The Endocrine System
... A group of ductless glands that release hormones into the circulatory system ...
... A group of ductless glands that release hormones into the circulatory system ...
The Endocrine System
... A group of ductless glands that release hormones into the circulatory system ...
... A group of ductless glands that release hormones into the circulatory system ...
The Endocrine System
... A group of ductless glands that release hormones into the circulatory system ...
... A group of ductless glands that release hormones into the circulatory system ...
1 Peyote Cactus San Pedro Cactus San Pedro Varieties
... As variant as they are, these groups confer psychedelic properties: methoxylation of the benzene ring e xerts amphetamine-like psychostimulant actions, presumably on dopaminergic and 5-HT2a receptor subtypes Psychedelic actions: full agonist action at post-synaptic serotonin 5-HT2a receptors Combina ...
... As variant as they are, these groups confer psychedelic properties: methoxylation of the benzene ring e xerts amphetamine-like psychostimulant actions, presumably on dopaminergic and 5-HT2a receptor subtypes Psychedelic actions: full agonist action at post-synaptic serotonin 5-HT2a receptors Combina ...
Amphetamines Megan Trimble 3/28/06
... The risk of HIV is not only increased by injection but also from the enhanced sexual feelings that arise from using these drugs – Amphetamine use can increase your libido or alter your perception in engaging in sexual activity – Rough sex is common with use which can lead to tears and abrasions resu ...
... The risk of HIV is not only increased by injection but also from the enhanced sexual feelings that arise from using these drugs – Amphetamine use can increase your libido or alter your perception in engaging in sexual activity – Rough sex is common with use which can lead to tears and abrasions resu ...
Circulatory shock Vasopressors
... adrenergic receptors relevant to vasopressor activity ▪ ά-1 in vascular walls, induces vasoconstriction. Also in the heart and can ↑ the duration of contraction but no ↑ chronotropy ▪ β-1 in the heart, mediate ↑ in inotropy and chronotropy with minimal vasoconstriction ▪ β-2 in blood vessels induce ...
... adrenergic receptors relevant to vasopressor activity ▪ ά-1 in vascular walls, induces vasoconstriction. Also in the heart and can ↑ the duration of contraction but no ↑ chronotropy ▪ β-1 in the heart, mediate ↑ in inotropy and chronotropy with minimal vasoconstriction ▪ β-2 in blood vessels induce ...
E5 - The human brain - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... The neurones keep going ‘till right inside the organ. Here they synapse with a motor neurone The transmitter secreted at these synapses is acetylcholine and this has an inhibitory effect on the organ Heart rate decreases, increased blood flow to the gut, constricts pupil to protect retina PNS functi ...
... The neurones keep going ‘till right inside the organ. Here they synapse with a motor neurone The transmitter secreted at these synapses is acetylcholine and this has an inhibitory effect on the organ Heart rate decreases, increased blood flow to the gut, constricts pupil to protect retina PNS functi ...
Vascular and Metabolic Effects of Circulating Epinephrine and
... A B S T R A C T Vascular and metabolic effects of circulating epinephrine and norepinephrine have been studied in relation to the plasma concentration of these amines in dogs. Intravenous infusion of epinephrine or norepinephrine (0.1,0.5, and 2.5 nmol x kg-i x min-') raised the plasma concentration ...
... A B S T R A C T Vascular and metabolic effects of circulating epinephrine and norepinephrine have been studied in relation to the plasma concentration of these amines in dogs. Intravenous infusion of epinephrine or norepinephrine (0.1,0.5, and 2.5 nmol x kg-i x min-') raised the plasma concentration ...
Biological Aspects of Psychology
... neurotransmitters “jump” across the gap between neurons, known as the synapse. The neurotransmitters then bind to their proper receptors on the dendrites of the receiving neuron (like a puzzle). ◦ Dendrites get excited when they detect neurotransmitters in their receptors & send info. to the cell ...
... neurotransmitters “jump” across the gap between neurons, known as the synapse. The neurotransmitters then bind to their proper receptors on the dendrites of the receiving neuron (like a puzzle). ◦ Dendrites get excited when they detect neurotransmitters in their receptors & send info. to the cell ...
Chapter4 Biological explanations and treatments
... Each of the millions of interconnecting nerves within the brain is known as a neuron. Activation of systems within the brain is the result of small electrical currents progressing along many different neurons. Critical to the flow of this current are the small gaps between neurons, known as synapses ...
... Each of the millions of interconnecting nerves within the brain is known as a neuron. Activation of systems within the brain is the result of small electrical currents progressing along many different neurons. Critical to the flow of this current are the small gaps between neurons, known as synapses ...
Effect of H antihistamines upon the central nervous system
... is to measure global (CBF) and regional cerebral blood flow (r-CBF). The cerebral circulation has its own self-regulating system that maintains brain perfusion constant between mean arterial pressure values of 60160 mmHg. Myogenic and metabolic mechanisms account for this phenomenon. From the metabo ...
... is to measure global (CBF) and regional cerebral blood flow (r-CBF). The cerebral circulation has its own self-regulating system that maintains brain perfusion constant between mean arterial pressure values of 60160 mmHg. Myogenic and metabolic mechanisms account for this phenomenon. From the metabo ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • The adrenal medulla, sweat glands, arrector pili muscles, kidneys, and most blood vessels receive only sympathetic fibers • The sympathetic division controls • Thermoregulatory responses to heat • Release of renin from the kidneys • Metabolic effects • Increases metabolic rates of cells • Raises b ...
... • The adrenal medulla, sweat glands, arrector pili muscles, kidneys, and most blood vessels receive only sympathetic fibers • The sympathetic division controls • Thermoregulatory responses to heat • Release of renin from the kidneys • Metabolic effects • Increases metabolic rates of cells • Raises b ...
endocrine_concept_map
... unable to detect Hormone B secreted by Cell M. In response to the increased levels of Hormone A, Cell M’s secretion of Hormone B increases. If Cell D could not produce Hormone A, Cell M would not be stimulated to release Hormone B. The concentrations of both hormones would be zero. Liver cells relea ...
... unable to detect Hormone B secreted by Cell M. In response to the increased levels of Hormone A, Cell M’s secretion of Hormone B increases. If Cell D could not produce Hormone A, Cell M would not be stimulated to release Hormone B. The concentrations of both hormones would be zero. Liver cells relea ...
File
... -- reflex arcs that result in physical movement are controlled by the Somatic NS; thus, an involuntary reflex is generated in muscles that tend to be voluntarily controlled – this, so we do not have to actually think about certain stimuli, we can simply react in a quicker, involuntary manner. Autono ...
... -- reflex arcs that result in physical movement are controlled by the Somatic NS; thus, an involuntary reflex is generated in muscles that tend to be voluntarily controlled – this, so we do not have to actually think about certain stimuli, we can simply react in a quicker, involuntary manner. Autono ...
see p. Psy15 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... lipophilic - readily penetrate into CNS, long T½ (e.g. 4-17 hours for IMIPRAMINE). divided doses may minimize side effects, but once-daily dosing (often at bedtime) is feasible because of long half-life and sedating properties. variable first pass metabolism in liver → low and inconsistent bio ...
... lipophilic - readily penetrate into CNS, long T½ (e.g. 4-17 hours for IMIPRAMINE). divided doses may minimize side effects, but once-daily dosing (often at bedtime) is feasible because of long half-life and sedating properties. variable first pass metabolism in liver → low and inconsistent bio ...
Prototype drug - Nursing Pharmacology
... Activation increases heart rate and force of contraction of heart. Increases release of renin ...
... Activation increases heart rate and force of contraction of heart. Increases release of renin ...
Section 4
... (5) Importance of the baroreceptor reflex Tonic regulation of blood pressure keep the arterial pressure relatively constant Pressure buffer system – reduce the blood pressure fluctuation during the daily events, such as changing of the posture, respiration, excitement, and so forth. ...
... (5) Importance of the baroreceptor reflex Tonic regulation of blood pressure keep the arterial pressure relatively constant Pressure buffer system – reduce the blood pressure fluctuation during the daily events, such as changing of the posture, respiration, excitement, and so forth. ...
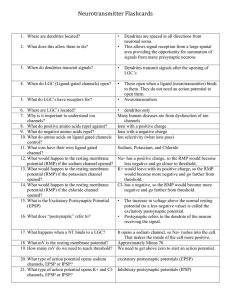
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... 98. What happens when the parasympathetic system is suppressed? 99. If a drug mimics the parasympathetic system, how will it affect the heart? 100. If a drug mimics the sympathetic system, how will it affect the heart? 101. What effect does epinephrine have on the heart rate? 102. What effect does a ...
... 98. What happens when the parasympathetic system is suppressed? 99. If a drug mimics the parasympathetic system, how will it affect the heart? 100. If a drug mimics the sympathetic system, how will it affect the heart? 101. What effect does epinephrine have on the heart rate? 102. What effect does a ...
File
... arterioles maintains arterial pressure, and variations in this tonic discharge are the mechanism by which carotid sinus feed-back regulation of blood pressure is affected. In addition, sympathetic discharge is decreased in fasting animals and increased when fasting animals are re-fed. These changes ...
... arterioles maintains arterial pressure, and variations in this tonic discharge are the mechanism by which carotid sinus feed-back regulation of blood pressure is affected. In addition, sympathetic discharge is decreased in fasting animals and increased when fasting animals are re-fed. These changes ...
Midterm review - February 26, 2004
... gentamicin). Requirements for minimum concentration (Cmin) for biological activity mean you have to keep levels above a threshold (gentamicin). Renal clearance declines in renal failure, and for renally excreted drugs a patient could accumulate toxic levels. Basic strategies in renal failure patient ...
... gentamicin). Requirements for minimum concentration (Cmin) for biological activity mean you have to keep levels above a threshold (gentamicin). Renal clearance declines in renal failure, and for renally excreted drugs a patient could accumulate toxic levels. Basic strategies in renal failure patient ...
Neurotransmitters: Their Role Within the Body
... drugs exert their effects by altering the actions of some neurotransmitter system, and the great majority of these act through transmitters other than glutamate or GABA. Addictive drugs such as cocaine, amphetamine, and heroin, for example, exert their effects primarily on the dopamine system. ...
... drugs exert their effects by altering the actions of some neurotransmitter system, and the great majority of these act through transmitters other than glutamate or GABA. Addictive drugs such as cocaine, amphetamine, and heroin, for example, exert their effects primarily on the dopamine system. ...
Pharmacology of the autonomic nervous system for dental students
... With respect to ’global function’, the sympathetic distribution is to effectors throughout the body, whereas the parasympathetic distribution is much more limited. In most of the blood vessels, only sympathetic nerves regulate the tone of smooth muscles. The sympathetic system is not essential for l ...
... With respect to ’global function’, the sympathetic distribution is to effectors throughout the body, whereas the parasympathetic distribution is much more limited. In most of the blood vessels, only sympathetic nerves regulate the tone of smooth muscles. The sympathetic system is not essential for l ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.