Classical Conditioning Documentary
... What important people or objects are in the ad? What outcomes are suggested for those who use or do not use the product? What do these points tell us about how advertisers attempt to condition the behavior of consumers? Connect Psychology Activity: Shaping In this video clip a dog trainer expl ...
... What important people or objects are in the ad? What outcomes are suggested for those who use or do not use the product? What do these points tell us about how advertisers attempt to condition the behavior of consumers? Connect Psychology Activity: Shaping In this video clip a dog trainer expl ...
Learned behavior
... produces a reward becomes more likely over time and any response that does not produce a reward becomes less likely over time. Skinner called this process operant conditioning, rather than instrumental conditioning. In operant conditioning the organism is free to respond at any time, and conditionin ...
... produces a reward becomes more likely over time and any response that does not produce a reward becomes less likely over time. Skinner called this process operant conditioning, rather than instrumental conditioning. In operant conditioning the organism is free to respond at any time, and conditionin ...
Learning - SchoolRack
... think about either the movie it was from or the person you were with when you saw the movie? If so, you experienced classical conditioning. The music has become a signal that triggers memories and emotions. ...
... think about either the movie it was from or the person you were with when you saw the movie? If so, you experienced classical conditioning. The music has become a signal that triggers memories and emotions. ...
Learning Review
... 15. Based on what researchers have found about the effect of modeling on behavior, • A) we can decrease violence in our society if we decrease the amount of violence on TV. • B) we can increase pro-social behavior if we increase the amount of it on TV. • C) all of the above. • D) none of the above; ...
... 15. Based on what researchers have found about the effect of modeling on behavior, • A) we can decrease violence in our society if we decrease the amount of violence on TV. • B) we can increase pro-social behavior if we increase the amount of it on TV. • C) all of the above. • D) none of the above; ...
Second-order conditioning
... when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to the situation weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be less likely to occur. ...
... when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to the situation weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be less likely to occur. ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 15. Based on what researchers have found about the effect of modeling on behavior, • A) we can decrease violence in our society if we decrease the amount of violence on TV. • B) we can increase pro-social behavior if we increase the amount of it on TV. • C) all of the above. • D) none of the above; ...
... 15. Based on what researchers have found about the effect of modeling on behavior, • A) we can decrease violence in our society if we decrease the amount of violence on TV. • B) we can increase pro-social behavior if we increase the amount of it on TV. • C) all of the above. • D) none of the above; ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 15. Based on what researchers have found about the effect of modeling on behavior, • A) we can decrease violence in our society if we decrease the amount of violence on TV. • B) we can increase pro-social behavior if we increase the amount of it on TV. • C) all of the above. • D) none of the above; ...
... 15. Based on what researchers have found about the effect of modeling on behavior, • A) we can decrease violence in our society if we decrease the amount of violence on TV. • B) we can increase pro-social behavior if we increase the amount of it on TV. • C) all of the above. • D) none of the above; ...
March 3 and 5
... Two types of Reinforcers Reward Punishment “Law of Effect” Rewarded behavior is more likely to recur Punished behavior is less likely to recur Behavior ...
... Two types of Reinforcers Reward Punishment “Law of Effect” Rewarded behavior is more likely to recur Punished behavior is less likely to recur Behavior ...
Redalyc. Pavlov and the Foundation of Behavior Therapy
... therapy alternatives to the psychoanalysis and related therapies were introduced almost fifty years ago (Wolpe, 1958), continued advancements in behavior therapy have largely been fueled by its foundation on conditioning principles and theories (Eifert & Plaud, 1998; Wolpe, 1990). In particular, beh ...
... therapy alternatives to the psychoanalysis and related therapies were introduced almost fifty years ago (Wolpe, 1958), continued advancements in behavior therapy have largely been fueled by its foundation on conditioning principles and theories (Eifert & Plaud, 1998; Wolpe, 1990). In particular, beh ...
Ciccarelli Chapter 5
... Conditioned taste aversions – refers to aversions to particular tastes acquired through classical conditioning; e.g., Researchers found that rats that were given a sweetened liquid and then injected with a drug or exposed to radiation that caused __________________ would not touch the liquid again ...
... Conditioned taste aversions – refers to aversions to particular tastes acquired through classical conditioning; e.g., Researchers found that rats that were given a sweetened liquid and then injected with a drug or exposed to radiation that caused __________________ would not touch the liquid again ...
Learning
... • Reinforcement - any event or stimulus, that when following a response, increases the probability that the response will occur again. – Primary reinforcer - any reinforcer that is naturally reinforcing by meeting a basic biological need, such as hunger, thirst, or touch. – Secondary reinforcer - an ...
... • Reinforcement - any event or stimulus, that when following a response, increases the probability that the response will occur again. – Primary reinforcer - any reinforcer that is naturally reinforcing by meeting a basic biological need, such as hunger, thirst, or touch. – Secondary reinforcer - an ...
File
... past history of rewards and punishments. he is famous for use of his operant conditioning aparatus which he used to study schedules of reinforcement on pidgeons and rats. ...
... past history of rewards and punishments. he is famous for use of his operant conditioning aparatus which he used to study schedules of reinforcement on pidgeons and rats. ...
7 CHAPTER Learning Chapter Preview Learning helps us adapt to
... associate stimuli and thus anticipate events. This laid the foundation for John B. Watson’s behaviorism, which held that psychology should be an objective science that studied only observable behavior. Pavlov would repeatedly present a neutral stimulus (NS, such as a tone) just before an uncondition ...
... associate stimuli and thus anticipate events. This laid the foundation for John B. Watson’s behaviorism, which held that psychology should be an objective science that studied only observable behavior. Pavlov would repeatedly present a neutral stimulus (NS, such as a tone) just before an uncondition ...
PsychScich06
... – Response occurs even if the illness was caused by a virus or some other condition – Especially likely to occur if the food was not part of the person’s usual diet. A food aversion can be formed in one trial ...
... – Response occurs even if the illness was caused by a virus or some other condition – Especially likely to occur if the food was not part of the person’s usual diet. A food aversion can be formed in one trial ...
Read - Work
... monkey-do, learning), appeared to show flaws in the Iaw of effect and to require mental representations in their explanation. But in 1938 Burrhus Friederich Skinner powerfully defended and advanced behaviorism when he published The Behavior of Organisms,which was arguably the most influential work o ...
... monkey-do, learning), appeared to show flaws in the Iaw of effect and to require mental representations in their explanation. But in 1938 Burrhus Friederich Skinner powerfully defended and advanced behaviorism when he published The Behavior of Organisms,which was arguably the most influential work o ...
Learning file RG 2
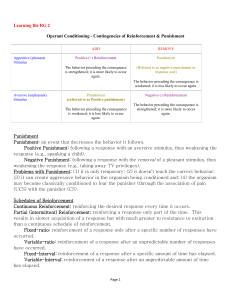
... Punishment: an event that decreases the behavior it follows. Positive Punishment: following a response with an aversive stimulus, thus weakening the response (e.g., spanking a child). Negative Punishment: following a response with the removal of a pleasant stimulus, thus weakening the response (e.g. ...
... Punishment: an event that decreases the behavior it follows. Positive Punishment: following a response with an aversive stimulus, thus weakening the response (e.g., spanking a child). Negative Punishment: following a response with the removal of a pleasant stimulus, thus weakening the response (e.g. ...
Unit 6 Learning
... so after 10 minutes my first set of cookies is done. After another ten minutes, my second set of cookies is done. I get to eat a cookie after each set is done baking. After every 10 math problems that I complete, I allow myself a 5 minute break. I look over my notes every night because I never know ...
... so after 10 minutes my first set of cookies is done. After another ten minutes, my second set of cookies is done. I get to eat a cookie after each set is done baking. After every 10 math problems that I complete, I allow myself a 5 minute break. I look over my notes every night because I never know ...
conditioned reinforcer
... • Based on the conclusion that animals can perceive the contingency between their behavior and the reinforcer. • When the outcomes are independent of the subject’s behavior – the subject develops a state of learned helplessness which is manifest in 2 ways • 1. there is a motivational loss indicated ...
... • Based on the conclusion that animals can perceive the contingency between their behavior and the reinforcer. • When the outcomes are independent of the subject’s behavior – the subject develops a state of learned helplessness which is manifest in 2 ways • 1. there is a motivational loss indicated ...
The History of Behaviorism designed by: Dylan Osborne
... In 1948, B.F. Skinner published Walden Two in which he described a utopian society founded upon behaviorist principles. The population of Walden Two is about one thousand people, all of whom seem to be healthy and happy. They live in communal dwellings, eat in common dining spaces, raise their chil ...
... In 1948, B.F. Skinner published Walden Two in which he described a utopian society founded upon behaviorist principles. The population of Walden Two is about one thousand people, all of whom seem to be healthy and happy. They live in communal dwellings, eat in common dining spaces, raise their chil ...
PSY304 Test 2 Review Reinforcement
... Some additional reinforcement terms Primary reinforcer: A reinforcer that acts without previous experience with it (e.g., food for a hungry organism). Conditioned/secondary reinforcer: A reinforcer that acts due to previous learning or experience (e.g., money). Generalized reinforcer: a reinforcer ...
... Some additional reinforcement terms Primary reinforcer: A reinforcer that acts without previous experience with it (e.g., food for a hungry organism). Conditioned/secondary reinforcer: A reinforcer that acts due to previous learning or experience (e.g., money). Generalized reinforcer: a reinforcer ...
Causes of unity and disunity in Psychology and Behaviorism
... disunity of psychology (e.g. Staats, 1981, 1983). What characteristics of PB would make a better approach account for unification of psychology than those of RB? -A very basic thing about psychology, and about behaviorism as part of psychology is that you won’t understand some of the actions of beha ...
... disunity of psychology (e.g. Staats, 1981, 1983). What characteristics of PB would make a better approach account for unification of psychology than those of RB? -A very basic thing about psychology, and about behaviorism as part of psychology is that you won’t understand some of the actions of beha ...
Basic Concepts and Principles of Behavior Analysis (PSY 5231-01)
... State the underlying assumptions of applied behavior analysis. Name and describe the basic tenets of radical behaviorism. Define, identify, and give examples of mentalisms and other explanatory fictions. Compare and contrast radical behaviorism with methodological behaviorism and other behavioral ph ...
... State the underlying assumptions of applied behavior analysis. Name and describe the basic tenets of radical behaviorism. Define, identify, and give examples of mentalisms and other explanatory fictions. Compare and contrast radical behaviorism with methodological behaviorism and other behavioral ph ...
Psychology: Pavlov, Watson, Skinner
... Albert Bandura argued that individuals, especially children learn aggressive responses from observing others, either personally or through the media and environment. ...
... Albert Bandura argued that individuals, especially children learn aggressive responses from observing others, either personally or through the media and environment. ...