Operant conditioning
... The Premack Principle, often called "grandma's rule," states that a high frequency activity can be used to reinforce low frequency behavior. Access to the preferred activity is contingent on completing the lowfrequency behavior. The high frequency behavior to use as a reinforcer can be determined by ...
... The Premack Principle, often called "grandma's rule," states that a high frequency activity can be used to reinforce low frequency behavior. Access to the preferred activity is contingent on completing the lowfrequency behavior. The high frequency behavior to use as a reinforcer can be determined by ...
psycholanalytic theory
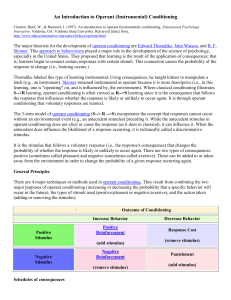
... • Punishment is an unpleasant stimulus that suppresses behavior. • Punishment is often used because it can quickly suppress behavior. However, psychologists suggest utilizing reinforcement due to the inherent weaknesses of punishment. ...
... • Punishment is an unpleasant stimulus that suppresses behavior. • Punishment is often used because it can quickly suppress behavior. However, psychologists suggest utilizing reinforcement due to the inherent weaknesses of punishment. ...
AP PSYCHOLOGY-Period 4 CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
... Extinction- the process of unlearning a behavior (when CS no longer causes the CR) Generalization- the tendency to respond to a similar CS (dogs respond to all types of bells, not just the one they were trained/conditioned with) Discrimination- when the subject is trained to tell the difference betw ...
... Extinction- the process of unlearning a behavior (when CS no longer causes the CR) Generalization- the tendency to respond to a similar CS (dogs respond to all types of bells, not just the one they were trained/conditioned with) Discrimination- when the subject is trained to tell the difference betw ...
Behavioralism-2
... BR: Classical or Operant? If classical explain UCS, UCR,CS, and CR A very bright (mildly painful) light is turned on a rat. The rat has learned that he can turn off the light by pressing a lever on the other side of his cage. As soon as the light comes on, the rat runs across the room and presses t ...
... BR: Classical or Operant? If classical explain UCS, UCR,CS, and CR A very bright (mildly painful) light is turned on a rat. The rat has learned that he can turn off the light by pressing a lever on the other side of his cage. As soon as the light comes on, the rat runs across the room and presses t ...
PSY304 Test 2 Review Reinforcement
... varies according to a mathematical distribution. Differential Reinforcement of Other Behavior (DRO): A reinforcer is delivered after a specified interval without a specific “target” response. • DRO is used to eliminate a response without punishment. Differential Reinforcement of Low Rates (DRL): A r ...
... varies according to a mathematical distribution. Differential Reinforcement of Other Behavior (DRO): A reinforcer is delivered after a specified interval without a specific “target” response. • DRO is used to eliminate a response without punishment. Differential Reinforcement of Low Rates (DRL): A r ...
Random - Wando High School
... a conditioned stimulus and other irrelevant stimuli. What is Discrimination? Back to Board ...
... a conditioned stimulus and other irrelevant stimuli. What is Discrimination? Back to Board ...
Skinner - IB Psychology.com
... Happiness and behavior "The experimental analysis of behavior has clearly shown that it is not the quantity of goods that count (as the laws of supply and demand suggest) but the contingent relation between goods and behavior. That is why, to the amazement of the American tourist, there are peopl ...
... Happiness and behavior "The experimental analysis of behavior has clearly shown that it is not the quantity of goods that count (as the laws of supply and demand suggest) but the contingent relation between goods and behavior. That is why, to the amazement of the American tourist, there are peopl ...
Andrea Enders ppt eme2040
... measure students against a OR certain criteria •Multi-media can be used to •Operant Conditioning; present content during (Skinner) – control over instruction responses (behavior to •Educational software used receive reward or avoid to develop prerequisite skills punishment) ...
... measure students against a OR certain criteria •Multi-media can be used to •Operant Conditioning; present content during (Skinner) – control over instruction responses (behavior to •Educational software used receive reward or avoid to develop prerequisite skills punishment) ...
Classical Conditioning
... When they were going together, a guy and his former girlfriend had a favorite CD which they frequently listened to together. Although she broke up with him over a year ago, whenever he hears a song from that CD he becomes depressed. ...
... When they were going together, a guy and his former girlfriend had a favorite CD which they frequently listened to together. Although she broke up with him over a year ago, whenever he hears a song from that CD he becomes depressed. ...
Document
... are less than successful. Why? They may underestimate some of the principles and delay a reward too long or accidentally reinforce unwanted behavior every so often (intermittently)…both reinforcement and punishment are VERY easy to apply incorrectly…. ...
... are less than successful. Why? They may underestimate some of the principles and delay a reward too long or accidentally reinforce unwanted behavior every so often (intermittently)…both reinforcement and punishment are VERY easy to apply incorrectly…. ...
Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning Chapter 7
... used as the UCS because it produced a salivation reflex. ...
... used as the UCS because it produced a salivation reflex. ...
Learning
... Variable interval. The amount of time that must elapse between reinforcement will vary or change. This schedule is the most resistant to extinction. - Examples: blue light sales at Kmart, the green light at KrispyKreme doughnuts, fishing. Can you think of some more examples? ...
... Variable interval. The amount of time that must elapse between reinforcement will vary or change. This schedule is the most resistant to extinction. - Examples: blue light sales at Kmart, the green light at KrispyKreme doughnuts, fishing. Can you think of some more examples? ...
Learning Today What is Learning? Learning The Biological Basis
... “satisfying state” (e.g., rewarded) will be strengthened, those that are followed by no reward or punishment are weakened. ...
... “satisfying state” (e.g., rewarded) will be strengthened, those that are followed by no reward or punishment are weakened. ...
Fall 2015 10-6 Chapter 7 Pt 1
... The initial stage of learning when a neutral stimulus is linked to an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. ...
... The initial stage of learning when a neutral stimulus is linked to an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. ...
Chapter 1 Consumers Rule
... generally easier to retrieve from memory. • Descriptive brand names easier to recall than names that do no provide cues to what the product is. – Viewing environment: Commercials shown first in a series of ads are recalled better than those shown last. ...
... generally easier to retrieve from memory. • Descriptive brand names easier to recall than names that do no provide cues to what the product is. – Viewing environment: Commercials shown first in a series of ads are recalled better than those shown last. ...
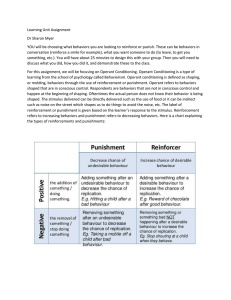
Learning Unit Assignment Dr Sharon Myer YOU will be choosing
... YOU will be choosing what behaviors you are looking to reinforce or punish. These can be behaviors in conversation (reinforce a smile for example), what you want someone to do (to leave, to get you something, etc.). You will have about 25 minutes to design this with your group. Then you will need to ...
... YOU will be choosing what behaviors you are looking to reinforce or punish. These can be behaviors in conversation (reinforce a smile for example), what you want someone to do (to leave, to get you something, etc.). You will have about 25 minutes to design this with your group. Then you will need to ...
Learning - Annenberg Learner
... >> ZIMBARDO: Learning allows us to do two important things in the quest for survival: first, to anticipate the future from past experience, and second, to control a complex and ever- changing environment. ...
... >> ZIMBARDO: Learning allows us to do two important things in the quest for survival: first, to anticipate the future from past experience, and second, to control a complex and ever- changing environment. ...
File - Coach Waters
... • A partial reinforcement schedule that rewards an unpredictable number of correct responses • This schedule is very resistant to extinction. • Sometimes called the “gambler’s schedule”; similar to a slot machine ...
... • A partial reinforcement schedule that rewards an unpredictable number of correct responses • This schedule is very resistant to extinction. • Sometimes called the “gambler’s schedule”; similar to a slot machine ...
Child Development Theories and Theorists Psychoanalytic Theories
... Used classical conditioning to study how ...
... Used classical conditioning to study how ...
Learning
... V = the strength of association between a CS and a US ΔVn = the change in the strength of association between the CS and US on a given trial Vmax = the asymptote for CS-US association strength after learning c = rate of conditioning (how fast the association is learned) ...
... V = the strength of association between a CS and a US ΔVn = the change in the strength of association between the CS and US on a given trial Vmax = the asymptote for CS-US association strength after learning c = rate of conditioning (how fast the association is learned) ...
Associative Learning
... V = the strength of association between a CS and a US ΔVn = the change in the strength of association between the CS and US on a given trial Vmax = the asymptote for CS-US association strength after learning c = rate of conditioning (how fast the association is learned) ...
... V = the strength of association between a CS and a US ΔVn = the change in the strength of association between the CS and US on a given trial Vmax = the asymptote for CS-US association strength after learning c = rate of conditioning (how fast the association is learned) ...
Applications of Classical Conditioning
... The initial stage of learning when a neutral stimulus is linked to an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. ...
... The initial stage of learning when a neutral stimulus is linked to an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. ...
History of Psychology - Reading Community Schools
... • Functionalism includes behavioral observation as well as introspection • Structuralisms ask what are the elements of a process • Functionalists ask what is the purpose of a process Adaptive practices ...
... • Functionalism includes behavioral observation as well as introspection • Structuralisms ask what are the elements of a process • Functionalists ask what is the purpose of a process Adaptive practices ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.