MOLECULAR BIOLOGY and GENETICS
... physical and chemical properties of the information containing biopolymers; nucleic acid and protein, and the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to Protein. The basic principles of molecular genetics are also introduced and some of the current techniques used in molecular biology research a ...
... physical and chemical properties of the information containing biopolymers; nucleic acid and protein, and the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to Protein. The basic principles of molecular genetics are also introduced and some of the current techniques used in molecular biology research a ...
protein - WSU Vancouver
... • Only heritable mutations are relevant to the evolutionary process because evolution is a process that occurs over generations • Not all mutations that occur in living things are heritable; there is an important difference in the heritability of mutations in multi-celled vs. single-celled organis ...
... • Only heritable mutations are relevant to the evolutionary process because evolution is a process that occurs over generations • Not all mutations that occur in living things are heritable; there is an important difference in the heritability of mutations in multi-celled vs. single-celled organis ...
Document
... 12. Centrifuge for 5 min at 3000 x g. The DNA might be visible as a small white pellet. 13. Carefully discard the supernatant. Drain the tube on a clean piece of absorbent paper, taking care that the pellet remains in the tube. 14. Add 18 ml of 70% ethanol, and invert several times to wash the DNA p ...
... 12. Centrifuge for 5 min at 3000 x g. The DNA might be visible as a small white pellet. 13. Carefully discard the supernatant. Drain the tube on a clean piece of absorbent paper, taking care that the pellet remains in the tube. 14. Add 18 ml of 70% ethanol, and invert several times to wash the DNA p ...
DNA and Cell Division
... The mRNA is directly involved in the protein-making process. mRNA tells the ribosome (Figure below) how to create a protein. The process of reading the mRNA code in the ribosome to make a protein is called translation (Figure below). Sets of three bases, called codons, are read in the ribosome; the ...
... The mRNA is directly involved in the protein-making process. mRNA tells the ribosome (Figure below) how to create a protein. The process of reading the mRNA code in the ribosome to make a protein is called translation (Figure below). Sets of three bases, called codons, are read in the ribosome; the ...
Bacteriophage l and Its Relatives
... molecule is replicated into two circular daughters. At about 12 minutes after infection replication switches to the ``rolling circle'' mechanism, which produces long head-to-tail linear concatemers of the genome, the appropriate substrate for packaging into the phage head. Most of the other early ge ...
... molecule is replicated into two circular daughters. At about 12 minutes after infection replication switches to the ``rolling circle'' mechanism, which produces long head-to-tail linear concatemers of the genome, the appropriate substrate for packaging into the phage head. Most of the other early ge ...
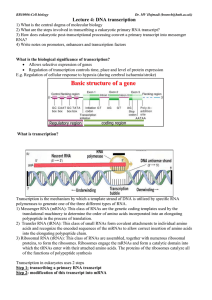
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Poly(A)polymerase and cleavage & polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) attach poly(A) generated from ATP ...
... Poly(A)polymerase and cleavage & polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) attach poly(A) generated from ATP ...
chapter 20 - Elizabeth C-1
... In an application called in vitro mutagenesis, specific mutations are introduced into the sequence of a cloned gene, and then the mutated gene is returned to a cell in such a way that it disables (“knocks out”) the normal cellular copies of the same gene. o If the introduced mutations alter or des ...
... In an application called in vitro mutagenesis, specific mutations are introduced into the sequence of a cloned gene, and then the mutated gene is returned to a cell in such a way that it disables (“knocks out”) the normal cellular copies of the same gene. o If the introduced mutations alter or des ...
KEY TERMS FOR Characteristics of Life
... • A mutation is any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA • Two types: – Base substitutions – replacement of one base with another • Can cause no change in protein, or a deformed protein – Base insertions / deletions – inserting extra bases, or deleting some (or both) • Causes a change in the pro ...
... • A mutation is any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA • Two types: – Base substitutions – replacement of one base with another • Can cause no change in protein, or a deformed protein – Base insertions / deletions – inserting extra bases, or deleting some (or both) • Causes a change in the pro ...
Genes in Context Gene–Environment Interplay
... transcription (Fig. 1a). The mRNA transcript is a copy of the DNA sequence that can further be ‘‘translated’’ into protein. The reading, or expression, of DNA can, like the books in our library, have limitless consequences. However, without the active process that triggers such expression, this pote ...
... transcription (Fig. 1a). The mRNA transcript is a copy of the DNA sequence that can further be ‘‘translated’’ into protein. The reading, or expression, of DNA can, like the books in our library, have limitless consequences. However, without the active process that triggers such expression, this pote ...
The Mitochondria as a Minimal Chassis:
... This large additional region homologous to the 3′ part of the cox1 gene (886 bp) should promote integration of RIP1m between the cox1 and atp8 genes in rho+ mtDNA (Fig. 1C). S. douglasii rather than bona fide S. cerevisiae cox1 sequences were used, because repeated sequences in S. cerevisiae mtDNA a ...
... This large additional region homologous to the 3′ part of the cox1 gene (886 bp) should promote integration of RIP1m between the cox1 and atp8 genes in rho+ mtDNA (Fig. 1C). S. douglasii rather than bona fide S. cerevisiae cox1 sequences were used, because repeated sequences in S. cerevisiae mtDNA a ...
pGLO
... survival. In nature, bacteria can transfer plasmids back and forth, allowing them to share these beneficial genes. This natural mechanism allows bacteria to adapt to new environments. The recent occurrence of bacterial resistance to antibiotics is due to the transmission of plasmids. Bio-Rad’s uniq ...
... survival. In nature, bacteria can transfer plasmids back and forth, allowing them to share these beneficial genes. This natural mechanism allows bacteria to adapt to new environments. The recent occurrence of bacterial resistance to antibiotics is due to the transmission of plasmids. Bio-Rad’s uniq ...
Genes chapt15
... • Elongation of translation involves the addition of amino acids: – a charged tRNA binds to the A site if its anticodon is complementary to the codon at the A site – peptidyl transferase forms a peptide ...
... • Elongation of translation involves the addition of amino acids: – a charged tRNA binds to the A site if its anticodon is complementary to the codon at the A site – peptidyl transferase forms a peptide ...
DNA ISOLATION FROM AGAROSE GELS WITH DEAE PAPER
... agarose. The bound DNA can now be stored at 4oC for several days. The DNA should always remain covered with buffer to prevent irreversible binding which may occur if the paper is allowed to dry out. ...
... agarose. The bound DNA can now be stored at 4oC for several days. The DNA should always remain covered with buffer to prevent irreversible binding which may occur if the paper is allowed to dry out. ...
Gene Section XPE (xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group E) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... protein is reported to recognize many types of DNA lesions and is inducible by treatment with DNAdamaging agents. After UV irradiation, dynamic nuclear accumulation of DDB1 from the cytoplasm was found after 24 h. The function of the gene product is not completely clarified yet. Band shift assays su ...
... protein is reported to recognize many types of DNA lesions and is inducible by treatment with DNAdamaging agents. After UV irradiation, dynamic nuclear accumulation of DDB1 from the cytoplasm was found after 24 h. The function of the gene product is not completely clarified yet. Band shift assays su ...
ppt 2015 edit
... Free ribosomes are located in the cytoplasm of the cell. They are not attached to any structure, but they may group together with other ribosomes to form polysomes (polyribosomes). In the cytoplasm, ribosomes are free floating. They can move all around the cell. • Bound ribosomes are located on the ...
... Free ribosomes are located in the cytoplasm of the cell. They are not attached to any structure, but they may group together with other ribosomes to form polysomes (polyribosomes). In the cytoplasm, ribosomes are free floating. They can move all around the cell. • Bound ribosomes are located on the ...
pEGFP-C1 - Newcastle University Staff Publishing Service
... initiation site (6) to further increase the translation efficiency in eukaryotic cells. The MCS in pEGFPC1 is between the EGFP coding sequences and the SV40 poly A. Genes cloned into the MCS will be expressed as fusions to the C-terminus of EGFP if they are in the same reading frame as EGFP and ther ...
... initiation site (6) to further increase the translation efficiency in eukaryotic cells. The MCS in pEGFPC1 is between the EGFP coding sequences and the SV40 poly A. Genes cloned into the MCS will be expressed as fusions to the C-terminus of EGFP if they are in the same reading frame as EGFP and ther ...
Unit 18: Genetics and Genetic Engineering
... techniques to enable interpretation of ratios. If this is not possible, simulations such as ‘Rebops’ will give learners a good understanding of the processes involved. For P5, learners can use the their own experimental data or be given a suitable data set which will allow interpretation. For P6 lea ...
... techniques to enable interpretation of ratios. If this is not possible, simulations such as ‘Rebops’ will give learners a good understanding of the processes involved. For P5, learners can use the their own experimental data or be given a suitable data set which will allow interpretation. For P6 lea ...
Enzymes
... ENZYMES ARE SPECIFIC • Every enzyme can only be used for one reaction. Each one can only bond with one substrate • So every time you have a new substrate, you need a new enzyme • This is called being SUBSTRATE SPECIFIC ...
... ENZYMES ARE SPECIFIC • Every enzyme can only be used for one reaction. Each one can only bond with one substrate • So every time you have a new substrate, you need a new enzyme • This is called being SUBSTRATE SPECIFIC ...
STR
... Sir Alec Jeffreys is credited with DNA profiling using RFLP. In September of 1984 after years of work, he saw his first series of blots on an X-ray. The technique was first used in forensics, when in 1985 he was asked by police to confirm the rape confession of 17 year old Richard Buckland, who was ...
... Sir Alec Jeffreys is credited with DNA profiling using RFLP. In September of 1984 after years of work, he saw his first series of blots on an X-ray. The technique was first used in forensics, when in 1985 he was asked by police to confirm the rape confession of 17 year old Richard Buckland, who was ...
Mutations - Miss Garry`s Biology Class Website!
... What is the effect of a mutation? Mutations are a natural process that can lead to: a. No effect nothing happens to the phenotype b. Beneficial effect phenotype is affected. The organism is better adapted to its environment c. Harmful effect phenotype is different. The organism is less adap ...
... What is the effect of a mutation? Mutations are a natural process that can lead to: a. No effect nothing happens to the phenotype b. Beneficial effect phenotype is affected. The organism is better adapted to its environment c. Harmful effect phenotype is different. The organism is less adap ...
Tulane University Matrix DNA Diagnostics Lab
... FORM 1- Instructions for submission of specimen for DNA testing The patient should be fully informed about the test. Nature of the test/Methodology: The test detects mutations in the gene(s) involved in the synthesis of proteins of connective tissue using Sanger sequencing. Sanger sequencing is high ...
... FORM 1- Instructions for submission of specimen for DNA testing The patient should be fully informed about the test. Nature of the test/Methodology: The test detects mutations in the gene(s) involved in the synthesis of proteins of connective tissue using Sanger sequencing. Sanger sequencing is high ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.