3 Intro to Restriction Enzymes
... Restriction Enzymes can be used to make RECOMBINANT DNA! • The gene you are interested in inserting (aka the “gene of interest”) can be cut using a restriction enzyme. • What will happen if I also cut the other organisms DNA with the same Restriciton Enzyme? ...
... Restriction Enzymes can be used to make RECOMBINANT DNA! • The gene you are interested in inserting (aka the “gene of interest”) can be cut using a restriction enzyme. • What will happen if I also cut the other organisms DNA with the same Restriciton Enzyme? ...
Bits and pieces come to life
... than normal levels of a chemical called lycopene. Lycopene is a bright red compound found in tomatoes and is studied for its potential to prevent some types of cancer. Church’s research showed that cells can be selected for any trait a researcher wishes to screen for, not just lycopene production. R ...
... than normal levels of a chemical called lycopene. Lycopene is a bright red compound found in tomatoes and is studied for its potential to prevent some types of cancer. Church’s research showed that cells can be selected for any trait a researcher wishes to screen for, not just lycopene production. R ...
Bits and pieces come to life
... than normal levels of a chemical called lycopene. Lycopene is a bright red compound found in tomatoes and is studied for its potential to prevent some types of cancer. Church’s research showed that cells can be selected for any trait a researcher wishes to screen for, not just lycopene production. R ...
... than normal levels of a chemical called lycopene. Lycopene is a bright red compound found in tomatoes and is studied for its potential to prevent some types of cancer. Church’s research showed that cells can be selected for any trait a researcher wishes to screen for, not just lycopene production. R ...
adjusted p-value 3.317x10-25 Position in the ranked list of CD40L
... Supplementary Figure 1: Global gene expression changes of CD40L stimulation are highly comparable in distinct Burkitt Lymphoma cell lines (Ramos and BL2). Geneset Enrichment Analyses were utilized to investigate the similarities of the CD40L effects on gene expression profiles of Ramos and BL2 cells ...
... Supplementary Figure 1: Global gene expression changes of CD40L stimulation are highly comparable in distinct Burkitt Lymphoma cell lines (Ramos and BL2). Geneset Enrichment Analyses were utilized to investigate the similarities of the CD40L effects on gene expression profiles of Ramos and BL2 cells ...
mRNA
... DNA – The Genetic Code DNA is essential for all living organisms. The genetic code (genotype) determines how an organism looks and functions (phenotype) ...
... DNA – The Genetic Code DNA is essential for all living organisms. The genetic code (genotype) determines how an organism looks and functions (phenotype) ...
a@%,,$, 03%
... 23. All of the following can be used to describe a cloning vector EXCEPT (A) a cloning vector is a genetic hitchhiker (B) a cloning vector is a genetically engineered plasmid (C) virus can act as a cloning vector (D) a cloning vector is an artificial lipid that can be used to control cell replicati ...
... 23. All of the following can be used to describe a cloning vector EXCEPT (A) a cloning vector is a genetic hitchhiker (B) a cloning vector is a genetically engineered plasmid (C) virus can act as a cloning vector (D) a cloning vector is an artificial lipid that can be used to control cell replicati ...
Discovery reveals how bacteria distinguish harmful versus helpful
... difference," says researcher Luciano Marraffini, head of the Laboratory of Bacteriology. "The full genome of viruses in their lytic, or destructive phase, is transcribed. Meanwhile, a few of the genes from a virus are transcribed during its lysogenic, or dormant phase." Viruses in their lytic phase ...
... difference," says researcher Luciano Marraffini, head of the Laboratory of Bacteriology. "The full genome of viruses in their lytic, or destructive phase, is transcribed. Meanwhile, a few of the genes from a virus are transcribed during its lysogenic, or dormant phase." Viruses in their lytic phase ...
Word - LangdonBiology.org
... (to protect against destruction), (2) the addition of a poly-A tail of about 250 adenines added to the 3’ end (serves as a timer regulating the lifespan of the message), and (3) splicing, which cuts out introns (interrupting sequences of DNA), leaving the exons (coding regions). mRNA encodes protein ...
... (to protect against destruction), (2) the addition of a poly-A tail of about 250 adenines added to the 3’ end (serves as a timer regulating the lifespan of the message), and (3) splicing, which cuts out introns (interrupting sequences of DNA), leaving the exons (coding regions). mRNA encodes protein ...
2015 Orientation
... What is the name of the scientist famous for his work on evolution? What is a circular piece of DNA called What is a nucleotide made up of? What are erythrocytes? And what do they carry around the body? In what organelle does mitosis occur? Name one hormone that regulates blood glucose concentration ...
... What is the name of the scientist famous for his work on evolution? What is a circular piece of DNA called What is a nucleotide made up of? What are erythrocytes? And what do they carry around the body? In what organelle does mitosis occur? Name one hormone that regulates blood glucose concentration ...
SBI 4UW DNA Barcoding Assignment 2014 / 50 marks
... h) State why CO1 cannot be used in plants, and also state where genes that may be used for DNA barcoding have been located in plants. [2] ...
... h) State why CO1 cannot be used in plants, and also state where genes that may be used for DNA barcoding have been located in plants. [2] ...
Unit 04 Part III - Doral Academy Preparatory
... patient to help them recover from a disease. It could be used to help those suffering ...
... patient to help them recover from a disease. It could be used to help those suffering ...
View PDF - Redactor Publishing
... Investigator of Laboratory for Molecular Diagnostic of Rare Diseases, Department of Hematology and Oncology. He has done laboratory and research activity coordinating team of Laboratory Technicians and Biologists in the field of hematological diseases with particular regard to thalassemia, haemoglob ...
... Investigator of Laboratory for Molecular Diagnostic of Rare Diseases, Department of Hematology and Oncology. He has done laboratory and research activity coordinating team of Laboratory Technicians and Biologists in the field of hematological diseases with particular regard to thalassemia, haemoglob ...
Chapter. 21(Genomes and Their Evolution)
... Gene Density and Noncoding DNA • Humans and other mammals have the lowest gene density, or number of genes, in a given length of DNA. • Multicellular eukaryotes have many introns within genes and noncoding DNA between genes. • Much evidence indicates that noncoding DNA plays important roles in the ...
... Gene Density and Noncoding DNA • Humans and other mammals have the lowest gene density, or number of genes, in a given length of DNA. • Multicellular eukaryotes have many introns within genes and noncoding DNA between genes. • Much evidence indicates that noncoding DNA plays important roles in the ...
CH 16 PPT
... Griffith: bacterial work; transformation: change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of external substance (DNA) by a cell Avery: transformation agent was DNA ...
... Griffith: bacterial work; transformation: change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of external substance (DNA) by a cell Avery: transformation agent was DNA ...
Transcription
... Types Messenger (mRNA) Structure Single strand of RNA nucleotides complementary to a gene on the DNA coding strand. Purpose Carry protein-building instructions to ribosome. ...
... Types Messenger (mRNA) Structure Single strand of RNA nucleotides complementary to a gene on the DNA coding strand. Purpose Carry protein-building instructions to ribosome. ...
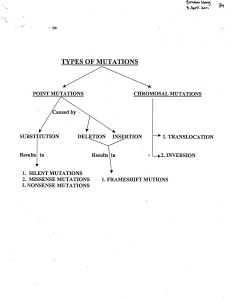
CHROMOSAL MUTATIONS SUBSTITUTION
... • · During translation, only the part of the protein that precedes the stop codon is produced, and the fragment may be digested by the proteases. ' Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell. ...
... • · During translation, only the part of the protein that precedes the stop codon is produced, and the fragment may be digested by the proteases. ' Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell. ...
viewpoint - Lindquist Lab
... basic concepts in immunology and revive, at least in part, the template theory—obviously the tertiary structure and function of a protein is not determined solely by its amino-acid sequence (Bussard, 2003). Similarly, Lindquist’s work on the role of [PS1+] in adapting to new environmental conditions ...
... basic concepts in immunology and revive, at least in part, the template theory—obviously the tertiary structure and function of a protein is not determined solely by its amino-acid sequence (Bussard, 2003). Similarly, Lindquist’s work on the role of [PS1+] in adapting to new environmental conditions ...
understanding dna molecule of heredity - Cal State LA
... The nucleotide is held together by a backbone made of sugars and phosphate group The backbone carries four types of molecules called bases It is the sequence of these four bases that encodes information The main job of the DNA is to encode the sequence of amino acids residues ...
... The nucleotide is held together by a backbone made of sugars and phosphate group The backbone carries four types of molecules called bases It is the sequence of these four bases that encodes information The main job of the DNA is to encode the sequence of amino acids residues ...