Biology 320 Invertebrate Zoology Fall 2005
... Hydrostatic skeleton – animal has a water-filled cavity (i.e. gastrovascular cavity, coelom, etc.). Muscle contractions displace water, generating force that can be used to do work ...
... Hydrostatic skeleton – animal has a water-filled cavity (i.e. gastrovascular cavity, coelom, etc.). Muscle contractions displace water, generating force that can be used to do work ...
Classification of Animals 2014 use for notes
... – What does this mean? • Their cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. ...
... – What does this mean? • Their cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. ...
Classification and Introduction to Animals Chapter 18 & 34
... •Haploid stage characterized by sperm and eggs produced by meiotic division •In most animal species, a small flagellated sperm fertilizes a larger non-motile egg, forming a zygote ...
... •Haploid stage characterized by sperm and eggs produced by meiotic division •In most animal species, a small flagellated sperm fertilizes a larger non-motile egg, forming a zygote ...
Evolutionary Trends in Animals
... In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term. ...
... In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term. ...
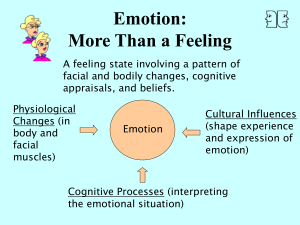
Emotion: More Than a Feeling
... An emotion-provoking stimulus activates a brain center called the “thalamus”, which simultaneously sends messages to the cortex, producing the feeling of an emotion, to the viscera, producing arousal, and to the skeletal muscles, producing behavior. Fear ...
... An emotion-provoking stimulus activates a brain center called the “thalamus”, which simultaneously sends messages to the cortex, producing the feeling of an emotion, to the viscera, producing arousal, and to the skeletal muscles, producing behavior. Fear ...
Introduction to Animals
... Sexual reproduction restores the diploid number and increases genetic variation. During the developmental process, the zygote undergoes many mitotic divisions. These identical cells must undergo differentiation. Differentiation is process of cell becoming different from each other and being speciali ...
... Sexual reproduction restores the diploid number and increases genetic variation. During the developmental process, the zygote undergoes many mitotic divisions. These identical cells must undergo differentiation. Differentiation is process of cell becoming different from each other and being speciali ...
Learning theories Classical conditioning • Automatic responses with
... Conditioned response/stimuli – Stimuli which evokes an emotional response. E.g. Pavlov’s dog’s tuning fork made the dogs salivate before food was even visible. Operant conditioning Skinner 1953 Learning which behaviours you want to do depending on the previous outcome ABC – Antecedent, Beh ...
... Conditioned response/stimuli – Stimuli which evokes an emotional response. E.g. Pavlov’s dog’s tuning fork made the dogs salivate before food was even visible. Operant conditioning Skinner 1953 Learning which behaviours you want to do depending on the previous outcome ABC – Antecedent, Beh ...
Psychology: Learning and Behaviour Lecture Notes Lecture 1
... Manny behaviours are not entirely learned or entirely innate Many fall somewhere in between Thus, it is possible to identify a continuum of behaviour Assumptions of Laboratory learning theories Laws of association can be developed in isolation without reference to innate behaviour An examp ...
... Manny behaviours are not entirely learned or entirely innate Many fall somewhere in between Thus, it is possible to identify a continuum of behaviour Assumptions of Laboratory learning theories Laws of association can be developed in isolation without reference to innate behaviour An examp ...
• Animal Diversity Overview • Ch 32 • Cell Specialization • Animals
... Animals can be categorized according to the symmetry of their bodies, or lack of it ...
... Animals can be categorized according to the symmetry of their bodies, or lack of it ...
An Introduction to Animal Diversity
... • Animals are heterotrophs that ingest their food • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes – Their cells lack cell walls – Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen ...
... • Animals are heterotrophs that ingest their food • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes – Their cells lack cell walls – Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen ...
Cognitive Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience/Motivation and
... One of the most influential ethnographic studies by Enkamn and Friesen, which is based on the comparison of facial expressions of emotions in different cultures, concluded that there are six basic types of emotions expressed in faces - namely sadness, happiness, disgust, surprise, anger and fear, in ...
... One of the most influential ethnographic studies by Enkamn and Friesen, which is based on the comparison of facial expressions of emotions in different cultures, concluded that there are six basic types of emotions expressed in faces - namely sadness, happiness, disgust, surprise, anger and fear, in ...
Resume - OPResume.com
... Email: [email protected] OBJECTIVE: To find a position using my skills as an Animal Health Technologist HIGHLIGHT OF QUALIFICATIONS ...
... Email: [email protected] OBJECTIVE: To find a position using my skills as an Animal Health Technologist HIGHLIGHT OF QUALIFICATIONS ...
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom – notes
... 6. ________________________- most animals have muscles or muscular/skeletal systems for movement or they have a way to move or circulate water for feeding. 7. ________________________ -most reproduction is sexual using sperm and egg cells; some animals like sponges and jellyfish can reproduce asexua ...
... 6. ________________________- most animals have muscles or muscular/skeletal systems for movement or they have a way to move or circulate water for feeding. 7. ________________________ -most reproduction is sexual using sperm and egg cells; some animals like sponges and jellyfish can reproduce asexua ...
Animal Behavior - OAKLAND
... – conditional: pairs a neutral stimulus with one eliciting a response until the neutral stimulus itself causes the response – operant: causes an animal to associate a certain behavior with pain or pleasure to either reinforce or discourage this behavior ...
... – conditional: pairs a neutral stimulus with one eliciting a response until the neutral stimulus itself causes the response – operant: causes an animal to associate a certain behavior with pain or pleasure to either reinforce or discourage this behavior ...
Motivation and Emotion
... • Emotion: a positive or negative feeling state typically including some combination of physiological arousal, cognitive appraisal, and behavioral expression ...
... • Emotion: a positive or negative feeling state typically including some combination of physiological arousal, cognitive appraisal, and behavioral expression ...
notes - Northwest Nazarene University
... There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed by the Creator into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonde ...
... There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed by the Creator into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonde ...
Name
... representatives of the major animal phyla are presented. The groups covered are the sponges, cnidarians, flatworms, rotifers, three lophophorate phyla, nemerteans, mollusks, annelids, nematodes, arthropods, echinoderms, and chordates. 1. How does the structure of a sponge relate to its method of nut ...
... representatives of the major animal phyla are presented. The groups covered are the sponges, cnidarians, flatworms, rotifers, three lophophorate phyla, nemerteans, mollusks, annelids, nematodes, arthropods, echinoderms, and chordates. 1. How does the structure of a sponge relate to its method of nut ...
What is an animal?
... The gastrula is made of two layers with an opening at one end The outer layer is the ectoderm ...
... The gastrula is made of two layers with an opening at one end The outer layer is the ectoderm ...
Chapter 26 Questions
... 5. Explain why many invertebrates are small. 6. What are two characteristics that all vertebrates share? 7. Into what phylum are vertebrates classified? 8. Are all animals mobile? ...
... 5. Explain why many invertebrates are small. 6. What are two characteristics that all vertebrates share? 7. Into what phylum are vertebrates classified? 8. Are all animals mobile? ...
Humans, Animals, and Society: An Introduction to
... as the species, the context of the association, and the function of the animal in question. There is a strong focus on the roles of animals in maintaining human health, from the health benefits of keeping companion animals to their use in various kinds of therapy and humane education programs. Chapt ...
... as the species, the context of the association, and the function of the animal in question. There is a strong focus on the roles of animals in maintaining human health, from the health benefits of keeping companion animals to their use in various kinds of therapy and humane education programs. Chapt ...
Ethical Issues and Non-Human Animals
... justification in using animals for research and those who do are guilty of speciesism. He argues it is wrong to do research on any organism that can feel pain, because an animal’s pain is as important as human pain. Regan(1984) mature mammals are “the subject of a life” which has a value independent ...
... justification in using animals for research and those who do are guilty of speciesism. He argues it is wrong to do research on any organism that can feel pain, because an animal’s pain is as important as human pain. Regan(1984) mature mammals are “the subject of a life” which has a value independent ...
Emotion in animals

Emotions in animals are the subjective feelings and emotions experienced by nonhuman animals. Emotions may be described as subjective, conscious experiences characterized primarily by psychophysiological expressions, biological reactions, and mental states.Charles Darwin was one of the first scientists to write about the existence and nature of emotions in nonhuman animals. His observational and sometimes anecdotal approach has developed into a more robust, hypothesis-driven, scientific approach. General hypotheses relating to correlates between humans and non-human animals also support the claim that non-human animals may feel emotions and that human emotions evolved from the same mechanisms. Several tests, such as cognitive bias tests and learned helplessness models, have been developed. Cognitive biases (feelings of optimism or pessimism) have been shown in a wide range of species including rats, dogs, cats, rhesus macaques, sheep, chicks, starlings, pigs and honeybees.Some behaviourists claim stimulus–response models provide a sufficient explanation for animal behaviours that have been described as emotional, and that it is unnecessary to postulate that animals are conscious. Other behaviourists further question whether animals feel emotions on the grounds that emotions aren't universal even among humans, that interpretations of animal behaviour are anthropomorphic, and that definitions of emotions lack robustness.