Dopamine Hypothesis of Mania
... sites in the brain”, and elation (mania) resulted from an excessive activity of catecholamines (6). He emphasised the role of norepinephrine and not dopamine. One of the supports of this hypothesis was the effect of amphetamines which release catecholamines. Low doses of amphetamines produce a sta ...
... sites in the brain”, and elation (mania) resulted from an excessive activity of catecholamines (6). He emphasised the role of norepinephrine and not dopamine. One of the supports of this hypothesis was the effect of amphetamines which release catecholamines. Low doses of amphetamines produce a sta ...
Low potential of dobutamine and dopexamine to block intestinal
... mucosal dysfunction, promote bacterial translocation, and eventually give rise to multiple organ failure (8, 9). A well-established action of the older catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine on the gut, which may limit their therapeutic usefulness, is the inhibition of propulsive intestinal m ...
... mucosal dysfunction, promote bacterial translocation, and eventually give rise to multiple organ failure (8, 9). A well-established action of the older catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine on the gut, which may limit their therapeutic usefulness, is the inhibition of propulsive intestinal m ...
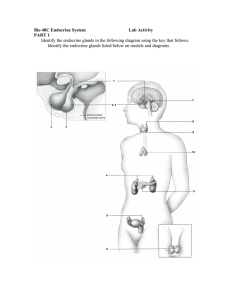
File - Endocrine System
... _____ adrenal glands (a-DRĒ-nal) This is a triangular shaped gland embedded in adipose tissue at the superior borders of the kidneys. It consists of an outer adrenal cortex and inner adrenal medulla.) _____ adrenal cortex _____ adrenal medulla (me-DUL-a) _____ pancreas (PAN-krē-as) (The pancreas is ...
... _____ adrenal glands (a-DRĒ-nal) This is a triangular shaped gland embedded in adipose tissue at the superior borders of the kidneys. It consists of an outer adrenal cortex and inner adrenal medulla.) _____ adrenal cortex _____ adrenal medulla (me-DUL-a) _____ pancreas (PAN-krē-as) (The pancreas is ...
Ganglionic Blocking Drugs and Nicotine
... is high at the time ganglion blockade is induced, tachycardia results. If heart rate is high, a decrease in rate may be seen. The extent of the hypotension, especially postural hypotension, produced by a ganglionic blocking agent also depends on the degree of sympathetic tone at the time of drug adm ...
... is high at the time ganglion blockade is induced, tachycardia results. If heart rate is high, a decrease in rate may be seen. The extent of the hypotension, especially postural hypotension, produced by a ganglionic blocking agent also depends on the degree of sympathetic tone at the time of drug adm ...
Pay Attention: Ritalin Acts Much Like Cocaine
... Methylphenidate flips the relationship, upping the signal and reducing the noise. After someone swallows methylphenidate, it enters the bloodstream and eventually finds the brain, where it blocks dopamine transporters and increases attention signaling. Again, cocaine acts the same way. But the two d ...
... Methylphenidate flips the relationship, upping the signal and reducing the noise. After someone swallows methylphenidate, it enters the bloodstream and eventually finds the brain, where it blocks dopamine transporters and increases attention signaling. Again, cocaine acts the same way. But the two d ...
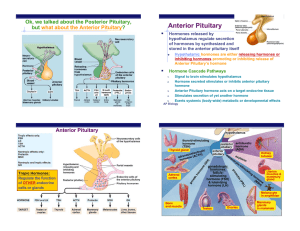
Self Quiz - Endocrine System
... A) Only anterior pituitary gland is permeable to GnRH. B) Only the anterior pituitary gland is vascular. C) Only the anterior pituitary gland is connected by neurons to the hypothalamus. D) Only the anterior pituitary gland is connected to a duct carrying GnRH. E) Only the anterior pituitary gland h ...
... A) Only anterior pituitary gland is permeable to GnRH. B) Only the anterior pituitary gland is vascular. C) Only the anterior pituitary gland is connected by neurons to the hypothalamus. D) Only the anterior pituitary gland is connected to a duct carrying GnRH. E) Only the anterior pituitary gland h ...
Hormonal Responses to Exercise
... Neuroendocrinology 神經內分泌學 • Sense information, organize appropriate responses, deliver messages to proper organs or tissues • Endocrine glands 腺體 release hormones directly into the blood • Hormones alter the activity of tissues that possess receptors to which the hormone can bind • The plasma hormo ...
... Neuroendocrinology 神經內分泌學 • Sense information, organize appropriate responses, deliver messages to proper organs or tissues • Endocrine glands 腺體 release hormones directly into the blood • Hormones alter the activity of tissues that possess receptors to which the hormone can bind • The plasma hormo ...
Endocrine System Notes - Wiki-Health
... functions through a network of glands throughout the body Glands- A group of cells that secrete chemicals Glands select and remove materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body The glands of the Endocrine System are (13 of them) ...
... functions through a network of glands throughout the body Glands- A group of cells that secrete chemicals Glands select and remove materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body The glands of the Endocrine System are (13 of them) ...
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
... drug also has vasodilatory effects that significantly improve cerebral and myocardial blood flow.21 These vasodilatory effects are due to nitric oxide—a mediator of vasodilation.21 Despite early promising studies, vasopressin has not been shown to be superior to epinephrine for treating CPA in human ...
... drug also has vasodilatory effects that significantly improve cerebral and myocardial blood flow.21 These vasodilatory effects are due to nitric oxide—a mediator of vasodilation.21 Despite early promising studies, vasopressin has not been shown to be superior to epinephrine for treating CPA in human ...
9b-9c-9i LN - Walnut High School
... skeletal muscles to break down glycogen and increase glucose levels. • It causes fat cells to break down fats for production of carbohydrates. • This makes more chemical _____________ available and helps raise the blood glucose level back to normal. ...
... skeletal muscles to break down glycogen and increase glucose levels. • It causes fat cells to break down fats for production of carbohydrates. • This makes more chemical _____________ available and helps raise the blood glucose level back to normal. ...
Drugs for Parkinson`s disease
... Levodopa Mechanism: (3) Levodopa itself has minimal pharmacologic activity, in contrast to its decarboxylated product, dopamine. (4) Levodopa is rapidly decarboxylated in the gastrointestinal tract. Prior to the advent of decarboxylase inhibitors (carbidopa), large oral doses of levodopa were requi ...
... Levodopa Mechanism: (3) Levodopa itself has minimal pharmacologic activity, in contrast to its decarboxylated product, dopamine. (4) Levodopa is rapidly decarboxylated in the gastrointestinal tract. Prior to the advent of decarboxylase inhibitors (carbidopa), large oral doses of levodopa were requi ...
CHAPTER 6 NEUROSYSTEM - NOTES
... • One of the body’s two communication systems • A set of glands that produce hormones-chemical messengers that circulate in the blood ...
... • One of the body’s two communication systems • A set of glands that produce hormones-chemical messengers that circulate in the blood ...
Chapter 8
... higher blood pressure / increase in body temperature 11. Amphetamines are absorbed by the blood and distributed rapidly ...
... higher blood pressure / increase in body temperature 11. Amphetamines are absorbed by the blood and distributed rapidly ...
Strattera (atomoxetine)
... Strattera (atomoxetine) is the first in a new class of nonstimulant medications to be approved for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Its mode of action is unlike that of the stimulants, methylphenidate and amphetamines. Strattera therefore appears to have little or no ...
... Strattera (atomoxetine) is the first in a new class of nonstimulant medications to be approved for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Its mode of action is unlike that of the stimulants, methylphenidate and amphetamines. Strattera therefore appears to have little or no ...
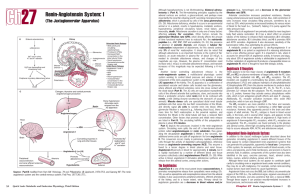
Renin-Angiotensin System: I
... walls, in the brain, and in several other organs, and appears to help mediate many of the known effects of angiotensin II. High levels of angiotensin II down-regulate AT1A receptors, while AT1B receptors are up-regulated. The AT1B receptors are found primarily in the pituitary and adrenal cortex, wh ...
... walls, in the brain, and in several other organs, and appears to help mediate many of the known effects of angiotensin II. High levels of angiotensin II down-regulate AT1A receptors, while AT1B receptors are up-regulated. The AT1B receptors are found primarily in the pituitary and adrenal cortex, wh ...
Lecture 4_Circulation of blood and its regulation. Features of
... Sensory innervations of heart and vessels is present by nerve ending. Receptors divided by it function on mechanoreceptors, which are reacted on the changing of arterial pressure and chemo receptors, which are reacted on the changing of chemical composition of blood. Irritation for mechanoreceptors ...
... Sensory innervations of heart and vessels is present by nerve ending. Receptors divided by it function on mechanoreceptors, which are reacted on the changing of arterial pressure and chemo receptors, which are reacted on the changing of chemical composition of blood. Irritation for mechanoreceptors ...
Active potential of contractive heart cells Phases of active potential 0
... Sensory innervations of heart and vessels is present by nerve ending. Receptors divided by it function on mechanoreceptors, which are reacted on the changing of arterial pressure and chemo receptors, which are reacted on the changing of chemical composition of blood. Irritation for mechanoreceptors ...
... Sensory innervations of heart and vessels is present by nerve ending. Receptors divided by it function on mechanoreceptors, which are reacted on the changing of arterial pressure and chemo receptors, which are reacted on the changing of chemical composition of blood. Irritation for mechanoreceptors ...
Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology (BIOL3020)
... - prescribed pain killer Heroin: - illegal to manufacture, possess, or sell - used as a pain-killer as well as a recreational drug - highly addictive! ...
... - prescribed pain killer Heroin: - illegal to manufacture, possess, or sell - used as a pain-killer as well as a recreational drug - highly addictive! ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 10
... formation of angiotensin I, which is converted into angiotensin II. Angiotensin II increases aldosterone production. Aldosterone increases water retention, which increases blood volume (and blood pressure). Angiotensin II also constricts blood vessels, which helps raise blood pressure. ...
... formation of angiotensin I, which is converted into angiotensin II. Angiotensin II increases aldosterone production. Aldosterone increases water retention, which increases blood volume (and blood pressure). Angiotensin II also constricts blood vessels, which helps raise blood pressure. ...
endocrine system - Living Bhakti Studies
... collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate your body’s growth, metabolism and sexual development. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and transported to the tissues and organs throughout your body. The ...
... collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate your body’s growth, metabolism and sexual development. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and transported to the tissues and organs throughout your body. The ...
Stress materials - Stephenson College
... body’s response to stress, including the metabolism of fat, glucose, and protein. 4. Distress is stress caused by adverse events that produce negative effects. 5. The endocrine glands are ductless glands that empty their hormonal products directly into the blood. Endocrine glands include the pituita ...
... body’s response to stress, including the metabolism of fat, glucose, and protein. 4. Distress is stress caused by adverse events that produce negative effects. 5. The endocrine glands are ductless glands that empty their hormonal products directly into the blood. Endocrine glands include the pituita ...
Epinephrine
... which action is mediated through adrenergic receptors. It is adrenergic receptor agonist. It binds to α1 receptors of liver cells, which activate inositol-phospholipid signaling pathway, signaling the phosphorylation of insulin, leading to reduced ability of insulin to bind to its receptors. Epineph ...
... which action is mediated through adrenergic receptors. It is adrenergic receptor agonist. It binds to α1 receptors of liver cells, which activate inositol-phospholipid signaling pathway, signaling the phosphorylation of insulin, leading to reduced ability of insulin to bind to its receptors. Epineph ...
Pellow, S., File, S.E. (1986). Anxiolytic and anxiogenic drug effects
... for the antagonist prazosin than for yohimbine (an antagonist of α2 receptors) (Hoffman et al., 1980). In this regard, it has been reported that stress-induced cognitive deficits were blocked by infusion of the α1 receptor antagonist (Ramos & Arnsten, 2007). ...
... for the antagonist prazosin than for yohimbine (an antagonist of α2 receptors) (Hoffman et al., 1980). In this regard, it has been reported that stress-induced cognitive deficits were blocked by infusion of the α1 receptor antagonist (Ramos & Arnsten, 2007). ...
Antidepressant drug overdoses in dogs
... you must closely monitor affected dogs. Treatment is symptomatic and supportive. You can use activated charcoal, but the risk of aspiration needs to be considered in a vomiting patient or one with neurologic signs. Seizures often abate with diazepam or barbiturate therapy. Metabolic acidosis may occ ...
... you must closely monitor affected dogs. Treatment is symptomatic and supportive. You can use activated charcoal, but the risk of aspiration needs to be considered in a vomiting patient or one with neurologic signs. Seizures often abate with diazepam or barbiturate therapy. Metabolic acidosis may occ ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.