DNA to Disease
... Name _______________________________________________________________________ DNA to Disease (23pts) Introduction We’ve learned that DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents, but have you ever thought about what exactly this DNA encodes for? How do our cells use DNA as a ...
... Name _______________________________________________________________________ DNA to Disease (23pts) Introduction We’ve learned that DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents, but have you ever thought about what exactly this DNA encodes for? How do our cells use DNA as a ...
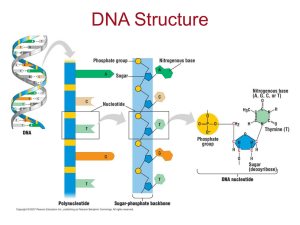
1. A nucleotide is a ______. 2. DNA consists of two antiparallel
... The function of ribosomes in the cell is _______ Similar to the complementary purine-pyrimidine relationship observed in DNA, which of the following choices pairs with adenine in RNA? If the DNA sequence is ATCGCTCC, the corresponding bases in mRNA are Vertebrate cells apparently possess a protein ...
... The function of ribosomes in the cell is _______ Similar to the complementary purine-pyrimidine relationship observed in DNA, which of the following choices pairs with adenine in RNA? If the DNA sequence is ATCGCTCC, the corresponding bases in mRNA are Vertebrate cells apparently possess a protein ...
Biotech
... technique to multiply a sample of DNA many times in a short period of time. It supplies the scientist with sufficient DNA for further testing. http://www.dnalc.org/resources/animations/pcr.html ...
... technique to multiply a sample of DNA many times in a short period of time. It supplies the scientist with sufficient DNA for further testing. http://www.dnalc.org/resources/animations/pcr.html ...
Topics in Computational Biology
... The genome contained within a human cell is very large and complex. It holds all of the genetic information necessary for its creation and function encoded with a total of six feet of DNA. The goals of the Human Genome Initiative (HGI), as framed by the National Institutes of Health and the Departme ...
... The genome contained within a human cell is very large and complex. It holds all of the genetic information necessary for its creation and function encoded with a total of six feet of DNA. The goals of the Human Genome Initiative (HGI), as framed by the National Institutes of Health and the Departme ...
Structural/functional study of a transcripton initiation
... Structural Biology of Protein & Nucleic Acid Complexes and Molecular Machines The group is engaged in the analysis of proteins and nucleic acids complexes using a number of molecular biology and structural biology techniques. Protein-nucleic acid complexes are prepared and crystallized for X-ray dif ...
... Structural Biology of Protein & Nucleic Acid Complexes and Molecular Machines The group is engaged in the analysis of proteins and nucleic acids complexes using a number of molecular biology and structural biology techniques. Protein-nucleic acid complexes are prepared and crystallized for X-ray dif ...
Modern Taxonomy
... from a common ancestor without indication as to how far removed species are from each other • Clade – a group of related organisms representing a complete branch of a biological tree • Derived characters – a character shared by all members of a branch but not present before the branch in cladograms ...
... from a common ancestor without indication as to how far removed species are from each other • Clade – a group of related organisms representing a complete branch of a biological tree • Derived characters – a character shared by all members of a branch but not present before the branch in cladograms ...
Genetic Disorders
... to infection, and blocks the pancreas, which stops digestive enzymes Caused by a mutation in a single gene ...
... to infection, and blocks the pancreas, which stops digestive enzymes Caused by a mutation in a single gene ...
Lecture TandT
... Transcription: From DNA to RNA – In transcription, • Genetic information is transferred from DNA to RNA. • RNA polymerase is the enzyme for the job. ...
... Transcription: From DNA to RNA – In transcription, • Genetic information is transferred from DNA to RNA. • RNA polymerase is the enzyme for the job. ...
Chapter 12 Notes - White Plains Public Schools
... RNA and DNA DNA= “Master plan” -Stays in the nucleus RNA= “Blueprint” – Leaves the nucleus to go to protein building sites (Ribosomes) in cytoplasm Chapter 12 Lesson 4 Mutations: Changes in DNA sequence that affect genetic information 2 Types 1. Gene mutations- changes in single genes 2. Chromos ...
... RNA and DNA DNA= “Master plan” -Stays in the nucleus RNA= “Blueprint” – Leaves the nucleus to go to protein building sites (Ribosomes) in cytoplasm Chapter 12 Lesson 4 Mutations: Changes in DNA sequence that affect genetic information 2 Types 1. Gene mutations- changes in single genes 2. Chromos ...
Investigating the effects of different types of mutations
... The sequence of DNA that encodes for a protein is called a gene. Genes encode for all proteinsfrom the enzymes needed in respiration to the tough keratin protein that makes up your fingernails. The first step in the production of a protein is creating a messenger that can pass from the DNA in the nu ...
... The sequence of DNA that encodes for a protein is called a gene. Genes encode for all proteinsfrom the enzymes needed in respiration to the tough keratin protein that makes up your fingernails. The first step in the production of a protein is creating a messenger that can pass from the DNA in the nu ...
DNA`s Discovery and Structure
... The DNA has a triplet code using only the 4 nucleotides, A,C,G and T. Only 3 nucleotides form a triplet which, when in a gene, codes for a part of a protein. There are 34 total different triplets that can be created but only 20 different amino acids. (Would a doublet code work just as well?? i.e. on ...
... The DNA has a triplet code using only the 4 nucleotides, A,C,G and T. Only 3 nucleotides form a triplet which, when in a gene, codes for a part of a protein. There are 34 total different triplets that can be created but only 20 different amino acids. (Would a doublet code work just as well?? i.e. on ...
Slide 1
... genes. The heritability of a trait may vary, depending on the range of populations and environments studied. ...
... genes. The heritability of a trait may vary, depending on the range of populations and environments studied. ...
Evolutionary genomics
... - in humans about 20% of our genome are LINE elements and about 15% are SINE elements. - if transposable elements insert into coding DNA regions, they will likely disrupt the function of that gene and experience purifying selection. - as expected, TEs are most abundant in non-coding heterochromatic ...
... - in humans about 20% of our genome are LINE elements and about 15% are SINE elements. - if transposable elements insert into coding DNA regions, they will likely disrupt the function of that gene and experience purifying selection. - as expected, TEs are most abundant in non-coding heterochromatic ...
Molecular Systematics
... –Types of single nucleotide mutations • Mutations in coding DNA – Synonymous – silent » Do not change the gene product » Degenerate genetic code – Nonsynonymous – change the gene product – Neutral – can be synonymous or nonsynonymous but more likely to be synonymous » Amino acid mutabilities » Where ...
... –Types of single nucleotide mutations • Mutations in coding DNA – Synonymous – silent » Do not change the gene product » Degenerate genetic code – Nonsynonymous – change the gene product – Neutral – can be synonymous or nonsynonymous but more likely to be synonymous » Amino acid mutabilities » Where ...
PowerPoint- Protein Shape
... protein. Therefore it is the genetic code: DNA base sequence that ultimately determine a protein’s sequence of amino acids. ...
... protein. Therefore it is the genetic code: DNA base sequence that ultimately determine a protein’s sequence of amino acids. ...
BACKGROUND: UvrC is a DNA repair enzyme found in all
... BACKGROUND: UvrC is a DNA repair enzyme found in all prokaryotes and its critical in maintaining DNA integrity. What You Need to Know: NCBI Protein Blast FASTA format Blastp Other sequence alignment tools… YOUR JOB: A. Find an amino acid sequence of UvrC from five different prokaryotic species (one ...
... BACKGROUND: UvrC is a DNA repair enzyme found in all prokaryotes and its critical in maintaining DNA integrity. What You Need to Know: NCBI Protein Blast FASTA format Blastp Other sequence alignment tools… YOUR JOB: A. Find an amino acid sequence of UvrC from five different prokaryotic species (one ...
Uses
... The 942-base-pair fragment & The 4,599-base-pair fragment would be cleaved into two fragments of 2,305 (3,247 - 942) and 2,294 (4,599 - 2,305) giving 3 total fragments. EcoRI and EagI,PvuII Construct the plasmid ...
... The 942-base-pair fragment & The 4,599-base-pair fragment would be cleaved into two fragments of 2,305 (3,247 - 942) and 2,294 (4,599 - 2,305) giving 3 total fragments. EcoRI and EagI,PvuII Construct the plasmid ...
Old Biology 1 Final Exam
... 8) Plants produce oxygen when they photosynthesize. Where does the oxygen come from? A) splitting water molecules B) ATP synthesis C) the electron transport chain D) chlorophyll 9) Hunting reduced northern elephant seal population size to as few as 20 individuals at the end of the 19th century. Thei ...
... 8) Plants produce oxygen when they photosynthesize. Where does the oxygen come from? A) splitting water molecules B) ATP synthesis C) the electron transport chain D) chlorophyll 9) Hunting reduced northern elephant seal population size to as few as 20 individuals at the end of the 19th century. Thei ...
Chapter 14, Mutation and DNA repair
... • Silent mutations – produce no change in amino acid sequence (due to degeneracy of the genetic code.) (aka synonymous mutations). – CUU codes for leucine, but so does CUC, CUA, CUG, UUA, and UUG. ...
... • Silent mutations – produce no change in amino acid sequence (due to degeneracy of the genetic code.) (aka synonymous mutations). – CUU codes for leucine, but so does CUC, CUA, CUG, UUA, and UUG. ...