Albert Bandura Paper
... person. Bandura believes that children imitate models or, “individuals that are observed,” (McLeod). There are many models for children while they’re growing up. Children are influenced by their parents, peers, teachers, and characters on television. These models influence a child’s behavior that th ...
... person. Bandura believes that children imitate models or, “individuals that are observed,” (McLeod). There are many models for children while they’re growing up. Children are influenced by their parents, peers, teachers, and characters on television. These models influence a child’s behavior that th ...
Cognitive-Behavioral Approaches
... • Identify a 6 month goal; write it according to guidelines. • Counselor, facilitate a discussion of strategies your partner can use to achieve their goal. • Switch roles. ...
... • Identify a 6 month goal; write it according to guidelines. • Counselor, facilitate a discussion of strategies your partner can use to achieve their goal. • Switch roles. ...
chapter 17
... Behavior occurs as the result of a complex interplay between inner processes (cognitions, motivations, personality factors) and ...
... Behavior occurs as the result of a complex interplay between inner processes (cognitions, motivations, personality factors) and ...
057 Learning by Observation
... Answer the following questions in YOUR OWN WORDS. You only have to do TWO of the questions marked with asterisks *** ...
... Answer the following questions in YOUR OWN WORDS. You only have to do TWO of the questions marked with asterisks *** ...
Noorudean tohmeh
... O Punishments should be swift O Punishments should be certain O Punishments shouldn’t give mixed ...
... O Punishments should be swift O Punishments should be certain O Punishments shouldn’t give mixed ...
TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION
... particular goals & expectations, will modulate the way a particular reinforcer/ punisher will affect his/her behavior. For example, a person who feels that making money is not an important goal will not work for it, despite the fact that it is associated with many primary reinforcers. A single ...
... particular goals & expectations, will modulate the way a particular reinforcer/ punisher will affect his/her behavior. For example, a person who feels that making money is not an important goal will not work for it, despite the fact that it is associated with many primary reinforcers. A single ...
Behavioral - Northside College Prep
... Cherry, Kendra. (No Date) What Is Behaviorism? psychology.about.com. Retrieved March 15th, 2010 from http://psychology.about.com/od/behavioralpsychology/f/behaviorism.htm Ormrod, J.E. (1999). Human learning. www.teachnet.edb.utexas.edu. Retrieved March 17th from http://teachnet.edb.utexas.edu/~lynda ...
... Cherry, Kendra. (No Date) What Is Behaviorism? psychology.about.com. Retrieved March 15th, 2010 from http://psychology.about.com/od/behavioralpsychology/f/behaviorism.htm Ormrod, J.E. (1999). Human learning. www.teachnet.edb.utexas.edu. Retrieved March 17th from http://teachnet.edb.utexas.edu/~lynda ...
Modeling - worldowiki
... implies that teachers get students to do something without the students realizing it, the way television ads try to manipulate us into buying what we don’t need, and that’s not what is going on here. This process is actually teaching metacognition— thinking about how to achieve goals and using strat ...
... implies that teachers get students to do something without the students realizing it, the way television ads try to manipulate us into buying what we don’t need, and that’s not what is going on here. This process is actually teaching metacognition— thinking about how to achieve goals and using strat ...
BF Skinner: Behaviorist He believe behavior is a result of
... Focus: How much our genes and environment influence our individual differences. Sample Questions: Does nature (genetics) or nurture (environment) play a more prominent role in our development? ...
... Focus: How much our genes and environment influence our individual differences. Sample Questions: Does nature (genetics) or nurture (environment) play a more prominent role in our development? ...
Journal Entry - Evolutionary Psychology
... Consider each of these theories presented by the “Why Sex?” PBS documentary. For each theory, state whether or not you believe it is a valid explanation for one aspect of human personality and socialization. Explain why you believe this way. Do you think these behaviors are more influenced by our fa ...
... Consider each of these theories presented by the “Why Sex?” PBS documentary. For each theory, state whether or not you believe it is a valid explanation for one aspect of human personality and socialization. Explain why you believe this way. Do you think these behaviors are more influenced by our fa ...
introduction to psychology and key people
... John B. Watson (1878-1958) Behaviorist- investigates observable behavior All behavior is the result of conditioning and occurs because the appropriate stimulus is present in the environment ...
... John B. Watson (1878-1958) Behaviorist- investigates observable behavior All behavior is the result of conditioning and occurs because the appropriate stimulus is present in the environment ...
General Psychology 1
... yet not be able to reproduce their jumps, because they can’t ice skate at all! On the other hand, if they could skate, their performance would in fact improve if they watch skaters who are better than they are ...
... yet not be able to reproduce their jumps, because they can’t ice skate at all! On the other hand, if they could skate, their performance would in fact improve if they watch skaters who are better than they are ...
It has been argued that because social cognitive theory places so
... The social-cognitive theory is a theoretical perspective in which learning by observing others is the focus of study. Social cognitive theory posits that an individual's behavior is primarily learned through his or her observation of others as well as through interaction with his or her environment ...
... The social-cognitive theory is a theoretical perspective in which learning by observing others is the focus of study. Social cognitive theory posits that an individual's behavior is primarily learned through his or her observation of others as well as through interaction with his or her environment ...
File - Farrell`s Class Page
... POSITIVE REINFORCER – Increases the frequency of the behavior when it is presented, (eg. rewarding good behavior with food or money). NEGATIVE REINFORCER – Increases the frequency of the behavior when adverse stimuli is removed, (eg. Rewarding good behavior by removing an unpleasant task like wa ...
... POSITIVE REINFORCER – Increases the frequency of the behavior when it is presented, (eg. rewarding good behavior with food or money). NEGATIVE REINFORCER – Increases the frequency of the behavior when adverse stimuli is removed, (eg. Rewarding good behavior by removing an unpleasant task like wa ...
2008 - KCSD Connect
... The Smith-Garcias are planning for their first baby. Both parents-to-be have had a psychology course and are looking forward to applying the principles they learned from theories and research that address child development. A. Summarize one main idea or finding of each of the following four research ...
... The Smith-Garcias are planning for their first baby. Both parents-to-be have had a psychology course and are looking forward to applying the principles they learned from theories and research that address child development. A. Summarize one main idea or finding of each of the following four research ...
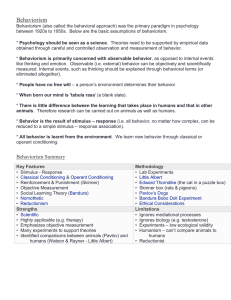
Behaviorism
... measured. Internal events, such as thinking should be explained through behavioral terms (or eliminated altogether). * People have no free will – a person’s environment determines their behavior * When born our mind is 'tabula rasa' (a blank slate). * There is little difference between the learning ...
... measured. Internal events, such as thinking should be explained through behavioral terms (or eliminated altogether). * People have no free will – a person’s environment determines their behavior * When born our mind is 'tabula rasa' (a blank slate). * There is little difference between the learning ...
Module 27 Notes Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning A type
... Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to the response (consequence) that behavior receives o Rewards and Punishments (Behavior that operates on the environment to ...
... Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to the response (consequence) that behavior receives o Rewards and Punishments (Behavior that operates on the environment to ...