The Epidemiology Triangle
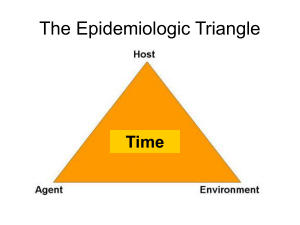
... related substance – Offers subsistence and lodging for a pathogen – Level of immunity, genetic make-up, state of health, and overall fitness within the host can determine the effect of a disease organism can have upon it. ...
... related substance – Offers subsistence and lodging for a pathogen – Level of immunity, genetic make-up, state of health, and overall fitness within the host can determine the effect of a disease organism can have upon it. ...
Emerging Diseases - UCLA Fielding School of Public Health
... sharing promoted the rapid spread of many infectious disease agents including the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis C (HCV) and genital chlamydiae which were unknown in the early part of the century. Changes in the Environment: Increasingly the growth of the population and the concomitan ...
... sharing promoted the rapid spread of many infectious disease agents including the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis C (HCV) and genital chlamydiae which were unknown in the early part of the century. Changes in the Environment: Increasingly the growth of the population and the concomitan ...
International Symposium on One Health and INDOHUN Annual
... The west African outbreak has broken through the barriers of isolation and into the general population, both in the countryside and the cities, and it was up and running before public-health personnel fully realized the ...
... The west African outbreak has broken through the barriers of isolation and into the general population, both in the countryside and the cities, and it was up and running before public-health personnel fully realized the ...
Beriberi, White Rice and Vitamin B: A Disease, a Cause and a Cure
... fully sensitive to the role of the social, political, and cultural context, here frequently a colonial one, in determining the problems tackled by scientists, the resources at their disposal, and the ways in which their ideas were received and implemented. He recognizes the contested nature of scien ...
... fully sensitive to the role of the social, political, and cultural context, here frequently a colonial one, in determining the problems tackled by scientists, the resources at their disposal, and the ways in which their ideas were received and implemented. He recognizes the contested nature of scien ...
Individuals with Bloodborne Infectious Diseases
... 4. Lone Star College-Kingwood is obligated to protect the privacy and confidentiality of any faculty member, student or staff member who has tested positive for an infectious disease. Dental personnel who pose a risk of transmitting an infectious disease must consult with appropriate health-care pro ...
... 4. Lone Star College-Kingwood is obligated to protect the privacy and confidentiality of any faculty member, student or staff member who has tested positive for an infectious disease. Dental personnel who pose a risk of transmitting an infectious disease must consult with appropriate health-care pro ...
Center for Disease Control (CDC) – National Center for Infectious
... http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/infectiousdiseases.html Click on the letter your disease starts with and you will see articles and other websites related to the topic. ...
... http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/infectiousdiseases.html Click on the letter your disease starts with and you will see articles and other websites related to the topic. ...
Immunity and Disease
... HIV attacks cells in the immune system called lymphocytes. Theses are the cells that normally fight antigens that cause disease. The body is left with no way to fight invading antigens, and the whole immune system breaks down. AIDS patients develop other diseases such as pneumonia, cancer, or tuberc ...
... HIV attacks cells in the immune system called lymphocytes. Theses are the cells that normally fight antigens that cause disease. The body is left with no way to fight invading antigens, and the whole immune system breaks down. AIDS patients develop other diseases such as pneumonia, cancer, or tuberc ...
Economic, Social, and/or Political Impact of Infectious Diseases
... continues, studies indicate that SARS will continue to be ‘the pandemic that could have been’ (3) ...
... continues, studies indicate that SARS will continue to be ‘the pandemic that could have been’ (3) ...
CIA National Infectious Disease Threat Report
... United States John C. Gannon, Chairman, National Intelligence Council am pleased to share with you this unclassified version of a new National Intelligence Estimate on the reemergence of the threat from infectious diseases worldwide and its implications for the United States. This report represents ...
... United States John C. Gannon, Chairman, National Intelligence Council am pleased to share with you this unclassified version of a new National Intelligence Estimate on the reemergence of the threat from infectious diseases worldwide and its implications for the United States. This report represents ...
ICD 9 Chap 11
... · Once a patient has been reported with code 042, this patient · Cannot be reported with V08 ever again, even after the manifestations have been resolved. ...
... · Once a patient has been reported with code 042, this patient · Cannot be reported with V08 ever again, even after the manifestations have been resolved. ...
STD, HIV, Hepatitis C, and other infectious diseases
... Sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs, are diseases that are mainly passed from one person to another through sexual activity. The most common include Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, genital warts, and HPV. Left untreated, STDs can lead to serious complications, including infertility, sever ...
... Sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs, are diseases that are mainly passed from one person to another through sexual activity. The most common include Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, genital warts, and HPV. Left untreated, STDs can lead to serious complications, including infertility, sever ...
Epidemiological Impact on the Economies of Poor Nations
... Global warming could cause another 50-80 million cases as diseasebearing mosquitoes move into new areas. While life expectancy has generally been increasing for decades, there has been a sharp reversal in recent years in sub-Saharan Africa. Causes may include the stresses of economic transition, det ...
... Global warming could cause another 50-80 million cases as diseasebearing mosquitoes move into new areas. While life expectancy has generally been increasing for decades, there has been a sharp reversal in recent years in sub-Saharan Africa. Causes may include the stresses of economic transition, det ...
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES I.
... Target 6A: Have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the spread of HIV/AIDS Target 6B: Achieve, by 2010, universal access to treatment for HIV/AIDS for all those who need it Target 6C: Have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the incidence of malaria and other major diseases – Prevalence and death ra ...
... Target 6A: Have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the spread of HIV/AIDS Target 6B: Achieve, by 2010, universal access to treatment for HIV/AIDS for all those who need it Target 6C: Have halted by 2015 and begun to reverse the incidence of malaria and other major diseases – Prevalence and death ra ...
PowerPoint for Communicable Diseases
... Infection occur when pathogens enter the body, multiply, and damage cells Bacteria-tiny one-celled organisms that live nearly everywhere o Common types: strep throat ( if not taken care of can cause heart damage), boils, bacterial pneumonia, impetigo, sinus infection, tuberculosis, hepatitis ...
... Infection occur when pathogens enter the body, multiply, and damage cells Bacteria-tiny one-celled organisms that live nearly everywhere o Common types: strep throat ( if not taken care of can cause heart damage), boils, bacterial pneumonia, impetigo, sinus infection, tuberculosis, hepatitis ...
The British Empire in North America The Clash of Culture Arriving in
... mumps, yellow fever, and pertussis (whooping cough). The indigenous Americas also had a number of endemic diseases, such as tuberculosis and an unusually virulent type of syphilis, which became rampant when brought back to the Old World. The transfer of disease between the Old and New Worlds was par ...
... mumps, yellow fever, and pertussis (whooping cough). The indigenous Americas also had a number of endemic diseases, such as tuberculosis and an unusually virulent type of syphilis, which became rampant when brought back to the Old World. The transfer of disease between the Old and New Worlds was par ...
FS_Live_Poultry_Newcastle_disease_FVSU.pdf
... and will cause a selflimiting conjunctivitis, most commonly seen in poultry workers. ...
... and will cause a selflimiting conjunctivitis, most commonly seen in poultry workers. ...
National Health Research Institutes
... drug resistance: Dr. Remko van Leeuwen, CEO at Madam Therapeutics, Amsterdam, Netherlands • Specific topics : 1.3 Suitability, safety, efficacy of therapies 1.4 Innovative therapeutic approaches and interventions. 2.3.1 Anti-microbial drug resistance 2.3.3 Potentially new and re-emerging epi ...
... drug resistance: Dr. Remko van Leeuwen, CEO at Madam Therapeutics, Amsterdam, Netherlands • Specific topics : 1.3 Suitability, safety, efficacy of therapies 1.4 Innovative therapeutic approaches and interventions. 2.3.1 Anti-microbial drug resistance 2.3.3 Potentially new and re-emerging epi ...
Infectious Diseases
... school will follow the infectious disease guidance from the Health Authority, in advising parents about whether or not a pupil should be in school. If a pupil in school becomes poorly, and is suspected of having an infectious disease, the pupil will be immediately removed from contact with other chi ...
... school will follow the infectious disease guidance from the Health Authority, in advising parents about whether or not a pupil should be in school. If a pupil in school becomes poorly, and is suspected of having an infectious disease, the pupil will be immediately removed from contact with other chi ...
SL 1979-192 - North Carolina General Assembly
... persons or animals, which have been exposed or are reasonably suspected of having been exposed to a communicable disease, for a period of time as may be necessary to prevent the spread of that disease. The term also means the authority to limit the freedom of movement of persons who have not receive ...
... persons or animals, which have been exposed or are reasonably suspected of having been exposed to a communicable disease, for a period of time as may be necessary to prevent the spread of that disease. The term also means the authority to limit the freedom of movement of persons who have not receive ...
Epidemiologist Program Manager
... Managerial medical epidemiological work. NATURE AND PURPOSE An employee in this class plans, supervises, and coordinates a statewide program for the control of communicable and/or chronic diseases. Responsibilities include directing an interdisciplinary team of public health professionals, such as s ...
... Managerial medical epidemiological work. NATURE AND PURPOSE An employee in this class plans, supervises, and coordinates a statewide program for the control of communicable and/or chronic diseases. Responsibilities include directing an interdisciplinary team of public health professionals, such as s ...
Slides 3
... Stirling A. Colgate, et al. 1989. Risk behavior-based model of the cubic growth of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA ...
... Stirling A. Colgate, et al. 1989. Risk behavior-based model of the cubic growth of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA ...
Out of Africa: How Localized Infections Might Become Global
... proportional decrease in both economic stability and the capacity for economic development This series of events would result in a further underfunding of the medical infrastructure and weakening of support to some the globe’s most exposed citizens ...
... proportional decrease in both economic stability and the capacity for economic development This series of events would result in a further underfunding of the medical infrastructure and weakening of support to some the globe’s most exposed citizens ...
2 tcp/rer/3402/edpr/fejzic
... Decresased food supply with higher prize Adoption of less productive and more costly system do decrease disease risk Constraints on national and international trade due to zoosanitary restrictions Indirect costs to turism and other related activities ...
... Decresased food supply with higher prize Adoption of less productive and more costly system do decrease disease risk Constraints on national and international trade due to zoosanitary restrictions Indirect costs to turism and other related activities ...
File - Mrs. R`s Health for PATH
... • Direct contact is rare in this route, for humans at least. More common are the indirect routes; foodstuffs or water become contaminated (by people not washing their hands before preparing food, or untreated sewage being released into a drinking water supply) and the people who eat and drink them b ...
... • Direct contact is rare in this route, for humans at least. More common are the indirect routes; foodstuffs or water become contaminated (by people not washing their hands before preparing food, or untreated sewage being released into a drinking water supply) and the people who eat and drink them b ...























