Extinction of the avoidance response and fear reduction through
... conditioning during extinction and its effect on residual fear compared to response prevention. Thirty-six rats, divided into three groups, were trained to avoid an electric shock in a one-way shuttle box. Extinction procedures were performed in one of the following three ways: 1) a Control Group ha ...
... conditioning during extinction and its effect on residual fear compared to response prevention. Thirty-six rats, divided into three groups, were trained to avoid an electric shock in a one-way shuttle box. Extinction procedures were performed in one of the following three ways: 1) a Control Group ha ...
Santos_bu_0017N_11140 - OpenBU
... stimulus and sensitization would show an increase in response through repeated exposure to a stimulus (Thompson & Spencer, 1966). Associative learning is produced by classical conditioning or operant conditioning. Classical conditioning is when a neutral stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stim ...
... stimulus and sensitization would show an increase in response through repeated exposure to a stimulus (Thompson & Spencer, 1966). Associative learning is produced by classical conditioning or operant conditioning. Classical conditioning is when a neutral stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stim ...
Historical Evolution of the Field of Conditioning and Learning
... lawful. Human voluntary behavior was thought to be caused by the mind, a transcendent thing which did not follow natural laws. It’s important to note that there have never been any observations which have supported this view. In all likelihood, Descartes had this view so that the then current Judeo- ...
... lawful. Human voluntary behavior was thought to be caused by the mind, a transcendent thing which did not follow natural laws. It’s important to note that there have never been any observations which have supported this view. In all likelihood, Descartes had this view so that the then current Judeo- ...
Organizational Behaviour
... Methods of shaping behavior Positive reinforcement- following a response ...
... Methods of shaping behavior Positive reinforcement- following a response ...
Latent inhibition as a function of US intensity in a two
... The experiment reported here examined the effect of US intensity on the magnitude of LI. Given that LI originates during the pre-exposure stage, it could be thought that the intensity of the US presented during conditioning should not affect the magnitude of this phenomenon. Nevertheless, LI reflect ...
... The experiment reported here examined the effect of US intensity on the magnitude of LI. Given that LI originates during the pre-exposure stage, it could be thought that the intensity of the US presented during conditioning should not affect the magnitude of this phenomenon. Nevertheless, LI reflect ...
Animal Behavior
... Communication behaviors are critical to the survival and reproductive success of animals. Animals have several types of communication behaviors. ...
... Communication behaviors are critical to the survival and reproductive success of animals. Animals have several types of communication behaviors. ...
Research
... Let’s get basic. Learning = acquiring knowledge, skills, attitudes and values. Learning happens all the time, formally and informally. Every child’s learning path combines study and personal experiences. And using their memories, kids recall and apply what they’ve learned. Associative learning and m ...
... Let’s get basic. Learning = acquiring knowledge, skills, attitudes and values. Learning happens all the time, formally and informally. Every child’s learning path combines study and personal experiences. And using their memories, kids recall and apply what they’ve learned. Associative learning and m ...
C ontribution of the anterior cingulate cortex to laser
... rats did not show significant nocifensive behavioral responses to the CS before it was paired with the US. Characteristic nocifensive behavior, such as licking, escaping etc., could be induced by the US. Subsequent to several CS and US pairings, rats began to respond to the CS within the first 0.5 s ...
... rats did not show significant nocifensive behavioral responses to the CS before it was paired with the US. Characteristic nocifensive behavior, such as licking, escaping etc., could be induced by the US. Subsequent to several CS and US pairings, rats began to respond to the CS within the first 0.5 s ...
File
... BEHAVIORISTS believe that personality is shaped by operant conditioning principles. When we receive positive reinforcement such as attention or praise for a behavior, we are likely to repeat that behavior. We will avoid negative situations becoming negatively reinforced for avoiding, reducing or ter ...
... BEHAVIORISTS believe that personality is shaped by operant conditioning principles. When we receive positive reinforcement such as attention or praise for a behavior, we are likely to repeat that behavior. We will avoid negative situations becoming negatively reinforced for avoiding, reducing or ter ...
Exercise #3 - Westmont homepage server
... Magazine training might well be called "arranging for a reinforcing stimulus for use in future conditioning." This step may also be thought of as an instance of a stimulus (the click of the dipper mechanism) acquiring discriminative control of behavior (running to the dipper cup and drinking). Stimu ...
... Magazine training might well be called "arranging for a reinforcing stimulus for use in future conditioning." This step may also be thought of as an instance of a stimulus (the click of the dipper mechanism) acquiring discriminative control of behavior (running to the dipper cup and drinking). Stimu ...
II - NIOS
... behaviours by punishing them and reward for good behaviours. The role of reinforcement is very crucial in operant conditioning. It can be positive or negative. Let us understand these two types of reinforcement. Positive Reinforcement : Reinforcement is any operation or action that increases the rat ...
... behaviours by punishing them and reward for good behaviours. The role of reinforcement is very crucial in operant conditioning. It can be positive or negative. Let us understand these two types of reinforcement. Positive Reinforcement : Reinforcement is any operation or action that increases the rat ...
personality development
... …is a tactic developed by the ego to protect against anxiety. Defense mechanisms are thought to safeguard the mind against feelings and thoughts that are too difficult for the conscious mind to cope with. (The arousal of anxiety is a crucial event in Freud’s theory of personality functioning. Anxiet ...
... …is a tactic developed by the ego to protect against anxiety. Defense mechanisms are thought to safeguard the mind against feelings and thoughts that are too difficult for the conscious mind to cope with. (The arousal of anxiety is a crucial event in Freud’s theory of personality functioning. Anxiet ...
WHY STUDY MOTIVATION
... motivation, and the social aspects of human behavior. This is why it is so important to study motivation as it applies to the work environment. WHAT IS MOTIVATION? In psychology, motivation refers to the initiation, direction, intensity and persistence of behavior (Geen, 1995). Motivation is a tempo ...
... motivation, and the social aspects of human behavior. This is why it is so important to study motivation as it applies to the work environment. WHAT IS MOTIVATION? In psychology, motivation refers to the initiation, direction, intensity and persistence of behavior (Geen, 1995). Motivation is a tempo ...
. Reciprocal Heuristics: A Discussion of the Relationship of the Study
... current opportunities for the study of animal learning provided by recent developments in behavioral ecology and field ethology. In the final section res~arch on social learning in animals is used to illustrate some difficultie~ which. may be encountered both in extrapolating laboratory findings to ...
... current opportunities for the study of animal learning provided by recent developments in behavioral ecology and field ethology. In the final section res~arch on social learning in animals is used to illustrate some difficultie~ which. may be encountered both in extrapolating laboratory findings to ...
Interactive Training for Synthetic Characters
... strategy for being rewarded. Typically, the context is a gesture or an utterance. In a sense, since the dog already “knows” the behavior, it can focus on learning the context in which the behavior is maximally reliable. Backward chaining is typically used to teach sequences of actions. There are two ...
... strategy for being rewarded. Typically, the context is a gesture or an utterance. In a sense, since the dog already “knows” the behavior, it can focus on learning the context in which the behavior is maximally reliable. Backward chaining is typically used to teach sequences of actions. There are two ...
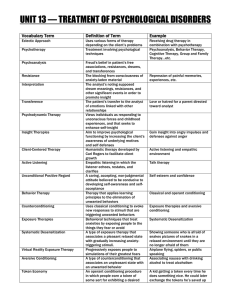
unit 13 — treatment of psychological disorders
... Therapy that applies learning principles to the elimination of unwanted behaviors Uses classical conditioning to evoke new responses to stimuli that are triggering unwanted behaviors Behavioral techniques that treat anxieties by exposing people to the things they fear or avoid A type of exposure the ...
... Therapy that applies learning principles to the elimination of unwanted behaviors Uses classical conditioning to evoke new responses to stimuli that are triggering unwanted behaviors Behavioral techniques that treat anxieties by exposing people to the things they fear or avoid A type of exposure the ...
Macro Organizational Behavior 2384
... Learners can perform at a level beyond what they would be capable of on their own Expert acts as a ‘bridge’ so learner can act as if they know how to complete the given ...
... Learners can perform at a level beyond what they would be capable of on their own Expert acts as a ‘bridge’ so learner can act as if they know how to complete the given ...
FREE Sample Here
... 6. Spence attempted to explain how reward influences the strength of behavior leading to reward. He assumed that experiences with reward produce: a. conditioning of an internal state that reinforces the behavior leading to reward. b. conditioning of an anticipatory goal response that produces intern ...
... 6. Spence attempted to explain how reward influences the strength of behavior leading to reward. He assumed that experiences with reward produce: a. conditioning of an internal state that reinforces the behavior leading to reward. b. conditioning of an anticipatory goal response that produces intern ...
An Interdisciplinary Behavior-Analytic Alternative to Cognitivist
... produce consequences, and to function with minute discriminative detail in complex, novel environmental contexts presupposes sensitivity to the consequences one produces. There is simply no other fathomable way a living thing could, save supernatural explanations or a prerequisite library of pre-mad ...
... produce consequences, and to function with minute discriminative detail in complex, novel environmental contexts presupposes sensitivity to the consequences one produces. There is simply no other fathomable way a living thing could, save supernatural explanations or a prerequisite library of pre-mad ...
Consumer Behavior
... If done enough times, the neutral object or situation becomes a mental signal for the pleasant or attractive one. It signals that the naturally pleasant or attractive object or situation is about to appear on the scene ...
... If done enough times, the neutral object or situation becomes a mental signal for the pleasant or attractive one. It signals that the naturally pleasant or attractive object or situation is about to appear on the scene ...
The Role of Dopamine in Locomotor ... 173
... The mesolimbic-mesocortical DA neurons also have been implicated in locomotor activity but their role remains equivoca1. Thus, it has been reported that bilateral 6-ONDA lesions of the origin of these neurons, the ventral tegmental area (VTA) results in no change in locomotion, decreased locomotion ...
... The mesolimbic-mesocortical DA neurons also have been implicated in locomotor activity but their role remains equivoca1. Thus, it has been reported that bilateral 6-ONDA lesions of the origin of these neurons, the ventral tegmental area (VTA) results in no change in locomotion, decreased locomotion ...
consumer learning
... More elaboration and associations during positive mood if the association is pleasurable Happy people may seek to avoid thinking to avoid spoiling the good mood Individuals will tend to be more critical of claims under bad mood ...
... More elaboration and associations during positive mood if the association is pleasurable Happy people may seek to avoid thinking to avoid spoiling the good mood Individuals will tend to be more critical of claims under bad mood ...
Psychology - Everglades High School
... them up in and I’ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief, and yes, even beggar-man and thief…” • Behaviorist school of thought emphasized the environment (nurture) • Focus on stimulus-response relat ...
... them up in and I’ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief, and yes, even beggar-man and thief…” • Behaviorist school of thought emphasized the environment (nurture) • Focus on stimulus-response relat ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.