than eliminates behaviors. The behavior may reappear when punishment is absent. 2. Punishment can lead to an increase in punished behavior. “Punishment” can be reinforcing. Some kids crave attention so badly that they misbehave to get any kind of attention – even puni ...
... 1. Punishment suppresses rather than eliminates behaviors. The behavior may reappear when punishment is absent. 2. Punishment can lead to an increase in punished behavior. “Punishment” can be reinforcing. Some kids crave attention so badly that they misbehave to get any kind of attention – even puni ...
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
... Chapter Check-up: Reinforcement Theory When professors give random pop quizzes or take random attendance, students often complain that they are adults, old enough to make their own decisions, and should therefore not be required to come to class. How do you reconcile this argument with what we know ...
... Chapter Check-up: Reinforcement Theory When professors give random pop quizzes or take random attendance, students often complain that they are adults, old enough to make their own decisions, and should therefore not be required to come to class. How do you reconcile this argument with what we know ...
Biological Influences on Learning
... large, familiar and unfamiliar objects (e.g., the mother) with low levels of arousal. Fear system develops, unfamiliar objects elicit high ...
... large, familiar and unfamiliar objects (e.g., the mother) with low levels of arousal. Fear system develops, unfamiliar objects elicit high ...
Name - Mr. Kern
... 1. Form of classical conditioning in which a food comes to be avoided. ______________ 2. Act of responding in the same way to stimuli that seem similar. __________________ 3. Method that involves relaxation and gradual exposure to a feared stimulus. _____________________ 4. Method that involves rela ...
... 1. Form of classical conditioning in which a food comes to be avoided. ______________ 2. Act of responding in the same way to stimuli that seem similar. __________________ 3. Method that involves relaxation and gradual exposure to a feared stimulus. _____________________ 4. Method that involves rela ...
Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since
... • Combined formal logic with radical empiricism. ...
... • Combined formal logic with radical empiricism. ...
Behaviorism - Simply Psychology
... Humanism (e.g. Rogers) rejects the scientific method of using experiments to measure and control variables because it creates an artificial environment and has low ecological validity. Humanism also rejects the nomothetic approach of behaviorism as they view humans as being unique and believe humans ...
... Humanism (e.g. Rogers) rejects the scientific method of using experiments to measure and control variables because it creates an artificial environment and has low ecological validity. Humanism also rejects the nomothetic approach of behaviorism as they view humans as being unique and believe humans ...
Chapter 15 Learning Behaviorism Historical Perspective
... 1. An increase in drive strength will increase the tendency to approach or avoid a goal 2. Whenever there are 2 competing responses, the stronger one (one w/ greater drive strength behind it) will sin out 3. The tendency to approach a positive goal increases the closer one is to the goal 4. The tend ...
... 1. An increase in drive strength will increase the tendency to approach or avoid a goal 2. Whenever there are 2 competing responses, the stronger one (one w/ greater drive strength behind it) will sin out 3. The tendency to approach a positive goal increases the closer one is to the goal 4. The tend ...
Learning/Behaviorism
... • Modeling/observation of prosocial behaviors increases the occurrence of those behaviors – Children who observe regular prosocial behaviors engage in those behaviors and exhibit prosocial attitudes – Adult behavior can also be influenced by prosocial behaviors ...
... • Modeling/observation of prosocial behaviors increases the occurrence of those behaviors – Children who observe regular prosocial behaviors engage in those behaviors and exhibit prosocial attitudes – Adult behavior can also be influenced by prosocial behaviors ...
Operant Conditioning - Gordon State College
... Defined performance goals and immediate reinforcement at work Parenting – reward good behavior, ignore whining, time-out ...
... Defined performance goals and immediate reinforcement at work Parenting – reward good behavior, ignore whining, time-out ...
observational learning
... Defined performance goals and immediate reinforcement at work Parenting – reward good behavior, ignore whining, time-out ...
... Defined performance goals and immediate reinforcement at work Parenting – reward good behavior, ignore whining, time-out ...
Contents Learning through Association
... In both classical conditioning and operant conditioning, experience plays a direct role in learning, either through association, reinforcement, or punishment. Yet another type of learning is learning through observation and imitation, called observational learning. While experience is certainly a gr ...
... In both classical conditioning and operant conditioning, experience plays a direct role in learning, either through association, reinforcement, or punishment. Yet another type of learning is learning through observation and imitation, called observational learning. While experience is certainly a gr ...
Behavior Analysis and Strategy Application after Brain Injury
... employee, as a result the employee begins to come to work late less often. ...
... employee, as a result the employee begins to come to work late less often. ...
Psychology as a Science
... • A perspective that focuses on the study of conscious experience, the individual’s freedom to choose, and the capacity for personal growth • Stressed the study of conscious experience and an individual’s free will • Healthy individuals should strive to reach their full potential. • Rejected idea th ...
... • A perspective that focuses on the study of conscious experience, the individual’s freedom to choose, and the capacity for personal growth • Stressed the study of conscious experience and an individual’s free will • Healthy individuals should strive to reach their full potential. • Rejected idea th ...
13 May 2003: Introduction to Animal Behavior • Why study Animal
... • emphasized behavioral plasticity: learning most animals can learn many things – Originated among philosophers and psychologists in the United States. – even complex behavior is forged from simple stimulus-response interactions ...
... • emphasized behavioral plasticity: learning most animals can learn many things – Originated among philosophers and psychologists in the United States. – even complex behavior is forged from simple stimulus-response interactions ...
Learning: Operant Conditioning
... the Skinner Box, the rat will learn to press the bar to get food. This is a type of reinforcement. Reinforcement – a consequence that occurs after a behavior and increases the chance that the behavior will occur again. Examples of consequences that people respond to are social approval, money, a ...
... the Skinner Box, the rat will learn to press the bar to get food. This is a type of reinforcement. Reinforcement – a consequence that occurs after a behavior and increases the chance that the behavior will occur again. Examples of consequences that people respond to are social approval, money, a ...
Operant Conditioning
... an organism associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, the organism associates its behaviors with consequences. Behaviors followed by reinforcements increase; those followed by punishers decrease. This simple but powerful principle has many applications and ...
... an organism associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, the organism associates its behaviors with consequences. Behaviors followed by reinforcements increase; those followed by punishers decrease. This simple but powerful principle has many applications and ...
chapter_review_sheet-teacher-website-ch8
... variable- varies or changes/ Fixed-ratio - paid after every 10 lawns cut / Variable-ratio slot machines- unpredictable number of pulls of lever / Fixed-interval - quiz every Friday / Variable interval- pop-quiz- never know when (Variable schedules are the best type of partial reinforcement schedules ...
... variable- varies or changes/ Fixed-ratio - paid after every 10 lawns cut / Variable-ratio slot machines- unpredictable number of pulls of lever / Fixed-interval - quiz every Friday / Variable interval- pop-quiz- never know when (Variable schedules are the best type of partial reinforcement schedules ...
Persuasion - Freeman Public Schools
... likely to result to a heuristic processing, a very low or casual form of analyzing evidence – If they are interested in the issue- use systematic processing or the central processing route ...
... likely to result to a heuristic processing, a very low or casual form of analyzing evidence – If they are interested in the issue- use systematic processing or the central processing route ...
Chap1
... Conditioning -- a stimulus that initially produces no response can acquire the ability to produce one. Learning occurs through pairing in time and place of one stimulus with another stimulus that produces a response. This is a kind of associative shifting, but the response is involuntary. ...
... Conditioning -- a stimulus that initially produces no response can acquire the ability to produce one. Learning occurs through pairing in time and place of one stimulus with another stimulus that produces a response. This is a kind of associative shifting, but the response is involuntary. ...
PSY 402
... Conditioning -- a stimulus that initially produces no response can acquire the ability to produce one. Learning occurs through pairing in time and place of one stimulus with another stimulus that produces a response. This is a kind of associative shifting, but the response is involuntary. ...
... Conditioning -- a stimulus that initially produces no response can acquire the ability to produce one. Learning occurs through pairing in time and place of one stimulus with another stimulus that produces a response. This is a kind of associative shifting, but the response is involuntary. ...