Reinforcing Effects of Psychostimulants in Humans Are Associated
... and Wise, 1977; Richardson et al., 1994; Self et al., 1996), its relevance in humans subjects, for whom its rewarding effects are associated with the subjective perception of pleasure or “high” (Fischman and Foltin, 1991), has not been investigated. It is also of importance to assess the role of DA ...
... and Wise, 1977; Richardson et al., 1994; Self et al., 1996), its relevance in humans subjects, for whom its rewarding effects are associated with the subjective perception of pleasure or “high” (Fischman and Foltin, 1991), has not been investigated. It is also of importance to assess the role of DA ...
Myers Update 2011
... disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination ...
... disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination ...
The Endocrine System!
... Adrenal Glands Become active when a person is angry or frightened Norepinephrine Epinephrine ...
... Adrenal Glands Become active when a person is angry or frightened Norepinephrine Epinephrine ...
Pharmacologic_Management_of_Parkinsonism
... MGP express primarily the excitatory D1 dopamine receptor, while the striatal neurons which project to the LGP and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differential effect on the two outflow pathways; the di ...
... MGP express primarily the excitatory D1 dopamine receptor, while the striatal neurons which project to the LGP and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differential effect on the two outflow pathways; the di ...
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Regulation of Melatonin Release in Chick
... Despite the capacity of the avian pineal gland for endogenous regulation of the rhythm of melatonin release, sympathetic innervation does play a role in the regulation of the melatonin rhythm. The innervation of the avian pineal gland is similar to that seen in other vertebrates (At&s Kappers, 1965) ...
... Despite the capacity of the avian pineal gland for endogenous regulation of the rhythm of melatonin release, sympathetic innervation does play a role in the regulation of the melatonin rhythm. The innervation of the avian pineal gland is similar to that seen in other vertebrates (At&s Kappers, 1965) ...
Islamic University
... ( )-The cornea has no blood vessels. ( )-The dynamic equilibrium receptors are found in the semicircular canals. ( )-In cretinism, the body proportions remain childlike. ( )-anterior pituitary is controlled by thalamus. ...
... ( )-The cornea has no blood vessels. ( )-The dynamic equilibrium receptors are found in the semicircular canals. ( )-In cretinism, the body proportions remain childlike. ( )-anterior pituitary is controlled by thalamus. ...
Lecture 17. The main methods in endocrinology
... insufficiency, those with secondary adrenocortical insufficiency will have a significant increase in plasma cortisol or 24 - h urinary corticosteroid levels.) To distinguish between primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency, me have to find the level of plasma ACTH: primary shows increased, and se ...
... insufficiency, those with secondary adrenocortical insufficiency will have a significant increase in plasma cortisol or 24 - h urinary corticosteroid levels.) To distinguish between primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency, me have to find the level of plasma ACTH: primary shows increased, and se ...
The thyroid hormones
... insufficiency, those with secondary adrenocortical insufficiency will have a significant increase in plasma cortisol or 24 - h urinary corticosteroid levels.) To distinguish between primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency, me have to find the level of plasma ACTH: primary shows increased, and se ...
... insufficiency, those with secondary adrenocortical insufficiency will have a significant increase in plasma cortisol or 24 - h urinary corticosteroid levels.) To distinguish between primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency, me have to find the level of plasma ACTH: primary shows increased, and se ...
Name of Disorder: Posttraumatic stress disorder Essay Title: The
... comorbidity with other stress-related conditions including aggression, anxiety, and depression [3]. However, unlike most other stress-related conditions, PTSD patients often present with abnormally low concentrations of the stress hormone, cortisol, while sympathetic catecholamine concentrations, re ...
... comorbidity with other stress-related conditions including aggression, anxiety, and depression [3]. However, unlike most other stress-related conditions, PTSD patients often present with abnormally low concentrations of the stress hormone, cortisol, while sympathetic catecholamine concentrations, re ...
Chapter 18- The Endocrine System
... E) There will be fewer hormones in the blood and fewer hormone by-products in the urine. 10) Each of the following is a lipid-soluble hormone EXCEPT: A) aldosterone B) thyroid hormone C) insulin D) nitric oxide E) cortisone 11) Which of the following classes of hormones is water-soluble? A) eicosano ...
... E) There will be fewer hormones in the blood and fewer hormone by-products in the urine. 10) Each of the following is a lipid-soluble hormone EXCEPT: A) aldosterone B) thyroid hormone C) insulin D) nitric oxide E) cortisone 11) Which of the following classes of hormones is water-soluble? A) eicosano ...
GI Drugs
... Drugs that affect GI motility (used for irritable bowel syndrome, GERD, prevention of vomiting) Physiology of GI motility Afferent: Bolus of food, mechanically or chemically, activates enterochromaffin cells to release 5-HT Interneurons: 5-HT binds to 5-HT3 receptors on afferent neurons Effer ...
... Drugs that affect GI motility (used for irritable bowel syndrome, GERD, prevention of vomiting) Physiology of GI motility Afferent: Bolus of food, mechanically or chemically, activates enterochromaffin cells to release 5-HT Interneurons: 5-HT binds to 5-HT3 receptors on afferent neurons Effer ...
28.2 Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Plant Hormones Plants do not have endocrine systems or fluids that continuously circulate. Phhytohormones affect the cells in which they are synthesized. They may also reach nearby cells by diffusion or travel upward with water from the roots or downward with sugars made by photosynthesis in the lea ...
... Plant Hormones Plants do not have endocrine systems or fluids that continuously circulate. Phhytohormones affect the cells in which they are synthesized. They may also reach nearby cells by diffusion or travel upward with water from the roots or downward with sugars made by photosynthesis in the lea ...
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) 2016
... NMF Consensus Group Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) Page 1 of 3 This RHW document is a modification of Neomed version. Dosage schedules remain the same. However, information on the commercial preparations not used at RHW is deleted. The risk rating is modified as per the local health district policy. ...
... NMF Consensus Group Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) Page 1 of 3 This RHW document is a modification of Neomed version. Dosage schedules remain the same. However, information on the commercial preparations not used at RHW is deleted. The risk rating is modified as per the local health district policy. ...
Document
... severe persistent asthma following previous treatment with a short-acting beta agonist such as salbutamol and is prescribed concurrently with a corticosteroid, such as beclometasone. The primary noticeable difference of salmeterol to salbutamol is that the duration of action lasts approximately 12 h ...
... severe persistent asthma following previous treatment with a short-acting beta agonist such as salbutamol and is prescribed concurrently with a corticosteroid, such as beclometasone. The primary noticeable difference of salmeterol to salbutamol is that the duration of action lasts approximately 12 h ...
cAlnOfficial Journalofthe c.AmericanHeart cjlssociation
... liver and other tissues. Investigations in patients with Parkinson's disease demonstrated that oral administration of levodopa in doses of 1 to 1.5 g produces cardiac and natriuretic effects approximating the responses observed with intravenous infusions of dopamine at rates of 2 to 4 1tg/kg/min.2 O ...
... liver and other tissues. Investigations in patients with Parkinson's disease demonstrated that oral administration of levodopa in doses of 1 to 1.5 g produces cardiac and natriuretic effects approximating the responses observed with intravenous infusions of dopamine at rates of 2 to 4 1tg/kg/min.2 O ...
L 2 parathyroid and calcium homeostasis 25th september 2012
... – Membrane transport in sweat glands, salivary glands, and intestinal mucosa – They also have some glucocorticoid activity ...
... – Membrane transport in sweat glands, salivary glands, and intestinal mucosa – They also have some glucocorticoid activity ...
Module 7 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... • The principle that if a neuron fires it will always fire at the same intensity • All action potentials are of the same strength. • A neuron does NOT fire at 30%, 45% or 90% but at 100% each time it fires. ...
... • The principle that if a neuron fires it will always fire at the same intensity • All action potentials are of the same strength. • A neuron does NOT fire at 30%, 45% or 90% but at 100% each time it fires. ...
Module 7-1
... • The principle that if a neuron fires it will always fire at the same intensity • All action potentials are of the same strength. • A neuron does NOT fire at 30%, 45% or 90% but at 100% each time it fires. ...
... • The principle that if a neuron fires it will always fire at the same intensity • All action potentials are of the same strength. • A neuron does NOT fire at 30%, 45% or 90% but at 100% each time it fires. ...
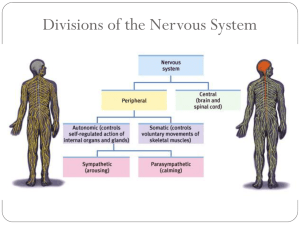
The Nervous System
... communication system that uses hormones to send messages through the bloodstream. • Hormones—chemical substances that carry messages through the body in blood. ...
... communication system that uses hormones to send messages through the bloodstream. • Hormones—chemical substances that carry messages through the body in blood. ...
Neyroleptiklər
... Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome Is a rare but serious side effect of neuroleptic (antipsychotic) therapy that can be lethal. It can arise at any time in the course of treatment and shows no predilection for age, duration of treatment, antipsychotic medication, or dose. ...
... Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome Is a rare but serious side effect of neuroleptic (antipsychotic) therapy that can be lethal. It can arise at any time in the course of treatment and shows no predilection for age, duration of treatment, antipsychotic medication, or dose. ...
Sympathomimetcs & Parasympatholytics
... Sympathomimetics Drugs that “mimic” the actions of the sympathetic neurotransmitters Stimulate Alpha, Beta-1, and Beta-2 receptors Also known as Adrenergics or Catecholamines ...
... Sympathomimetics Drugs that “mimic” the actions of the sympathetic neurotransmitters Stimulate Alpha, Beta-1, and Beta-2 receptors Also known as Adrenergics or Catecholamines ...
Power Point - Science Olympiad
... Parathyroid These four little glands are embedded in the thyroid gland They secrete parathyroid hormone which regulates the amount of calcium in the blood and its absorption by bones ...
... Parathyroid These four little glands are embedded in the thyroid gland They secrete parathyroid hormone which regulates the amount of calcium in the blood and its absorption by bones ...
BCH 560 hormones (adrenal gland)
... released into the plasma in free form as soon as the free hormone concentration decreases. Plasma-binding proteins also protect the hormone from peripheral metabolism (notably by liver enzymes) and increase the half-life of biologically active forms. Because of their lipophilic nature, steroid hormo ...
... released into the plasma in free form as soon as the free hormone concentration decreases. Plasma-binding proteins also protect the hormone from peripheral metabolism (notably by liver enzymes) and increase the half-life of biologically active forms. Because of their lipophilic nature, steroid hormo ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.