PPT NOTES_AP Biology Chapter 23 Notes
... o The _________________________ effect occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population Allele frequencies in the small founder population can be ______________________ from those in the larger parent population o The __________________________ effect is a sudden reduction in ...
... o The _________________________ effect occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population Allele frequencies in the small founder population can be ______________________ from those in the larger parent population o The __________________________ effect is a sudden reduction in ...
Name - Humble ISD
... definite end. Modern plants and animals- and, of course, humans- are subject to the forces of natural selection today, just as they were millions of years ago. In this activity, you will study the stages in the evolution of the horse in order to answer the questions: 1. Study the diagram of the four ...
... definite end. Modern plants and animals- and, of course, humans- are subject to the forces of natural selection today, just as they were millions of years ago. In this activity, you will study the stages in the evolution of the horse in order to answer the questions: 1. Study the diagram of the four ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... brought by tRNA and attached to the 1st amino acid. 5.) This continues until the “Stop” codon is reached. ...
... brought by tRNA and attached to the 1st amino acid. 5.) This continues until the “Stop” codon is reached. ...
Why Do Names Keep Changing
... - Humans average 8.4 introns / gene - Most excised at mRNA stage but some are left depending on the type of cell or the time ...
... - Humans average 8.4 introns / gene - Most excised at mRNA stage but some are left depending on the type of cell or the time ...
No Slide Title
... What is frequency of k allele in population? q2 = frequency of PKU in population = 0.0001. q = square root of q2 or 0.01. Frequency of allele k Therefore p the frequency of the K allele = 1 0.01 = 0.99 Frequency of carriers (heterozygotes) in population is 2pq = 2*0.99*0.01 = 0.0198 or almost 2% of ...
... What is frequency of k allele in population? q2 = frequency of PKU in population = 0.0001. q = square root of q2 or 0.01. Frequency of allele k Therefore p the frequency of the K allele = 1 0.01 = 0.99 Frequency of carriers (heterozygotes) in population is 2pq = 2*0.99*0.01 = 0.0198 or almost 2% of ...
BiotechnologySimple
... genetic material (DNA) as the original organism – an EXACT COPY of the donor ...
... genetic material (DNA) as the original organism – an EXACT COPY of the donor ...
Pattern Recognition in Biological Sequences
... Signal-based methods look for short sequences that are almost invariably found in and around protein coding region. These signals represent binding sites of molecules involved in gene transcription process, in post-transcriptional modifications, etc. This is perhaps the way the gene expression machi ...
... Signal-based methods look for short sequences that are almost invariably found in and around protein coding region. These signals represent binding sites of molecules involved in gene transcription process, in post-transcriptional modifications, etc. This is perhaps the way the gene expression machi ...
Additional Lab Exercise: Amino Acid Sequence in
... sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, messenger RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in the formation of the final protein molecule. In DNA, a ...
... sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, messenger RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in the formation of the final protein molecule. In DNA, a ...
Genome projects and model organisms
... Circular chromosome of 580,070 bp Only 470 predicted genes for DNA replication, transcription and translation, DNA repair, cellular transport and energy ...
... Circular chromosome of 580,070 bp Only 470 predicted genes for DNA replication, transcription and translation, DNA repair, cellular transport and energy ...
Tools_and_Methods_of_Genetic_Engineering
... 3. alternates heat (denaturation) and cooling (RNA primers & DNA polmerase) by about 20 times to create enough DNA to perform studies 4. A single copy of DNA is not enough to do analyses upon, so many copies are created Gel electrophoresis fig 20.8, page 393 1. separates macromolecules (DNA, RNA, pr ...
... 3. alternates heat (denaturation) and cooling (RNA primers & DNA polmerase) by about 20 times to create enough DNA to perform studies 4. A single copy of DNA is not enough to do analyses upon, so many copies are created Gel electrophoresis fig 20.8, page 393 1. separates macromolecules (DNA, RNA, pr ...
Rhesus ALK-7 / ALK7 / ACVR1C Protein (Fc Tag)
... < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method ...
... < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method ...
Fishy Genetics: From DNA to Protein: The Central Dogma of Biology
... DNA is a very complex molecule. It stores the information for making proteins in the codes of its bases: A,T,C, & G. Proteins are long chain molecules (polymers) that are made of amino acids (monomers). There are 20 different amino acids. Prote ...
... DNA is a very complex molecule. It stores the information for making proteins in the codes of its bases: A,T,C, & G. Proteins are long chain molecules (polymers) that are made of amino acids (monomers). There are 20 different amino acids. Prote ...
Darwin`s revolution
... Darwin’s revolution • Evolution provides the unifying principle that underlies all of biology • In terms of the scientific method; support for this hypothesis comes from many observatiosn and experiments • Which is why this is called now, a theory of evolution ...
... Darwin’s revolution • Evolution provides the unifying principle that underlies all of biology • In terms of the scientific method; support for this hypothesis comes from many observatiosn and experiments • Which is why this is called now, a theory of evolution ...
Nucleic Acids Placemat
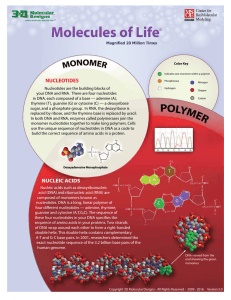
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
the language of biology - Gonzaga College High School
... English: sentences strung together give a single, coherent story Biology: there are often two versions of the story, one version coming from each parent of the organism. Figuring out version of the story gets "told" is the study of dominant and recessive genes. The biological story is the pattern o ...
... English: sentences strung together give a single, coherent story Biology: there are often two versions of the story, one version coming from each parent of the organism. Figuring out version of the story gets "told" is the study of dominant and recessive genes. The biological story is the pattern o ...
Evidence For Evolution File
... miller found his “ocean” teeming with amino acids the building blocks of protein! ...
... miller found his “ocean” teeming with amino acids the building blocks of protein! ...
Slide 1
... – Students should have an understanding of basic molecular biological techniques used in plant improvement – Techniques will be covered, but focus will be on Applications of the technology, not ...
... – Students should have an understanding of basic molecular biological techniques used in plant improvement – Techniques will be covered, but focus will be on Applications of the technology, not ...