DNA bracelet activity pack
... Today we are going to make a DNA bracelet just for you that is a copy of the pattern sequence of DNA held inside your genes. Does anyone know what a gene is? Not to be confused with a pair of trousers! A gene is a tiny code of genetic information that gives your body instructions. We all have genes ...
... Today we are going to make a DNA bracelet just for you that is a copy of the pattern sequence of DNA held inside your genes. Does anyone know what a gene is? Not to be confused with a pair of trousers! A gene is a tiny code of genetic information that gives your body instructions. We all have genes ...
Lecture A Version A Final Exam Bio 93 Fall 2011 Fill
... e. bind to sequences just after the start site of transcription. 23. Which of the following modifications is least likely to alter the rate at which a DNA fragment moves through a gel during electrophoresis? a. altering the nucleotide sequence of the DNA fragment b. digesting the DNA fragment with a ...
... e. bind to sequences just after the start site of transcription. 23. Which of the following modifications is least likely to alter the rate at which a DNA fragment moves through a gel during electrophoresis? a. altering the nucleotide sequence of the DNA fragment b. digesting the DNA fragment with a ...
B. gal-4 and gal-7
... its difficulties (either of gal classification or of allele ratios) and a third haploidization was totally inconclusive. No meiotic linkage of gal-7 to linkage group markers has been found over the years, although sane gal-7 is present on a number of mapping strains. I also failed to find linkage wi ...
... its difficulties (either of gal classification or of allele ratios) and a third haploidization was totally inconclusive. No meiotic linkage of gal-7 to linkage group markers has been found over the years, although sane gal-7 is present on a number of mapping strains. I also failed to find linkage wi ...
1. Suppose the nucleotide composition of a DNA virus was found to
... From the genetic code, we can see that the amino acid His has two potential codons, while the amino acids Met and Trp each have only one possible codon. So, there are two different mRNA nucleotide sequences that could code for the tripeptide. Once the potential mRNA nucleotide sequences have been de ...
... From the genetic code, we can see that the amino acid His has two potential codons, while the amino acids Met and Trp each have only one possible codon. So, there are two different mRNA nucleotide sequences that could code for the tripeptide. Once the potential mRNA nucleotide sequences have been de ...
DNA Packing
... Repeated cycle of steps for PCR: 1. Sample is heated to separate DNA strands 2. Sample is cooled and primer binds to specific ...
... Repeated cycle of steps for PCR: 1. Sample is heated to separate DNA strands 2. Sample is cooled and primer binds to specific ...
Chapter 3
... Helix uncoils, strands separate Each strand of DNA is able to pair with its ______________ base Chemical bonds form between neighboring nucleotides (& H bonds form between bases) Original DNA is now 2 identical strands, one goes to each of 2 daughter cells DNA ______________: catalyzes the addition ...
... Helix uncoils, strands separate Each strand of DNA is able to pair with its ______________ base Chemical bonds form between neighboring nucleotides (& H bonds form between bases) Original DNA is now 2 identical strands, one goes to each of 2 daughter cells DNA ______________: catalyzes the addition ...
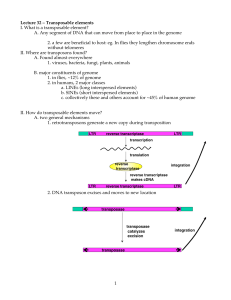
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (l ...
... 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (l ...
Lecture 6 S - BEHESHTI MAAL
... Bacteria after cell death and lysis could release DNA into environment Recipient cell can take up DNA fragments and incorporate into their own DNA – Resulting in a hybrid (recombinant cell) ...
... Bacteria after cell death and lysis could release DNA into environment Recipient cell can take up DNA fragments and incorporate into their own DNA – Resulting in a hybrid (recombinant cell) ...
Unit A Glossary
... 4. Atrium (plural: atria) One of the two upper chambers in the human heart that receives blood returning from the body or lungs. 5. Chromosome A strand of DNA—and sometimes associated proteins— that contains the genes that store hereditary information. 6. Co-dominance A condition in which two traits ...
... 4. Atrium (plural: atria) One of the two upper chambers in the human heart that receives blood returning from the body or lungs. 5. Chromosome A strand of DNA—and sometimes associated proteins— that contains the genes that store hereditary information. 6. Co-dominance A condition in which two traits ...
Setting up a transformation--how will the competent cells be treated?
... infected with phage P2 (spi, or sensitive to P2 inhibition), spi+ conferred by red and gam genes in “stuffer” • Only phage lacking stuffer (they don’t have spi gene) can make plaques on lawn of E. coli containing a P2 lysogen ...
... infected with phage P2 (spi, or sensitive to P2 inhibition), spi+ conferred by red and gam genes in “stuffer” • Only phage lacking stuffer (they don’t have spi gene) can make plaques on lawn of E. coli containing a P2 lysogen ...
The human genome of is found where in the human body?
... sequence of DNA to be cut and pasted at will • Plasmids, small loops of bacterial DNA, can be modified with any DNA • Because the genetic code is universal, DNA will be read in the same way ...
... sequence of DNA to be cut and pasted at will • Plasmids, small loops of bacterial DNA, can be modified with any DNA • Because the genetic code is universal, DNA will be read in the same way ...
2014
... A) It is located in the mitochondria. B) It is located in the nucleus. C) It uses NH4+ as a nitrogen source D) It uses glutamine as a nitrogen source Circle the correct answer 8. [2 points] Which of the following statements about topoisomerases is incorrect? A) Type II topoisomerases change the link ...
... A) It is located in the mitochondria. B) It is located in the nucleus. C) It uses NH4+ as a nitrogen source D) It uses glutamine as a nitrogen source Circle the correct answer 8. [2 points] Which of the following statements about topoisomerases is incorrect? A) Type II topoisomerases change the link ...
Structure of DNA
... • PCR primers are short, single stranded DNA molecules (15-40 bp) • They are manufactured commercially and can be ordered to match any DNA sequence • Primers are sequence specific, they will bind to a particular sequence in a genome • As you design primers with a longer length (15 → 40 bp), the prim ...
... • PCR primers are short, single stranded DNA molecules (15-40 bp) • They are manufactured commercially and can be ordered to match any DNA sequence • Primers are sequence specific, they will bind to a particular sequence in a genome • As you design primers with a longer length (15 → 40 bp), the prim ...
Transformation
... Transformation :is a process in which cells take up foreign DNA from their environment. bacteria take up exogenous (foreign) DNA and produce the genetic products (proteins) encoded in the foreign DNA. Under proper conditions, a cell that is incubated with plasmid DNA can absorb the plasmid into i ...
... Transformation :is a process in which cells take up foreign DNA from their environment. bacteria take up exogenous (foreign) DNA and produce the genetic products (proteins) encoded in the foreign DNA. Under proper conditions, a cell that is incubated with plasmid DNA can absorb the plasmid into i ...
Exam301ANS
... 2. the p53 protein can move from cell to cell, causing cancer. 3. p53 is a kinase, which can phosphorylate many different cells cycle proteins. 4. p53 is involved in cell-cycle regulation in a wide variety of human cell types. ...
... 2. the p53 protein can move from cell to cell, causing cancer. 3. p53 is a kinase, which can phosphorylate many different cells cycle proteins. 4. p53 is involved in cell-cycle regulation in a wide variety of human cell types. ...
MTC19: transcription and gene expression 02/10/07
... Genes consist of exons (sequences to be subsequently translated into proteins) separated by introns, which can contain other control regions or even other genes to allow more complex control networks Gene promoters define both the starting point and the direction of transcription Promoter regions ar ...
... Genes consist of exons (sequences to be subsequently translated into proteins) separated by introns, which can contain other control regions or even other genes to allow more complex control networks Gene promoters define both the starting point and the direction of transcription Promoter regions ar ...
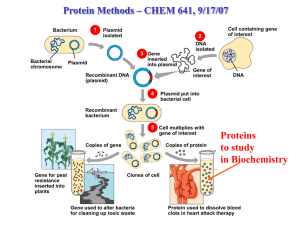
Discovery of Recombinant DNA
... plasmids could make bacteria resistant to antibiotics. In 1972, Cohen's investigations, combined with those of Herbert Boyer, led to the development of methods to combine and transplant genes. This discovery signalled the birth of genetic engineering, and he received National Medal of Science (1988) ...
... plasmids could make bacteria resistant to antibiotics. In 1972, Cohen's investigations, combined with those of Herbert Boyer, led to the development of methods to combine and transplant genes. This discovery signalled the birth of genetic engineering, and he received National Medal of Science (1988) ...
Cancer is known as a real threat to human health
... develop because of damage to DNA. Most often when DNA becomes damaged the body is able to repair it. In cancer cells, the damaged DNA is not repaired. In normal cells, there are some ways to protect DNA from being damaged, one of which is called methylation. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume tha ...
... develop because of damage to DNA. Most often when DNA becomes damaged the body is able to repair it. In cancer cells, the damaged DNA is not repaired. In normal cells, there are some ways to protect DNA from being damaged, one of which is called methylation. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume tha ...
Introduction Activity: From DNA to Protein File
... This overview provides a sequence of learning activities to help you understand that proteins and DNA are not just abstract concepts in biology textbooks, but rather crucial components of our bodies that affect functions and characteristics that you are familiar with. You will learn about the functi ...
... This overview provides a sequence of learning activities to help you understand that proteins and DNA are not just abstract concepts in biology textbooks, but rather crucial components of our bodies that affect functions and characteristics that you are familiar with. You will learn about the functi ...
CHAPTER 17 RECOMBINANT DNA AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
... b. The restriction enzyme is used to cut DNA at specific points during production of rDNA. c. It is called a restriction enzyme because it restricts growth of viruses but it acts a molecular scissors to cleave any piece of DNA at a specific site. 7. Restriction enzymes cleave vector (plasmid) and fo ...
... b. The restriction enzyme is used to cut DNA at specific points during production of rDNA. c. It is called a restriction enzyme because it restricts growth of viruses but it acts a molecular scissors to cleave any piece of DNA at a specific site. 7. Restriction enzymes cleave vector (plasmid) and fo ...
SBI 4U Genetics 6
... certain genes with DNA from other areas. Called recombinant DNA Bacteria have restriction enzymes that will cut up invading viral DNA. Scientists can use a special type of restriction enzyme called restriction endonuclease because they cleave double-stranded DNA in the middle of the strand by ...
... certain genes with DNA from other areas. Called recombinant DNA Bacteria have restriction enzymes that will cut up invading viral DNA. Scientists can use a special type of restriction enzyme called restriction endonuclease because they cleave double-stranded DNA in the middle of the strand by ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.