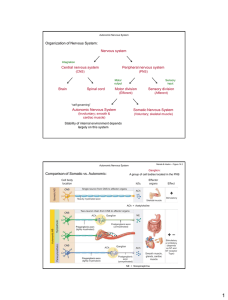
Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system
... Divisions of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): 1) Sympathetic Division: (“fight or flight”) • Readies body for stressful situations • Heightens mental alertness • metabolic rate ...
... Divisions of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): 1) Sympathetic Division: (“fight or flight”) • Readies body for stressful situations • Heightens mental alertness • metabolic rate ...
Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system
... Divisions of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): 1) Sympathetic Division: (“fight or flight”) • Readies body for stressful situations • Heightens mental alertness • metabolic rate ...
... Divisions of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): 1) Sympathetic Division: (“fight or flight”) • Readies body for stressful situations • Heightens mental alertness • metabolic rate ...
Renal system
... Decreased activity of digestive system is a sympathetic response Piloerection is a sympathetic response Increased metabolic rate is a sympathetic response Glucose is released into blood as a sympathetic response Lipolysis is a sympathetic response Increased alertness is a sympathetic response Ejacul ...
... Decreased activity of digestive system is a sympathetic response Piloerection is a sympathetic response Increased metabolic rate is a sympathetic response Glucose is released into blood as a sympathetic response Lipolysis is a sympathetic response Increased alertness is a sympathetic response Ejacul ...
Antiemetic drugs
... • A gastroprokinetic agent, gastrokinetic, or prokinetic, is a type of drug which enhances gastrointestinal motility by increasing the frequency of contractions in the small intestine or making them stronger, but without disrupting their rhythm. • They are used to treat irritable bowel syndrome, gas ...
... • A gastroprokinetic agent, gastrokinetic, or prokinetic, is a type of drug which enhances gastrointestinal motility by increasing the frequency of contractions in the small intestine or making them stronger, but without disrupting their rhythm. • They are used to treat irritable bowel syndrome, gas ...
Antipsychotics
... Occurs in pts. hypersensitive to the Ex.Py. effects of antipsychotics. Due to excessively rapid blockade of postsynaptic dopamine receptors. The syndrome begins with marked muscle rigidity. If sweating is impaired, a fever may ensue. The stress leukocytosis and high fever associated with this syndro ...
... Occurs in pts. hypersensitive to the Ex.Py. effects of antipsychotics. Due to excessively rapid blockade of postsynaptic dopamine receptors. The syndrome begins with marked muscle rigidity. If sweating is impaired, a fever may ensue. The stress leukocytosis and high fever associated with this syndro ...
Adrenoceptor Antagonists
... block of β2 receptors. In bronchial asthma it is preferable to use selective β1 receptor blockers if they are needed for other conditions. C. Effects on the eye: Reduce intraocular pressure (useful for glaucoma) due to reduction in aqueous ...
... block of β2 receptors. In bronchial asthma it is preferable to use selective β1 receptor blockers if they are needed for other conditions. C. Effects on the eye: Reduce intraocular pressure (useful for glaucoma) due to reduction in aqueous ...
All of the following glands consist of paired or multiple structures
... The secretion of hormones by the anterior pituitary is often controlled by releasing hormones secreted by the ________. ...
... The secretion of hormones by the anterior pituitary is often controlled by releasing hormones secreted by the ________. ...
ACTH
... • Autocrine communication: cells secrete chemical messengers that in some situations bind to receptors on the original cells. ...
... • Autocrine communication: cells secrete chemical messengers that in some situations bind to receptors on the original cells. ...
6. Physiology of heart. Physiological bases of hemo dynamic
... Sensory innervations of heart and vessels is present by nerve ending. Receptors divided by it function on mechanoreceptors, which are reacted on the changing of arterial pressure and chemo receptors, which are reacted on the changing of chemical composition of blood. Irritation for mechanoreceptors ...
... Sensory innervations of heart and vessels is present by nerve ending. Receptors divided by it function on mechanoreceptors, which are reacted on the changing of arterial pressure and chemo receptors, which are reacted on the changing of chemical composition of blood. Irritation for mechanoreceptors ...
adrenergic agents - NC State Veterinary Medicine
... Currently, this class includes non-selective (timolol, levobunolol, metipranolol, carteolol) and β 1 specific (betaxolol) agents. How blockade of the β-receptors of the ciliary body (CB) epithelium leads to ocular hypotensive effects of these drugs is not known. It is suspected that the tonic sympat ...
... Currently, this class includes non-selective (timolol, levobunolol, metipranolol, carteolol) and β 1 specific (betaxolol) agents. How blockade of the β-receptors of the ciliary body (CB) epithelium leads to ocular hypotensive effects of these drugs is not known. It is suspected that the tonic sympat ...
Drug and Active Principle:
... If no action potential follows, Ca2+ is taken up by the SR and the myofilaments relax. Clinically important drugs (with the exception of dantrolene) all interfere with neural control of the muscle cell. Centrally acting muscle relaxants, lower muscle tone by augmenting the activity of intraspi ...
... If no action potential follows, Ca2+ is taken up by the SR and the myofilaments relax. Clinically important drugs (with the exception of dantrolene) all interfere with neural control of the muscle cell. Centrally acting muscle relaxants, lower muscle tone by augmenting the activity of intraspi ...
8Aldosterone 8Na + secretion 8 H 2 O reabsorption9 urine volume
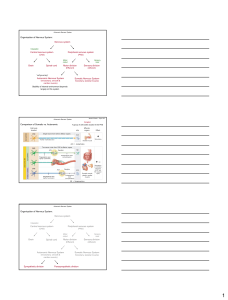
... • 3. Identify hormones, their organ of secretion, the type of molecule their structure represents, their primary target organ, the effect of the hormone on the body, and any pathologies associated with the deficiency or excess of the hormone. ...
... • 3. Identify hormones, their organ of secretion, the type of molecule their structure represents, their primary target organ, the effect of the hormone on the body, and any pathologies associated with the deficiency or excess of the hormone. ...
Document
... How is the adrenal medulla able to affect target cells throughout the body? a. It releases hormones into ducts within itself. b. Epinephrine and norepinephrine act as hormones and travel through capillaries. c. Effects are shorter lasting than those produced by sympathetic innervation. d. It has lon ...
... How is the adrenal medulla able to affect target cells throughout the body? a. It releases hormones into ducts within itself. b. Epinephrine and norepinephrine act as hormones and travel through capillaries. c. Effects are shorter lasting than those produced by sympathetic innervation. d. It has lon ...
Blood Pressure Response to Central and/or Peripheral Inhibition of
... JESSIE BLACK, BERNARD WAEBER, MARGARET R. BRESNAHAN, IRENE GAVRAS, AND HARALAMBOS GAVRAS SUMMARY We studied the effects on blood pressure and heart rate of two different phenylethanolamine JV-methyltransferase (PNMT) inhibitors in normotensive, in two-kidney renal hypertensive, and in deoxycorticost ...
... JESSIE BLACK, BERNARD WAEBER, MARGARET R. BRESNAHAN, IRENE GAVRAS, AND HARALAMBOS GAVRAS SUMMARY We studied the effects on blood pressure and heart rate of two different phenylethanolamine JV-methyltransferase (PNMT) inhibitors in normotensive, in two-kidney renal hypertensive, and in deoxycorticost ...
St. John`s Wort
... Although St. John’s Wort is widely used and accepted in Europe, specifically Germany, it is not FDA approved in the United States for medical purposes Since it is not regulated in the U.S., there is no regulatory oversight of the manufacturing, distributing and labeling of St. John’s Wort, therefore ...
... Although St. John’s Wort is widely used and accepted in Europe, specifically Germany, it is not FDA approved in the United States for medical purposes Since it is not regulated in the U.S., there is no regulatory oversight of the manufacturing, distributing and labeling of St. John’s Wort, therefore ...
Chapter 11 Quiz
... 1. Endocrine glands secrete their products into ducts. A.True B. False 2. Those hormones that are nonpolar can pass through the plasma membrane and are called A. hydrophilic. B. hydrophobic. C. lipophilic. D. Both hydrophobic and lipophilic are correct. 3. Responsiveness of cells to hormones is dete ...
... 1. Endocrine glands secrete their products into ducts. A.True B. False 2. Those hormones that are nonpolar can pass through the plasma membrane and are called A. hydrophilic. B. hydrophobic. C. lipophilic. D. Both hydrophobic and lipophilic are correct. 3. Responsiveness of cells to hormones is dete ...
The Nervous system
... The forebrain consists of cerebrum, thalamus and hypothalamus. Cerebrum forms the major part of the human brain. A deep cleft divides the cerebrum longitudinally into two halves, which are termed as the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The hemispheres are connected by a tract of nerve fibres cal ...
... The forebrain consists of cerebrum, thalamus and hypothalamus. Cerebrum forms the major part of the human brain. A deep cleft divides the cerebrum longitudinally into two halves, which are termed as the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The hemispheres are connected by a tract of nerve fibres cal ...
Trauma: The Mind/Body Connection.1998
... with patients with other psychiatric diagnoses. Elevated levels of these hormones in the bloodstream may be experienced by the post-trauma patient as anxiety, panic, and agitation. Serotinergic dysfunction is probable in persons diagnosed with PTSD, as evidenced primarily by drug studies. Serotonin, ...
... with patients with other psychiatric diagnoses. Elevated levels of these hormones in the bloodstream may be experienced by the post-trauma patient as anxiety, panic, and agitation. Serotinergic dysfunction is probable in persons diagnosed with PTSD, as evidenced primarily by drug studies. Serotonin, ...
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTICS -study of rational use of drugs in the
... Presence of ganglia in ANS (absent in SomNS) ganglion - collection of nerve cell bodies located outside the CNS [dendrites are so small so illustration of neuron is usually body at axon lang) c. Action/effect: ANS - automatic, independent, involuntary ; SomNS - voluntary (skeletal muscle) Synaptic N ...
... Presence of ganglia in ANS (absent in SomNS) ganglion - collection of nerve cell bodies located outside the CNS [dendrites are so small so illustration of neuron is usually body at axon lang) c. Action/effect: ANS - automatic, independent, involuntary ; SomNS - voluntary (skeletal muscle) Synaptic N ...
Pharm II - 2-22
... Which of the following is evidence that contradicts with the dopamine hypothesis? a. Dopamine underactivity in the prefrontal cortex causes negative symptoms b.Time delay in reduction of psychotic symptoms after treatment c. Anti-schizophrenic drugs block dopamine receptors d.Amphetamine can induce ...
... Which of the following is evidence that contradicts with the dopamine hypothesis? a. Dopamine underactivity in the prefrontal cortex causes negative symptoms b.Time delay in reduction of psychotic symptoms after treatment c. Anti-schizophrenic drugs block dopamine receptors d.Amphetamine can induce ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Lecture 9
... > 140 mm/hg & diastolic > 90 mm/hg on 2 or more occasions after initial screening • Essential HTN = most common. About 90% of clients. * Exact Origin - unknown. Contributing Factors - family hx, hyperlipidemia, African American background, diabetes, obesity, aging, stress, excessive ETOH & smoking. ...
... > 140 mm/hg & diastolic > 90 mm/hg on 2 or more occasions after initial screening • Essential HTN = most common. About 90% of clients. * Exact Origin - unknown. Contributing Factors - family hx, hyperlipidemia, African American background, diabetes, obesity, aging, stress, excessive ETOH & smoking. ...
16. ADRENAL GLAND Adrenal gland
... provides the substrate required (amino acids) in the liver for the formation of glucose. As a result of the increase in the production of glucose in the liver, there is a complementary process of the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen in the liver. Furthermore, in order to ensure that more g ...
... provides the substrate required (amino acids) in the liver for the formation of glucose. As a result of the increase in the production of glucose in the liver, there is a complementary process of the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen in the liver. Furthermore, in order to ensure that more g ...
Unit 2B Review
... Describe the differences between excitatory and inhibitory, and explain how neurons fire differently for a stronger stimulus. Also mention whether or not the speed of transmission changes with the stimulus. ...
... Describe the differences between excitatory and inhibitory, and explain how neurons fire differently for a stronger stimulus. Also mention whether or not the speed of transmission changes with the stimulus. ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.