Pharmacology Block 3 Notes Autonomic Pharmacology I
... o NE is NOT broken down in the synapse, instead is taken back up by the presynaptic neuron or nearby glial cells If taken back up by the neuron, is broken down by monoamine oxidase (MAO) If MAO is inhibited, you don’t get breakdown of NE in the neuron, meaning more of it will be released into th ...
... o NE is NOT broken down in the synapse, instead is taken back up by the presynaptic neuron or nearby glial cells If taken back up by the neuron, is broken down by monoamine oxidase (MAO) If MAO is inhibited, you don’t get breakdown of NE in the neuron, meaning more of it will be released into th ...
Drugs: Antagonists, agonists, and reuptake inhibitors Drugs—why
... Dopamine antagonists are traditionally used to treat schizophrenia and related mental disorders. A person with schizophrenia may have an overactive dopamine system. Dopamine antagonists can help regulate this system by "turning down" dopamine activity. Cocaine and other drugs of abuse can alter dopa ...
... Dopamine antagonists are traditionally used to treat schizophrenia and related mental disorders. A person with schizophrenia may have an overactive dopamine system. Dopamine antagonists can help regulate this system by "turning down" dopamine activity. Cocaine and other drugs of abuse can alter dopa ...
Endocrine Glands
... and stimulate skeletal growth Releases by presence of ACTH from pituitary but only slightly Adrenal medulla Chromaffin cells secretes epinephrine (75%) and norepinephrine Is released when sympathetic nervous system is activated (stress) Effects Mimic the effects of the sympathetic nervous system Eff ...
... and stimulate skeletal growth Releases by presence of ACTH from pituitary but only slightly Adrenal medulla Chromaffin cells secretes epinephrine (75%) and norepinephrine Is released when sympathetic nervous system is activated (stress) Effects Mimic the effects of the sympathetic nervous system Eff ...
Nervous System P2
... • The cerebrum also provides the with information about the normal position of body parts. • The cerebellum uses this information to initiate responses that are coordinated and balanced. – This helps us when preventing a fall or when learning a new motor skill such as walking or ...
... • The cerebrum also provides the with information about the normal position of body parts. • The cerebellum uses this information to initiate responses that are coordinated and balanced. – This helps us when preventing a fall or when learning a new motor skill such as walking or ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... The endocrine system is responsible for coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals known as hormones. Unlike the nervous system, the effects of the endocrine system are sustained for longer periods of time. The endocrine system ...
... The endocrine system is responsible for coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals known as hormones. Unlike the nervous system, the effects of the endocrine system are sustained for longer periods of time. The endocrine system ...
Practice Quiz
... adenoma in the adenohypophysis which secretes excessive amounts of Growth Hormone. Which of the following are to be expected: a. She grows abnormally tall b. Plasma levels of IGF-1 will be high. c. Plasma levels of GHRH will be high d. Bones of the face, hands, and feet will ...
... adenoma in the adenohypophysis which secretes excessive amounts of Growth Hormone. Which of the following are to be expected: a. She grows abnormally tall b. Plasma levels of IGF-1 will be high. c. Plasma levels of GHRH will be high d. Bones of the face, hands, and feet will ...
Carin Martinson
... hippocampus ◦ Same effects on depression treatment as: TCA (tricyclic antidepressant) and SSRI’s (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) ...
... hippocampus ◦ Same effects on depression treatment as: TCA (tricyclic antidepressant) and SSRI’s (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) ...
PHL 313 practical
... (e.g., enzyme inhibitor) or a physiologic agent (e.g., hormone), that prevents the action of another molecule. ...
... (e.g., enzyme inhibitor) or a physiologic agent (e.g., hormone), that prevents the action of another molecule. ...
Autonomous nervous systems
... – sympathetic chain ganglia – collateral ganglia – innervate organs ...
... – sympathetic chain ganglia – collateral ganglia – innervate organs ...
Parkinson Meds
... On off effect= long term use of the drug may have an irregulr response to the drug….. Reduce the maintanence dose and substitute another anti parkinson’s drug ...
... On off effect= long term use of the drug may have an irregulr response to the drug….. Reduce the maintanence dose and substitute another anti parkinson’s drug ...
The Nervous System
... • Efferent/Motor: From brain to effectors o Effectors (muscles or glands): end of last motor neuron • Interneurons: short neurons in spinal cord that connect afferent and efferent neurons Neurons (c 71) • Cell body: contains the nucleus, keeps cell alive • Dendrites: receive chemical signals from ot ...
... • Efferent/Motor: From brain to effectors o Effectors (muscles or glands): end of last motor neuron • Interneurons: short neurons in spinal cord that connect afferent and efferent neurons Neurons (c 71) • Cell body: contains the nucleus, keeps cell alive • Dendrites: receive chemical signals from ot ...
neurons
... Sympathetic Nervous System • The part of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body to deal with perceived threats • Fight or flight response – Heart rate increases, digestion stops, and the bronchial tubes in your lungs expands…increasing the amount of oxygen to the brain and muscles. Pupi ...
... Sympathetic Nervous System • The part of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body to deal with perceived threats • Fight or flight response – Heart rate increases, digestion stops, and the bronchial tubes in your lungs expands…increasing the amount of oxygen to the brain and muscles. Pupi ...
fff-Antipsychotics (Neuroleptics)
... It possesses antiemetic activity (modifies gastric motility). It was found to antagonize dopamine D2- receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the brain stem. 2- Pyrrolidinyl-containing benzamides a) Sulpiride (Dogmatil) Sulpiride has little sedative effect and lack EPS which is due to prefere ...
... It possesses antiemetic activity (modifies gastric motility). It was found to antagonize dopamine D2- receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the brain stem. 2- Pyrrolidinyl-containing benzamides a) Sulpiride (Dogmatil) Sulpiride has little sedative effect and lack EPS which is due to prefere ...
Endocrine Glands - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... glucose uptake in cells and storage as glycogen in the liver. •A fall in blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreas to secrete glucagon, which causes the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose. ...
... glucose uptake in cells and storage as glycogen in the liver. •A fall in blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreas to secrete glucagon, which causes the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose. ...
neuron_synapse powerpoint
... Resting Potential • The state of a neuron when it is at rest and capable of generating an action potential • The neuron is set and ready to fire ...
... Resting Potential • The state of a neuron when it is at rest and capable of generating an action potential • The neuron is set and ready to fire ...
Essentials of Biology Sylvia S. Mader
... • Voluntary control of skeletal muscles is provided by the brain. ...
... • Voluntary control of skeletal muscles is provided by the brain. ...
9.98 Neuropharmacology
... Reboexitine is a drug that specifically blocks NE uptake Cocaine blocks the transport of DA, NE and 5-HT 4. Modulation of metabolism Inside the terminal the transmitters are also catabolized by 2 enzymes: Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and monoamide oxidase (MAO) Degradation of catecholamines p ...
... Reboexitine is a drug that specifically blocks NE uptake Cocaine blocks the transport of DA, NE and 5-HT 4. Modulation of metabolism Inside the terminal the transmitters are also catabolized by 2 enzymes: Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and monoamide oxidase (MAO) Degradation of catecholamines p ...
I can File
... evaluate the use of hormone therapy in the treatment of humans (growth hormone and aging, anabolic steroids and human performance) explain that scientific knowledge and theories develop through hypotheses, the collection of evidence, investigation and the ability to provide explanations discus ...
... evaluate the use of hormone therapy in the treatment of humans (growth hormone and aging, anabolic steroids and human performance) explain that scientific knowledge and theories develop through hypotheses, the collection of evidence, investigation and the ability to provide explanations discus ...
Chapter 15
... mammary glands. All lactating mothers know about the complex "letdown" reflex that involves the oxytocin neurons of the hypothalamus. Oxytocin releasemay be stimulated by the somatic sensationsgeneratedby a suckling baby. But the sight or cry of a baby (even someone else,s)can also trigger the relea ...
... mammary glands. All lactating mothers know about the complex "letdown" reflex that involves the oxytocin neurons of the hypothalamus. Oxytocin releasemay be stimulated by the somatic sensationsgeneratedby a suckling baby. But the sight or cry of a baby (even someone else,s)can also trigger the relea ...
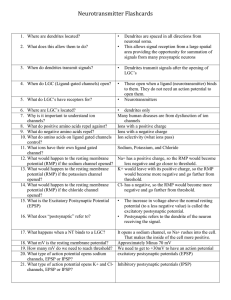
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... 98. What happens when the parasympathetic system is suppressed? 99. If a drug mimics the parasympathetic system, how will it affect the heart? 100. If a drug mimics the sympathetic system, how will it affect the heart? 101. What effect does epinephrine have on the heart rate? 102. What effect does a ...
... 98. What happens when the parasympathetic system is suppressed? 99. If a drug mimics the parasympathetic system, how will it affect the heart? 100. If a drug mimics the sympathetic system, how will it affect the heart? 101. What effect does epinephrine have on the heart rate? 102. What effect does a ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.