Vocabulary Terms
... Prion – (pronounced PREE-on) An infectious agent made only of proteins. Prions cause Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (Mad Cow) in cows and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) in humans. The disease is spread through abnormal proteins that cause other normal proteins to change to the prion's ab ...
... Prion – (pronounced PREE-on) An infectious agent made only of proteins. Prions cause Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (Mad Cow) in cows and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) in humans. The disease is spread through abnormal proteins that cause other normal proteins to change to the prion's ab ...
Introduction to Infection (and Disease Prevention) Directions
... b) Some examples of infectious diseases include: c) Some examples of non-infectious diseases are: d) The four main types of pathogens are: e) Give two examples of diseases caused by each type of pathogen: ...
... b) Some examples of infectious diseases include: c) Some examples of non-infectious diseases are: d) The four main types of pathogens are: e) Give two examples of diseases caused by each type of pathogen: ...
PLECONARIL – A NEW DRUG FOR ENTEROVIRAL INFECTIONS
... working out how diseases spread and cluster into groups and how they can be defeated. Testing the drugs now being researched includes using the common cold viruses (Rhinoviruses which are also included in the Picornavirus family) to judge the effect. Many drugs, eg, Disoxaril, Enviroxime, Piradovir ...
... working out how diseases spread and cluster into groups and how they can be defeated. Testing the drugs now being researched includes using the common cold viruses (Rhinoviruses which are also included in the Picornavirus family) to judge the effect. Many drugs, eg, Disoxaril, Enviroxime, Piradovir ...
Immunization - Abbott Animal Hospital
... Canine Parainfluenza: a cause of infectious tracheobronchitis or kennel cough. Parainfluenza is often a mild respiratory infection in otherwise healthy dogs. Rabies: is always fatal and attacks the nervous system, and is transmitted chiefly through the bite of an infected animal. Canine Leptospirosi ...
... Canine Parainfluenza: a cause of infectious tracheobronchitis or kennel cough. Parainfluenza is often a mild respiratory infection in otherwise healthy dogs. Rabies: is always fatal and attacks the nervous system, and is transmitted chiefly through the bite of an infected animal. Canine Leptospirosi ...
Everything the School Nurse is Required to Tell You
... reported to the Nurse at the time of the incident. After-school or out-of-school Functions: First aid kit provided for school-sponsored activities and custodians for preliminary treatment. All exposure accidents must be reported to the nurse at the earliest time possible upon return to school. ...
... reported to the Nurse at the time of the incident. After-school or out-of-school Functions: First aid kit provided for school-sponsored activities and custodians for preliminary treatment. All exposure accidents must be reported to the nurse at the earliest time possible upon return to school. ...
Diseases - WordPress.com
... • The sickle shaped cells carry little oxygen. • Symptoms include; joint and abdominal pain, high fever and jaundice. It can lead to weakness, wasting away (emaciation), kidney and heart failure. • Treatment & control: during crises patients can be given oxygen, drugs for pain and blood transfusions ...
... • The sickle shaped cells carry little oxygen. • Symptoms include; joint and abdominal pain, high fever and jaundice. It can lead to weakness, wasting away (emaciation), kidney and heart failure. • Treatment & control: during crises patients can be given oxygen, drugs for pain and blood transfusions ...
ASTMH Leadership May 2015 Hill Day Prep (PPT)
... through the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute for Infectious Diseases, the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, and the U.S. Naval Medical Research Center. Provide at least $32 billion to the National Institutes of Health with a commensurate funding to the National Institute of Allergy and I ...
... through the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute for Infectious Diseases, the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, and the U.S. Naval Medical Research Center. Provide at least $32 billion to the National Institutes of Health with a commensurate funding to the National Institute of Allergy and I ...
Pathogens Defence Mechanisms UNIT 11.4 Controlling infectious
... How can we stop pathogens getting in? 3. The breathing organs produce a sticky liquid ...
... How can we stop pathogens getting in? 3. The breathing organs produce a sticky liquid ...
Military Medicine - U.S. Military HIV Research Program
... international health problems, particularly in the area of tropical infectious diseases. Cutting edge vaccine development continues today in HIV, malaria, dengue and enteric diseases. The U.S. Military HIV Research Program (MHRP) is dedicated to HIV vaccine development, prevention, disease surveilla ...
... international health problems, particularly in the area of tropical infectious diseases. Cutting edge vaccine development continues today in HIV, malaria, dengue and enteric diseases. The U.S. Military HIV Research Program (MHRP) is dedicated to HIV vaccine development, prevention, disease surveilla ...
Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases Course 173:255
... adults with exposure to poultry in Asia: 800 subjects from KPP, Thailand and 800 subjects from Kampong Cham Province, ...
... adults with exposure to poultry in Asia: 800 subjects from KPP, Thailand and 800 subjects from Kampong Cham Province, ...
PEDS 9409 Pediatric Infectious Diseases
... Discuss the presentation of simple and complex pediatric infectious diseases. Identify when the assistance of the subspecialist is warranted. Describe the principles of infection control. Describe the basic techniques of bacterial and viral diagnostics and explain their use in the clinical setting ...
... Discuss the presentation of simple and complex pediatric infectious diseases. Identify when the assistance of the subspecialist is warranted. Describe the principles of infection control. Describe the basic techniques of bacterial and viral diagnostics and explain their use in the clinical setting ...
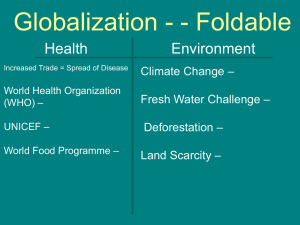
Globalization and the Environment
... Globalization and the Environment Globalization is an umbrella term for a complex series of economic, social, technological, cultural, and political changes seen as increasing interdependence, integration and interaction and interaction among people and companies in disparate locations. • Positive- ...
... Globalization and the Environment Globalization is an umbrella term for a complex series of economic, social, technological, cultural, and political changes seen as increasing interdependence, integration and interaction and interaction among people and companies in disparate locations. • Positive- ...
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: ______ VIRUS SPREAD SIMULATOR I. 1
... 1) Ebola virus particles occupy an infected person’s ____________ and other bodily fluids, which can enter another person through the __________, mucous membranes, scratches on the __________or from a hypodermic needle — not from from the __________ or from insects. The bodies of people who have die ...
... 1) Ebola virus particles occupy an infected person’s ____________ and other bodily fluids, which can enter another person through the __________, mucous membranes, scratches on the __________or from a hypodermic needle — not from from the __________ or from insects. The bodies of people who have die ...
fvrcp - Oak Harbor Pet Haven
... Panleukopenia (also known as feline distemper and infectious feline enteritis) is a highly contagious disease characterized by a short course and high mortality rate. The disease is caused by a parvovirus similar to the parvovirus seen in dogs. It is very resistant and may remain infectious in the e ...
... Panleukopenia (also known as feline distemper and infectious feline enteritis) is a highly contagious disease characterized by a short course and high mortality rate. The disease is caused by a parvovirus similar to the parvovirus seen in dogs. It is very resistant and may remain infectious in the e ...
COMMUNITY HEALTH AND EPIDEMIOLOGY EPID 828
... Forums of discussion. Each student will be assigned one or two weeks in which they have to contribute with an update of a recent discussion on an infectious disease related event. Student should summ ...
... Forums of discussion. Each student will be assigned one or two weeks in which they have to contribute with an update of a recent discussion on an infectious disease related event. Student should summ ...
RT A Infection control & Medical Emergencies
... Can grow in or on an animal or plant and cause diseases. Host: animal or plant that provides life support to another organism. Disease: Any change from the normal structure or function in the human body. Infection: Growth of a microorganism on or in a host. ...
... Can grow in or on an animal or plant and cause diseases. Host: animal or plant that provides life support to another organism. Disease: Any change from the normal structure or function in the human body. Infection: Growth of a microorganism on or in a host. ...
A. Gonorrhea, caused by Neisseria gonorrhea, gram negative
... pleomorphic, Gram-negative rod requiring X-factor for growth. Chancroid is characterized by a single or multiple soft, tender genital ulcers and enlarged, painful groin lymph nodes. II. Viral STDs are at least as common as bacterial STDs but they are not yet curable. A. Genital herpes simplex is a v ...
... pleomorphic, Gram-negative rod requiring X-factor for growth. Chancroid is characterized by a single or multiple soft, tender genital ulcers and enlarged, painful groin lymph nodes. II. Viral STDs are at least as common as bacterial STDs but they are not yet curable. A. Genital herpes simplex is a v ...
Case studies in pediatric infectious disease
... of the infection to manifestations. In addition, public health concerns, the need to identify sources, and risk posed to others are comprehensively discussed. Hence each scenario provides a useful and interesting means of addressing broader aspects of each infection, including infection control and ...
... of the infection to manifestations. In addition, public health concerns, the need to identify sources, and risk posed to others are comprehensively discussed. Hence each scenario provides a useful and interesting means of addressing broader aspects of each infection, including infection control and ...
Global Climate Change and Infectious Diseases
... Climate change, if it occurs at the level projected by current global circulation models, may have important and far-reaching effects on infectious diseases, especially those transmitted by poikilothermic arthropods such as mosquitoes and ticks. Although most scientists agree that global climate cha ...
... Climate change, if it occurs at the level projected by current global circulation models, may have important and far-reaching effects on infectious diseases, especially those transmitted by poikilothermic arthropods such as mosquitoes and ticks. Although most scientists agree that global climate cha ...
Risk factors for tuberculosis exposure should
... Recent immigrants (within 5 years) from high-prevalence countries Travel history to high-prevalence countries or significant contact with indigenous persons from such countries ...
... Recent immigrants (within 5 years) from high-prevalence countries Travel history to high-prevalence countries or significant contact with indigenous persons from such countries ...
Chapter 1
... resulting from the tsunami of 2004 in Indonesia and hurricane Katrina in the United States in 2005. Approximately 1.5 billion people do not have access to safe drinking water. This, and starvation, depletes a healthy immune system and leads to high child mortality rates. Natural catastrophic events ...
... resulting from the tsunami of 2004 in Indonesia and hurricane Katrina in the United States in 2005. Approximately 1.5 billion people do not have access to safe drinking water. This, and starvation, depletes a healthy immune system and leads to high child mortality rates. Natural catastrophic events ...
Joint Health and Wellbeing Strategy for Rotherham
... Social Prescribing – What is it? • Social prescribing is a framework for linking patients with non-medical needs affecting their health, wellbeing and ability to self-manage, to sources of support within the ...
... Social Prescribing – What is it? • Social prescribing is a framework for linking patients with non-medical needs affecting their health, wellbeing and ability to self-manage, to sources of support within the ...
2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE Normal flora – Many microbes
... multiplying and resulting in infection ...
... multiplying and resulting in infection ...