AP Psychology Syllabus
... observational learning (e.g., contingencies). Describe basic classical conditioning phenomena, such as acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, discrimination, and higher-order learning. Predict the effects of operant conditioning (e.g., positive reinforcement, negative rei ...
... observational learning (e.g., contingencies). Describe basic classical conditioning phenomena, such as acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, discrimination, and higher-order learning. Predict the effects of operant conditioning (e.g., positive reinforcement, negative rei ...
AS-Learning-Checklis..
... The Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) – Is a stimulus that produces an unlearned response. In Pavlov's the UCS was meat powder. The Unconditioned Response (UCR) -- This is the response to the unconditioned stimulus that the experimenter measures. In Pavlov's the UCR was salivation. The Neutral Stimulus – ...
... The Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) – Is a stimulus that produces an unlearned response. In Pavlov's the UCS was meat powder. The Unconditioned Response (UCR) -- This is the response to the unconditioned stimulus that the experimenter measures. In Pavlov's the UCR was salivation. The Neutral Stimulus – ...
Info-QcABA
... diagnoses means strains on IBI waiting lists at the CRDITED. These factors have led the CRDITED de la Montérégie Est to introduce a broader range of services to meet the needs of the greatest number of children possible. The new structure involves 4 types of services which include parent training, s ...
... diagnoses means strains on IBI waiting lists at the CRDITED. These factors have led the CRDITED de la Montérégie Est to introduce a broader range of services to meet the needs of the greatest number of children possible. The new structure involves 4 types of services which include parent training, s ...
introductiontopsychology
... The dog sees the food and salivates. Then the dog sees the food at the same time as a bell is rung. It salivates. Then the dog hears the bell, associates it with the food, and salivates. The dog has been conditioned to salivate at the sound of the bell. ...
... The dog sees the food and salivates. Then the dog sees the food at the same time as a bell is rung. It salivates. Then the dog hears the bell, associates it with the food, and salivates. The dog has been conditioned to salivate at the sound of the bell. ...
animal behaviour - Careerline Courses
... The light is the conditioned stimulus (CS) and the salivation now a conditioned response (CR). If the conditioned behaviour is not reinforced (i.e. if the conditioned stimulus is presented repeatedly without the unconditioned stimulus) then the conditioned response slowly disappears. This is called ...
... The light is the conditioned stimulus (CS) and the salivation now a conditioned response (CR). If the conditioned behaviour is not reinforced (i.e. if the conditioned stimulus is presented repeatedly without the unconditioned stimulus) then the conditioned response slowly disappears. This is called ...
Overview of
... independent variable may effect behaviors other than the response class. Allows you to determine whether changes in behavior ...
... independent variable may effect behaviors other than the response class. Allows you to determine whether changes in behavior ...
Chapter 3
... Ways to Enhance Attention Another great example of surprise – certainly goes against expectations ...
... Ways to Enhance Attention Another great example of surprise – certainly goes against expectations ...
What is Social Psychology? - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... directly observe& measure, i.e. overt behavior. Behaviorist identified a series of principles to explain the specific process through which these learning occurs through experiments. Experiments were conducted on animals (rats, dogs, pigeons) believe the same principles applied to human. ...
... directly observe& measure, i.e. overt behavior. Behaviorist identified a series of principles to explain the specific process through which these learning occurs through experiments. Experiments were conducted on animals (rats, dogs, pigeons) believe the same principles applied to human. ...
a PowerPoint presentation of Module 52
... Sometimes, insight is not helpful to recover from some mental health problems. The client might know the right changes to make, but finds that it’s hard to change actual behavior. Behavior therapy uses the principles of learning, especially classical and operant conditioning, to help reduce unwa ...
... Sometimes, insight is not helpful to recover from some mental health problems. The client might know the right changes to make, but finds that it’s hard to change actual behavior. Behavior therapy uses the principles of learning, especially classical and operant conditioning, to help reduce unwa ...
CBCC-KA Examination Study Objectives
... Discuss the difficulty of differentiating between the potential genetic and environmental influences on the health and behavior of an adult canine Describe the influence of natural and artificial selection on the development and behavior of the canine species List three potential outcomes of g ...
... Discuss the difficulty of differentiating between the potential genetic and environmental influences on the health and behavior of an adult canine Describe the influence of natural and artificial selection on the development and behavior of the canine species List three potential outcomes of g ...
AP Psychology Syllabus - St. Mary Parish Schools
... Students research a topic of their choice, subject to IRB approval. The final project must incorporate a review of literature, discussion of method, presentation and evaluation of results, and a conclusion. Review of Literature Students research a topic of their choice. The final paper must develop ...
... Students research a topic of their choice, subject to IRB approval. The final project must incorporate a review of literature, discussion of method, presentation and evaluation of results, and a conclusion. Review of Literature Students research a topic of their choice. The final paper must develop ...
Introduction to Psych 2015 - Student Version
... • Ignored Introspection and psychoanalysis and all mental process ...
... • Ignored Introspection and psychoanalysis and all mental process ...
skinner s reinforcement theory - Cambridge Center for Behavioral
... set number of responses (e.g., piecework in a factory). With interval schedules, reinforcement is given after a set amount of time has passed (e.g., a weekly quiz). With variable-ratio schedules, reinforcement occurs after a given average number of responses, but exactly which response will produce ...
... set number of responses (e.g., piecework in a factory). With interval schedules, reinforcement is given after a set amount of time has passed (e.g., a weekly quiz). With variable-ratio schedules, reinforcement occurs after a given average number of responses, but exactly which response will produce ...
marin_C05 - Napa Valley College
... Reinforcement – consequences of a response that increase the probability it will ...
... Reinforcement – consequences of a response that increase the probability it will ...
Understanding Motivation
... view of how self can affect the understanding of how much a person’s actions can influence his or her success. Self is defined as the beliefs one holds about one’s abilities and relationships to others. Persons who have and internal locus of control tend to achieve more than those who operate from a ...
... view of how self can affect the understanding of how much a person’s actions can influence his or her success. Self is defined as the beliefs one holds about one’s abilities and relationships to others. Persons who have and internal locus of control tend to achieve more than those who operate from a ...
PERSONALITY THEORY AND ASSESSMENT
... stimuli that proceed the response and consequences following the behavior to discover the CAUSE-EFFECT RELATIONSHIP. By changing the reinforcers in the environment, Skinner believed he could change the behavior, a therapeutic process known as BEHAVIOR MODIFICATION. ...
... stimuli that proceed the response and consequences following the behavior to discover the CAUSE-EFFECT RELATIONSHIP. By changing the reinforcers in the environment, Skinner believed he could change the behavior, a therapeutic process known as BEHAVIOR MODIFICATION. ...
Single-Subject/Small-n Research and Designs
... • Traditional versus behavioral coaching • football skills • Traditional: verbal instructions, some modeling, and if not correct then yelling, berating, punishment • Behavioral: systematic verbal feedback, positive and negative reinforcement with verbal reinforcement ...
... • Traditional versus behavioral coaching • football skills • Traditional: verbal instructions, some modeling, and if not correct then yelling, berating, punishment • Behavioral: systematic verbal feedback, positive and negative reinforcement with verbal reinforcement ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... or object, he cried. In this regard, Watson appeared to have successfully paired a stimulus (furry animal or object) with a response (crying). In Watson’s day, the popular psychological perspective focused on internal urges. Through his experimental work, Watson was attempting to show that human beh ...
... or object, he cried. In this regard, Watson appeared to have successfully paired a stimulus (furry animal or object) with a response (crying). In Watson’s day, the popular psychological perspective focused on internal urges. Through his experimental work, Watson was attempting to show that human beh ...
Long-term memories
... Accuracy of matching-to-sample performance as a function of delay between the sample and choice stimuli for independent groups of pigeons that were previously trained with delays of 0, 2, 4, or 6 seconds. (Based on “Forgetting Functions,” by R. J. Sargisson & K. G. White, 2001, Animal Learning & ...
... Accuracy of matching-to-sample performance as a function of delay between the sample and choice stimuli for independent groups of pigeons that were previously trained with delays of 0, 2, 4, or 6 seconds. (Based on “Forgetting Functions,” by R. J. Sargisson & K. G. White, 2001, Animal Learning & ...
Positive reinforcement as an intervention for children with attention
... Reinforcing a behavior will increase the likelihood that the behavior will reoccur. Using a positive reinforcement intervention for increasing appropriate behaviors in children can result in decreasing inappropriate or problem behaviors. Children diagnosed with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disord ...
... Reinforcing a behavior will increase the likelihood that the behavior will reoccur. Using a positive reinforcement intervention for increasing appropriate behaviors in children can result in decreasing inappropriate or problem behaviors. Children diagnosed with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disord ...
Essentials of Contemporary Management 3e
... • Focuses on outcomes that lead to higher motivation and job satisfaction, and those outcomes that can prevent dissatisfaction. Motivator needs relate to the nature of the work itself—autonomy, responsibility, interesting work. Hygiene needs are related to the physical and psychological context of ...
... • Focuses on outcomes that lead to higher motivation and job satisfaction, and those outcomes that can prevent dissatisfaction. Motivator needs relate to the nature of the work itself—autonomy, responsibility, interesting work. Hygiene needs are related to the physical and psychological context of ...
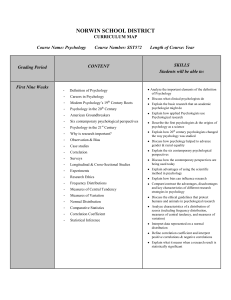
NORWIN SCHOOL DISTRICT
... Discuss how twin studies & adoption studies are used to learn about the influences of nature & nurture Describe the research findings related to the environmental influences of early brain development, parents, peers and our culture ...
... Discuss how twin studies & adoption studies are used to learn about the influences of nature & nurture Describe the research findings related to the environmental influences of early brain development, parents, peers and our culture ...
Public service motivation 1
... variable intervals or according to a variable ratio schedule (reinforcement after long varying periods or after varying numbers of occurrences), requires more time for behavior acquisition, but extinction occurs more slowly when the reinforcement seasons. ...
... variable intervals or according to a variable ratio schedule (reinforcement after long varying periods or after varying numbers of occurrences), requires more time for behavior acquisition, but extinction occurs more slowly when the reinforcement seasons. ...
Appetitive and aversive olfactory learning induce similar
... An animal in which a comparative analysis of appetitive and aversive learning is possible is the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Honey bees are well known for their impressive ...
... An animal in which a comparative analysis of appetitive and aversive learning is possible is the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Honey bees are well known for their impressive ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.