IACP DNA Brochure (For PDF)
... research and (() increased awareness of the crime reduction potential of forensic DNA by executive and legislative bodies at the State! Local! and National levels! as well as by the general public# In fact! many law enforcement officials consider forensic DNA analysis the most significant advance in ...
... research and (() increased awareness of the crime reduction potential of forensic DNA by executive and legislative bodies at the State! Local! and National levels! as well as by the general public# In fact! many law enforcement officials consider forensic DNA analysis the most significant advance in ...
Anticancer Antibiotics
... •The phleomycins (11) are related in that one of the thiazole rings has been reduced to its C-44,45-dihydro analog. The phleomycins have substantial antitumor activity but are very nephrotoxic for clinical use. The cliomycins (12), tallysomycins (13), zorbamycins (14), zorbonamycins, platomycins, a ...
... •The phleomycins (11) are related in that one of the thiazole rings has been reduced to its C-44,45-dihydro analog. The phleomycins have substantial antitumor activity but are very nephrotoxic for clinical use. The cliomycins (12), tallysomycins (13), zorbamycins (14), zorbonamycins, platomycins, a ...
Document
... 21. Compare and contrast photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Again be specific about reactions energy requirements etc. 22. How is cellular energy stored? 23. Compare and contrast cellular respiration and fermentation. Once again be specific. What chemical processes are occurring in each and h ...
... 21. Compare and contrast photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Again be specific about reactions energy requirements etc. 22. How is cellular energy stored? 23. Compare and contrast cellular respiration and fermentation. Once again be specific. What chemical processes are occurring in each and h ...
t - nslc.wustl.edu
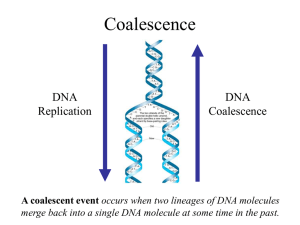
... mutating per unit time (only neutral mutations are allowed). This model assumes that when a nucleotide site mutates it is equally likely to mutate to any of the three other nucleotide states. Suppose further that mutation is such a rare occurrence that in any time unit it is only likely for at most ...
... mutating per unit time (only neutral mutations are allowed). This model assumes that when a nucleotide site mutates it is equally likely to mutate to any of the three other nucleotide states. Suppose further that mutation is such a rare occurrence that in any time unit it is only likely for at most ...
PureLink® Quick Plasmid Miniprep Kits
... 1. Harvest. Centrifuge 1–5 mL of the overnight LB-culture. (Use 1–2 × 109 E. coli cells for each sample.) Remove all medium. 2. Resuspend. Add 250 μL Resuspension Buffer (R3) with RNase A to the cell pellet and resuspend the pellet until it is homogeneous. 3. Lyse. Add 250 μL Lysis Buffer (L7). M ...
... 1. Harvest. Centrifuge 1–5 mL of the overnight LB-culture. (Use 1–2 × 109 E. coli cells for each sample.) Remove all medium. 2. Resuspend. Add 250 μL Resuspension Buffer (R3) with RNase A to the cell pellet and resuspend the pellet until it is homogeneous. 3. Lyse. Add 250 μL Lysis Buffer (L7). M ...
Biotechnology - Department of Plant Biology
... cell by restricting invasion by foreign DNA. Cells modify their own DNA so that it is not cleaved by the restriction enzymes. Different restriction enzymes (from different species or even strains of bacteria) recognize different sequences of bases in DNA. When isolated and purified, restriction enzy ...
... cell by restricting invasion by foreign DNA. Cells modify their own DNA so that it is not cleaved by the restriction enzymes. Different restriction enzymes (from different species or even strains of bacteria) recognize different sequences of bases in DNA. When isolated and purified, restriction enzy ...
chapter 19 the organization and control of eukaryotic
... methylation and histone deacetylation cooperate to repress transcription. In some species, DNA methylation is responsible for long-term inactivation of genes during cellular differentiation. Once methylated, genes usually stay that way through successive cell divisions. Methylation enzymes rec ...
... methylation and histone deacetylation cooperate to repress transcription. In some species, DNA methylation is responsible for long-term inactivation of genes during cellular differentiation. Once methylated, genes usually stay that way through successive cell divisions. Methylation enzymes rec ...
DNA and Gene Expression (chaps 12-15)
... 42 A cell may meet the need for large quantities of a specific protein by: A. increasing the half-life of the mRNA that specifies the protein. B. having multiple copies of the gene that codes for that protein. C. continuously synthesizing the mRNA molecule that specifies that protein. D. All of thes ...
... 42 A cell may meet the need for large quantities of a specific protein by: A. increasing the half-life of the mRNA that specifies the protein. B. having multiple copies of the gene that codes for that protein. C. continuously synthesizing the mRNA molecule that specifies that protein. D. All of thes ...
Behavioral Objectives
... Cloning of animals is now a reality. A diploid nucleus from bioengineered animal is inserted into enucleated eggs from a donor. These eggs are inserted into the uterus and when development is finished the surrogate mother gives birth to the cloned animals. The Human Genome Project The Human Genome P ...
... Cloning of animals is now a reality. A diploid nucleus from bioengineered animal is inserted into enucleated eggs from a donor. These eggs are inserted into the uterus and when development is finished the surrogate mother gives birth to the cloned animals. The Human Genome Project The Human Genome P ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY and GENETICS
... physical and chemical properties of the information containing biopolymers; nucleic acid and protein, and the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to Protein. The basic principles of molecular genetics are also introduced and some of the current techniques used in molecular biology research a ...
... physical and chemical properties of the information containing biopolymers; nucleic acid and protein, and the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to Protein. The basic principles of molecular genetics are also introduced and some of the current techniques used in molecular biology research a ...
Poster PreDetector_new
... cells. The emergence of position weight matrices based programs has facilitated the access to this approach. However, a tool that automatically estimates the reliability of the predictions and would allow users to extend predictions in genomic regions generally regarded with no regulatory functions ...
... cells. The emergence of position weight matrices based programs has facilitated the access to this approach. However, a tool that automatically estimates the reliability of the predictions and would allow users to extend predictions in genomic regions generally regarded with no regulatory functions ...
enzyme powerpoint
... molecules together, or to break molecules apart. The curve on the bottom compares how much energy it take with an enzyme… a lot less! ...
... molecules together, or to break molecules apart. The curve on the bottom compares how much energy it take with an enzyme… a lot less! ...
lecture 03 - phylogenetics - Cal State LA
... process by which we infer the evolutionary history of a group based on the traits we see today - the best phylogenetic tree is the one which requires the fewest changes in traits (characters) to account for modern character states in surviving lineages - i.e., assumes that the minimum number of chan ...
... process by which we infer the evolutionary history of a group based on the traits we see today - the best phylogenetic tree is the one which requires the fewest changes in traits (characters) to account for modern character states in surviving lineages - i.e., assumes that the minimum number of chan ...
What is Genetic Modification?
... throughout modern biotechnology: in food and enzyme technology, in industry and medicine, and in agriculture and horticulture. Microorganisms are among the most widely used GMOs, with applications ranging from pharmaceutical ...
... throughout modern biotechnology: in food and enzyme technology, in industry and medicine, and in agriculture and horticulture. Microorganisms are among the most widely used GMOs, with applications ranging from pharmaceutical ...
Gene Reg Flyer 0113_D3.indd
... DNA methylation and histone modifications, as well as the role of noncoding RNAs in regulatory pathways. Agilent provides the tools needed to gain a better understanding of epigenetic control mechanisms that play a role in cancer, human diseases, and cell development. ...
... DNA methylation and histone modifications, as well as the role of noncoding RNAs in regulatory pathways. Agilent provides the tools needed to gain a better understanding of epigenetic control mechanisms that play a role in cancer, human diseases, and cell development. ...
Thank-you for attending Biol120 Mock Final Exam, brought to you by
... b) It attaches the chromosome to and walks along microtubules c) It condenses chromosomes d) It regulates cell division 8. Based on his experiments Mendel found he was able to predict that: a) Half of the offspring will have the same genotype as one of their parents. b) As gametes are formed half th ...
... b) It attaches the chromosome to and walks along microtubules c) It condenses chromosomes d) It regulates cell division 8. Based on his experiments Mendel found he was able to predict that: a) Half of the offspring will have the same genotype as one of their parents. b) As gametes are formed half th ...
Solutions for Recombinant DNA Unit Exam
... 2. cDNA libraries lack the endogenous promoters found in the genome. 3. One may have multiple cDNAs for the same gene due to alternative splicing. 4. cDNA libraries will not contain genes that are not expressed in the cells used to generate the cDNA library. ii) You transform arg– bacterial cells wi ...
... 2. cDNA libraries lack the endogenous promoters found in the genome. 3. One may have multiple cDNAs for the same gene due to alternative splicing. 4. cDNA libraries will not contain genes that are not expressed in the cells used to generate the cDNA library. ii) You transform arg– bacterial cells wi ...
10.2 Genetics 2 - Mendel, etc Higher level only
... Protein Synthesis – more info. It is the order of the bases in the DNA that determine the order of the amino acids in a protein. Each group of three bases is a triplet. Each triplet codes for a particular amino acid. DNA is found in the nucleus only. Proteins made at ribosomes in cytoplasm. ...
... Protein Synthesis – more info. It is the order of the bases in the DNA that determine the order of the amino acids in a protein. Each group of three bases is a triplet. Each triplet codes for a particular amino acid. DNA is found in the nucleus only. Proteins made at ribosomes in cytoplasm. ...
Molecular population genetics Magnus Nordborg* and Hideki Innan
... regardless of whether the sites were sampled from the same or different populations, or even from different species (see Figure 1). It is also true in the presence of recombination, although different sites will then typically have different trees. Selectively neutral mutations at a site can be thou ...
... regardless of whether the sites were sampled from the same or different populations, or even from different species (see Figure 1). It is also true in the presence of recombination, although different sites will then typically have different trees. Selectively neutral mutations at a site can be thou ...
25.10 Translation: Transfer RNA and Protein
... The replication of DNA viruses is straightforward: the cell replicates the viral DNA, the viral DNA is transcribed to RNA and many copies of the capsid proteins are made. After an RNA virus infects a cell either the cell must transcribe and produce proteins directly from the viral RNA template, or e ...
... The replication of DNA viruses is straightforward: the cell replicates the viral DNA, the viral DNA is transcribed to RNA and many copies of the capsid proteins are made. After an RNA virus infects a cell either the cell must transcribe and produce proteins directly from the viral RNA template, or e ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.