International Symposium on Infectious Diseases of Livestock
... concern must be paid to some pet birds, because of the severity and wide-spread nature of the disease. During the presentations of Avian diseases in this symposium, emphasis was placed on the prophylactic measures. Efforts have been made to seek and select some effective vaccination programs in each ...
... concern must be paid to some pet birds, because of the severity and wide-spread nature of the disease. During the presentations of Avian diseases in this symposium, emphasis was placed on the prophylactic measures. Efforts have been made to seek and select some effective vaccination programs in each ...
AEMT Transition - Unit 20 - Infectious Disease
... Prevention estimates that influenza kills somewhere between 3,000 and 50,000 people each year in the United States. • In 2009, Influenza A (H1N1) killed more than 18,000 people and was found in 214 countries. • The WHO designated H1N1 a pandemic. ...
... Prevention estimates that influenza kills somewhere between 3,000 and 50,000 people each year in the United States. • In 2009, Influenza A (H1N1) killed more than 18,000 people and was found in 214 countries. • The WHO designated H1N1 a pandemic. ...
An Update on Emerging Infectious Diseases
... The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on this map do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the World Health Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its fro ...
... The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on this map do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the World Health Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its fro ...
SIR models and CAs
... • Effective and fast control measures are needed • Models allow you to predict (estimate) when you don’t KNOW ...
... • Effective and fast control measures are needed • Models allow you to predict (estimate) when you don’t KNOW ...
Outbreak Investigation and Response
... monitor disease burden. HAIs in hospitals alone result in up to $33 billion in excess medical costs every year. The area of HAI demonstrates the profound impact state health agencies can have when armed with reliable data. In the relatively short time that state public health has been formally engag ...
... monitor disease burden. HAIs in hospitals alone result in up to $33 billion in excess medical costs every year. The area of HAI demonstrates the profound impact state health agencies can have when armed with reliable data. In the relatively short time that state public health has been formally engag ...
92. Applications of REPLIKINS® in FMDV surveillance and vaccine production
... • Named “Replikins” because of their close quantitative relationship to rapid replication and outbreaks • Discovered in the disease organism’s genome • Small peptides strictly defined by the presence and concentration of certain amino acids, and the spaces between them • Increase in the number of ...
... • Named “Replikins” because of their close quantitative relationship to rapid replication and outbreaks • Discovered in the disease organism’s genome • Small peptides strictly defined by the presence and concentration of certain amino acids, and the spaces between them • Increase in the number of ...
Disease Reporting - Northern Kentucky Health Department
... During business hours call 859.363.2070. If calling outside of normal business hours, call ...
... During business hours call 859.363.2070. If calling outside of normal business hours, call ...
CCIW Infectious Disease Disclosure Policy
... CCIW Policy Regarding Disclosure of Infectious Diseases CCIW member schools shall be required to formally disclose to competing schools any outbreak or cluster of any infectious diseases or conditions that, in the member school’s discretion, pose a serious risk to the health or safety of students, s ...
... CCIW Policy Regarding Disclosure of Infectious Diseases CCIW member schools shall be required to formally disclose to competing schools any outbreak or cluster of any infectious diseases or conditions that, in the member school’s discretion, pose a serious risk to the health or safety of students, s ...
Epidemics and Pandemic 8.L.1.2
... 10. Scientists are trying to prevent an epidemic of a highly contagious disease. What information should the scientists study first? A. how the disease reproduces C. the symptoms of the disease B. the treatment of the disease D. how the disease is transmitted 11. Which antibiotic was developed from ...
... 10. Scientists are trying to prevent an epidemic of a highly contagious disease. What information should the scientists study first? A. how the disease reproduces C. the symptoms of the disease B. the treatment of the disease D. how the disease is transmitted 11. Which antibiotic was developed from ...
(TB) at Cornell - Cornell Health
... third of the world’s population estimated to be infected with the bacteria that causes TB, and more than 8 million TB disease cases every year, TB is very much with us today, endemic in 125 countries and affecting all others. The World Health Organization has declared TB a global health emergency. T ...
... third of the world’s population estimated to be infected with the bacteria that causes TB, and more than 8 million TB disease cases every year, TB is very much with us today, endemic in 125 countries and affecting all others. The World Health Organization has declared TB a global health emergency. T ...
Case Study
... Core Case Study: The Global HIV/AIDS Epidemic Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); many secondary infections No vaccine to prevent or cure AIDS Expensive drugs—live longer 25 Million deaths, so far (1981 2007; alter country’s age structure ...
... Core Case Study: The Global HIV/AIDS Epidemic Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); many secondary infections No vaccine to prevent or cure AIDS Expensive drugs—live longer 25 Million deaths, so far (1981 2007; alter country’s age structure ...
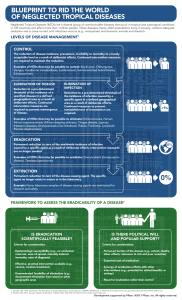
blueprint to rid the world of neglected tropical diseases
... BLUEPRINT TO RID THE WORLD OF NEGLECTED TROPICAL DISEASES Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of communicable diseases that occur in tropical and subtropical conditions in 149 countries and affect more than 1 billion people. These diseases mainly affect populations living in pover ...
... BLUEPRINT TO RID THE WORLD OF NEGLECTED TROPICAL DISEASES Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of communicable diseases that occur in tropical and subtropical conditions in 149 countries and affect more than 1 billion people. These diseases mainly affect populations living in pover ...
Using Social Media for Disease Surveillance
... These informal data are already changing the public health landscape. Nowhere was this clearer than with the 2009 emergence of the novel influenza A (H1N1) virus. In March and early April of that year, while much of the world was focusing on the threat of avian influenza originating in Asia, HealthM ...
... These informal data are already changing the public health landscape. Nowhere was this clearer than with the 2009 emergence of the novel influenza A (H1N1) virus. In March and early April of that year, while much of the world was focusing on the threat of avian influenza originating in Asia, HealthM ...
Goal 7 EOG REVIEW
... Disease: any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Noninfectious diseases: diseases that are inherited and are not spread from one organism to another Pathogen: any microbe that causes disease Infectious disease: disease that caused by a pathogen and can be spread fro ...
... Disease: any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Noninfectious diseases: diseases that are inherited and are not spread from one organism to another Pathogen: any microbe that causes disease Infectious disease: disease that caused by a pathogen and can be spread fro ...
HEALTH AND MEDICINE
... A SICK PERSON MUST WANT TO GET WELL A SICK PERSON MUST SEEK COMPETENT HELP ...
... A SICK PERSON MUST WANT TO GET WELL A SICK PERSON MUST SEEK COMPETENT HELP ...
Transmission of HIV
... Globally 33 million living with HIV 2.7 million new infections each year 2 million HIV-related deaths each year ...
... Globally 33 million living with HIV 2.7 million new infections each year 2 million HIV-related deaths each year ...
Dear Sir, We very much agree with the message conveyed by Lange
... have profound effects on the ecological health of environments that humans share with nonhuman animals and plants.(4) Variations in temperature, rainfall and humidity are expected to affect the transmission and infection rates of pathogens that are already present in the region, including vector-bor ...
... have profound effects on the ecological health of environments that humans share with nonhuman animals and plants.(4) Variations in temperature, rainfall and humidity are expected to affect the transmission and infection rates of pathogens that are already present in the region, including vector-bor ...
NON-HUMAN PRIMATES
... laboratory animals needed in the U.S. are non-human primates. Approximately 30 different species are studied by the research community.1 Many historic scientific breakthroughs, such as the discovery of the Rh factor and the development of a live polio virus vaccine were achieved through research wit ...
... laboratory animals needed in the U.S. are non-human primates. Approximately 30 different species are studied by the research community.1 Many historic scientific breakthroughs, such as the discovery of the Rh factor and the development of a live polio virus vaccine were achieved through research wit ...
Clinical finding: Infection with HIV-1 is associated with a progressive
... an infected person into the body of an uninfected person. A period of rapid viral replication ensues, leading to an abundance of virus in the peripheral blood. During primary infection, the level of HIV may reach several million virus particles per milliliter of blood. This response is accompanied b ...
... an infected person into the body of an uninfected person. A period of rapid viral replication ensues, leading to an abundance of virus in the peripheral blood. During primary infection, the level of HIV may reach several million virus particles per milliliter of blood. This response is accompanied b ...
A Webquest on Pandemics
... How do we protect health care workers (in the current outbreak of Ebola in West Africa over 125 health care worker have died)? How do we carry out “forward defense” with disease? How do we fund the enormous cost of tracking and preventing the spread of pandemics? Who should be in charge? WHO? What p ...
... How do we protect health care workers (in the current outbreak of Ebola in West Africa over 125 health care worker have died)? How do we carry out “forward defense” with disease? How do we fund the enormous cost of tracking and preventing the spread of pandemics? Who should be in charge? WHO? What p ...
Lecture 13
... In some parts of Eastern Europe and the former USSR, up to 90% of all children suffer from environmentally linked diseases. ...
... In some parts of Eastern Europe and the former USSR, up to 90% of all children suffer from environmentally linked diseases. ...
Epidemiology - Thomas-Estabrook
... • Endemic Diseases– diseases that occur regularly in a population as a matter of course • Epidemic– An unexpectedly large number of cases of an illness, specific health-related behavior, or other healthrelated event in a particular population. ...
... • Endemic Diseases– diseases that occur regularly in a population as a matter of course • Epidemic– An unexpectedly large number of cases of an illness, specific health-related behavior, or other healthrelated event in a particular population. ...
File
... THREATS TO HUMAN HEALTH PRESENTED BY VIRUSES When it was discovered that bacteria could cause disease, there were ...
... THREATS TO HUMAN HEALTH PRESENTED BY VIRUSES When it was discovered that bacteria could cause disease, there were ...
Chicken Infectious Anemia
... o Primarily causes T-cells suppression. o It is often complicated by secondary viral, bacterial, or fungal infections. o The disease produced in young chickens most frequently involves severe bone marrow depletion with a reduction in hematocrit values. o It plays a major role in a number of multifac ...
... o Primarily causes T-cells suppression. o It is often complicated by secondary viral, bacterial, or fungal infections. o The disease produced in young chickens most frequently involves severe bone marrow depletion with a reduction in hematocrit values. o It plays a major role in a number of multifac ...
File
... Commonly known as non-communicable diseases, abbreviated as NCDs, non-infectious diseases are those that are caused by factors such as genetics, environment, and lifestyle, and not by pathogens (disease-causing organisms). Non-infectious diseases do not pass on from one person to another. Common non ...
... Commonly known as non-communicable diseases, abbreviated as NCDs, non-infectious diseases are those that are caused by factors such as genetics, environment, and lifestyle, and not by pathogens (disease-causing organisms). Non-infectious diseases do not pass on from one person to another. Common non ...